Exploring Crystalline Symmetry in Nature, Arts, and Industry
Discover the beauty of symmetry in the crystalline state through nature, arts, and industry. Explore the basic concepts of symmetry and crystallography in two and three dimensions. Uncover the intricate patterns of symmetry in animated nature, works of art, and industrial designs. Delve into the physics of crystallography and the definition of crystals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
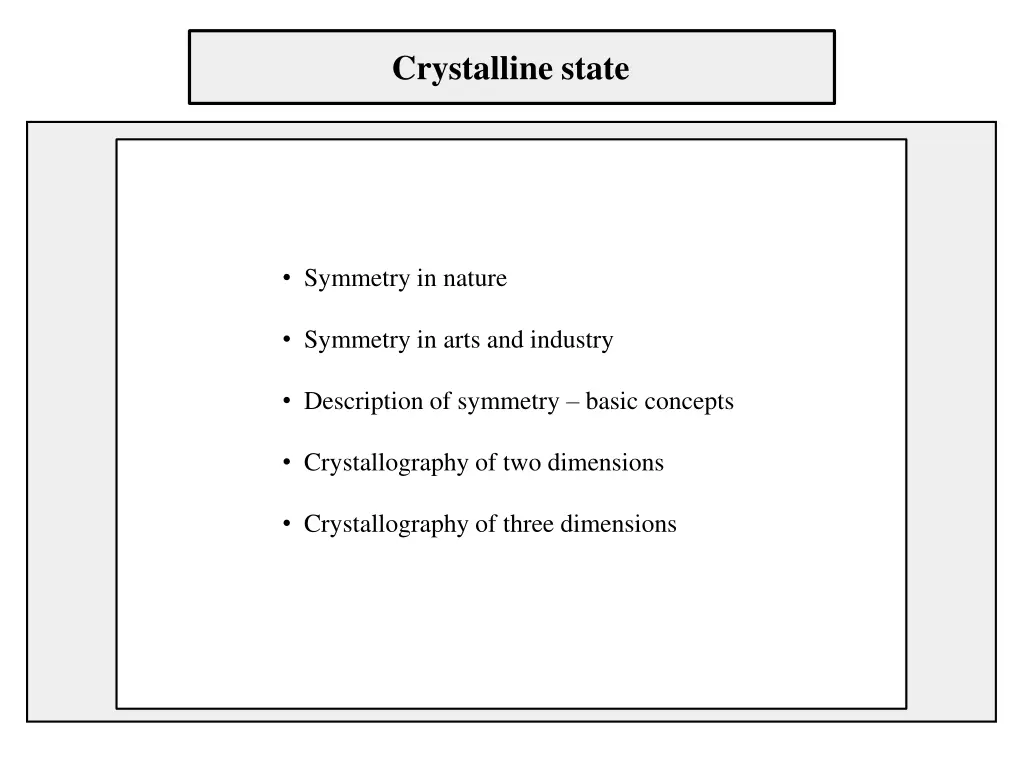
Crystalline state Symmetry in nature Symmetry in arts and industry Description of symmetry basic concepts Crystallography of two dimensions Crystallography of three dimensions
Symmetry in animated nature http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/07/SymmetryOfLifeFormsOnEarth.jpg/300px-SymmetryOfLifeFormsOnEarth.jpg http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/11/Sterappel_dwarsdrsn.jpg/220px-Sterappel_dwarsdrsn.jpg apple animals
Symmetry in animated nature http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/52/Braus_1921_395.png/200px-Braus_1921_395.png http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/Braus_1921_396.png/435px-Braus_1921_396.png certain degree of asymmetry is eligible
Symmetry of works of art http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Catedral_Metropolitana_de_Sao_Paulo_1_Brasil-edit-01.jpg/220px-Catedral_Metropolitana_de_Sao_Paulo_1_Brasil-edit-01.jpg http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Isfahan_Lotfollah_mosque_ceiling_symmetric.jpg/220px-Isfahan_Lotfollah_mosque_ceiling_symmetric.jpg http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7e/Coat_of_arms_of_Isle_of_Man.svg/220px-Coat_of_arms_of_Isle_of_Man.svg.png ceiling of triskelion Isle of Man Lotfollah mosque Iran S o Paulo Cathedral
Symmetry in industry 17-fold Five-fold rotational symmetry rotational symmetry
Translational symmetry large-scale production https://encrypted-tbn1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRPVwZdNQ_MKqL3BVlPfFPr-tXkzc9Esl1BXRHVY1zcThS0wcA7 tiling perfect translational symmetry puzzle apparent translational symmetry aperiodic tiling R. Penrose
Physics crystallography http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8c/Insulincrystals.jpg/300px-Insulincrystals.jpg http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/68/Stohrem.jpg/220px-Stohrem.jpg structure of SrTiO3crystal HR TEM imaging insulin crystals
Crystal - definition various formulations A crystal is a solid where the atoms form a periodic arrangement A crystal is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions A crystal is any solid having an essentially discrete diffraction diagram A crystal is a solid that is characterized by a small number of types of constituents and a small number of their mutual configurations ideal crystal infinite, without defects, zero temperature (in some cases) definition of structural defects
Symmetry basic attribute of crystals repetition of motif oper cia opakovania mot vu translation transl cia rotation rot cia reflection zrkadlenie inversion inverzia
Symmetry operations opercie symetrie Symmetry operation is a transformation of the crystal into a state indistinguishable from the starting state. proper operations vlastn oper cie improper operations nevlastn oper cie reflection translation inversion rotation source and target are congruent zhodn source and target are enantiomorph protitvar transformation matrix transformation matrix
Possible rotation axes B B m integer - A T A Only 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6-fold rotation axes are allowed in crystallography
Point symmetry elements bodov prvky symetrie A symmetry element is a point (or points) of reference about which symmetry operations can take place symmetry operation (without translations) symmetry elements 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6-fold rotation axis 1, 2, 3, 4 a 6-n sobn rota n os rotation 6 4 3 2 1 m 2D mirror line zrkadlov priamka 3D mirror plane zrkadlov rovina reflection center of inversion stred inverzie inversion i in 2D i = 2 only in 3D
Compound symmetry elements 2D zloen prvky symetrie compound symmetry operations translational component symmetry operation symmetry elements glide line sklzn priamka glide symmetry operation sklzn oper cia symetrie g fractional part of translation combined with reflection T/2 T
Space lattice priestorov (krytlov) mrieka A space lattice is an infinite array of points showing how particles (atoms, ions or molecules) are arranged at different sites in three (two) dimensional spaces. Each point has identical and identically oriented surroundings crystal structure space lattice + motif kry t lov trukt ra
Vectors lattice vectors mrie kov vektory a, b, c shortest vectors maximum number of right angles minimum volume of the parallelepiped basis vectors vektory b zy set of three noncoplanar lattice vectors basic vectors z kladn vektory special choice Bravais rules
Cells bunky unit cell z kladn (element rna) bunka generated by basic vectors a, b, c parallelepiped primitive cell primit vna bunka contains only one lattice point parallelepiped Niggli cell Niggliho bunka primitive generated by the shortest lattice vectors Wigner-Seitz cell Wignerova-Seitzova bunka primitive preserves the point symmetry of the lattice
Lattice parametersmriekov parametre unit cell parallelepiped c sixs lattice parameters mrie kov parametre b magnitudes of basic vectors and the angles between them a cell volume
Lattice planes mriekov roviny set of lattice planes osnova mrie kov ch rov n interplanar distance medzirovinn vzdialenos
Miller indices Millerove indexy relatively prime numbers proportional to the inverses of intercepts of the plane c integers b a Miller indices
Symbols and conventions one specific plane all equivalent planes one specific direction all equivalent directions minus sign multiplicity n important parameter Hexagonal or trigonal lattice systems Bravais-Miller indices a3 a2 a1
