Exploring Concepts in Applied Design, Arts, Language, Literature, and Mathematics
Dive into the diverse concepts of Applied Design, Arts, Language Acquisition, Language & Literature, and Mathematics, including topics such as innovation, creativity, communication, relationships, sustainability, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
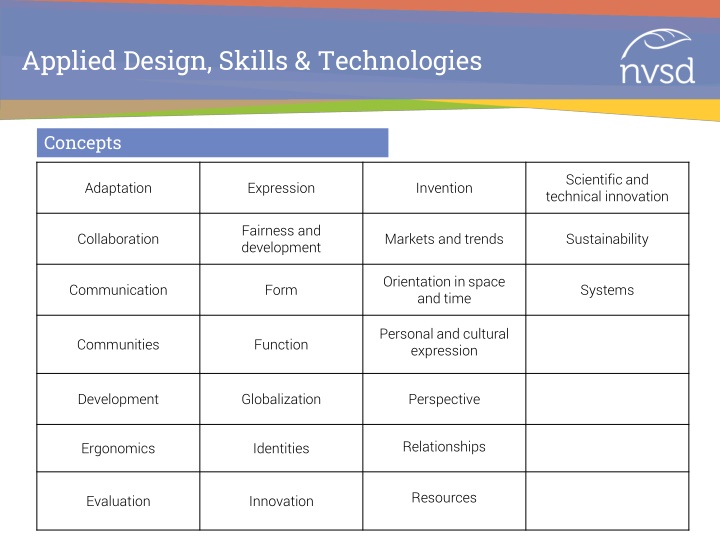
Applied Design, Skills & Technologies Concepts Scientific and technical innovation Adaptation Expression Invention Fairness and development Collaboration Markets and trends Sustainability Orientation in space and time Communication Form Systems Personal and cultural expression Communities Function Development Globalization Perspective Relationships Ergonomics Identities Resources Evaluation Innovation
Arts Concepts Aesthetics Contrast Interaction Representation Authenticity Creativity Interpretation Rhythm Audience Development Media Role Space (spatial awareness) Balance Expression Movement Boundaries Genre Narrative Structure Change Form/organization Pattern Style Composition Function (how it works) Play Symmetry Communication Harmony Visual culture Presentation Connections Identity Relationships Conflict/co-operation Innovation Repetition
Language Acquisition Concepts Accent Conventions Idiom Purpose Argument Creativity Inference Structure Audience Culture Meaning Stylistic choices Bias Empathy Message Theme Communications Form Patterns Voice Connections Function Point of view Word choice Context
Language & Literature Concepts Accent Allegory Critical literacy Cycles Directionality Emotions Empathy Envy Fluency Form/organization Function Genre Idiom Imagery Imperatives Inference Influence Intertextuality Knowledge Logic Structure Style Stylistic choices Summary Symbolism Systems Theme Voice Word choice Meaning Message Metaphor Motivation Paraphrase Patterns Perspective Point of view Power Prejudice Presentation Purpose Reading rate Relationship Responsibility Self regulation Self expression Setting Antagonist/protagonist Argument Audience Background Beliefs/values Bias Cause/effect Change Character Communication Communities Conflict/co-operation Connections Context Conventions Creativity
Mathematics Concepts Change (sequence, cycles, growth) Personal/cultural expression Quantity Globalization Sustainability System Causation Interaction Cause/effect Justification Probability Proportion Communication Logic Repetition Connections Measurement Relationships Development Models Equivalence Numbers Representation Scientific and technical innovation Form/organization Order Orientation in space/time Simplification Formula/generalization Function (how does it work) Space Patterns
Physical & Health Education Concepts Adaptation Development Perspective Balance Energy Refinement Beliefs / values Environment Relationships Causation Fitness Responsibilities Choice Function Space Communication Identity Systems Connections Interaction Continuity & change Movement
Sciences Concepts Balance Environment Mathematics Quantity Cause/effect Equilibrium Matter Relationships Change/continuity Equivalence Measurement Representation Conditions Evidence Model(s) Responsibility Communication Evolution Movement Simplification Communities Form Order Systems Culture Function Organization Theory Cycle Generalization Organism Time/space Development Interaction Patterns Transfer Energy Justification Population Transformation
Social Studies Concepts Beliefs/values Causality (cause & consequence) Change Cooperation Ideology Resources Culture Innovation & revolution Scale Cycle Interdependence Management & intervention Model Scarcity Choice Disparity & equity Significance Civilization Diversity Supply & demand Communication Economics Networks Sustainability Communities Global interactions Systems Patterns & trends Conflict Globalization Perspective Time, place and space Connections Governance Poverty Trade Consumption Growth Power Identity Processes Continuity

















