Exploring Earth, Space, and Beyond with Year 5 Knowledge Mat
Discover fascinating insights into Earth, space, and the solar system with subject-specific vocabulary and prior knowledge about celestial bodies, orbits, forces, and more. Dive into the wonders of the universe!
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
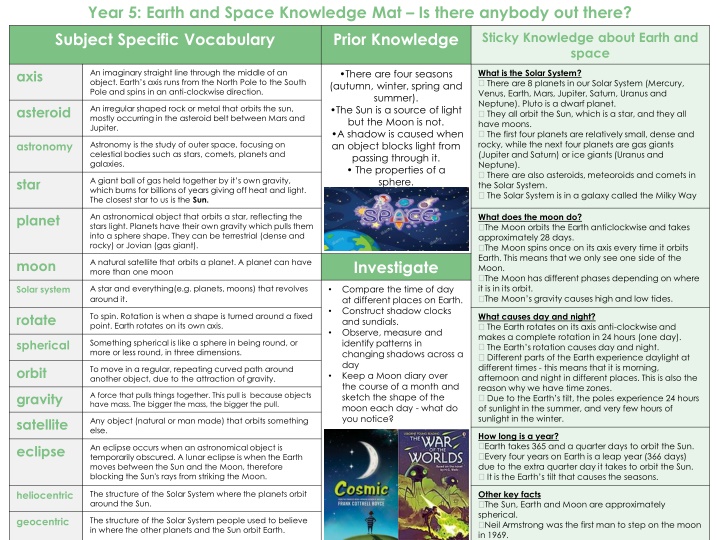
Year 5: Earth and Space Knowledge Mat Is there anybody out there? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about Earth and space axis An imaginary straight line through the middle of an object. Earth s axis runs from the North Pole to the South Pole and spins in an anti-clockwise direction. There are four seasons (autumn, winter, spring and summer). The Sun is a source of light but the Moon is not. A shadow is caused when an object blocks light from passing through it. The properties of a sphere. What is the Solar System? There are 8 planets in our Solar System (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune). Pluto is a dwarf planet. They all orbit the Sun, which is a star, and they all have moons. The first four planets are relatively small, dense and rocky, while the next four planets are gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn) or ice giants (Uranus and Neptune). There are also asteroids, meteoroids and comets in the Solar System. The Solar System is in a galaxy called the Milky Way An irregular shaped rock or metal that orbits the sun, mostly occurring in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. asteroid astronomy Astronomy is the study of outer space, focusing on celestial bodies such as stars, comets, planets and galaxies. star A giant ball of gas held together by it s own gravity, which burns for billions of years giving off heat and light. The closest star to us is the Sun. An astronomical object that orbits a star, reflecting the stars light. Planets have their own gravity which pulls them into a sphere shape. They can be terrestrial (dense and rocky) or Jovian (gas giant). planet What does the moon do? The Moon orbits the Earth anticlockwise and takes approximately 28 days. The Moon spins once on its axis every time it orbits Earth. This means that we only see one side of the Moon. The Moon has different phases depending on where it is in its orbit. The Moon s gravity causes high and low tides. Investigate moon A natural satellite that orbits a planet. A planet can have more than one moon A star and everything(e.g. planets, moons) that revolves around it. Compare the time of day at different places on Earth. Construct shadow clocks and sundials. Observe, measure and identify patterns in changing shadows across a day Keep a Moon diary over the course of a month and sketch the shape of the moon each day - what do you notice? Solar system rotate To spin. Rotation is when a shape is turned around a fixed point. Earth rotates on its own axis. What causes day and night? The Earth rotates on its axis anti-clockwise and makes a complete rotation in 24 hours (one day). The Earth s rotation causes day and night. Different parts of the Earth experience daylight at different times - this means that it is morning, afternoon and night in different places. This is also the reason why we have time zones. Due to the Earth s tilt, the poles experience 24 hours of sunlight in the summer, and very few hours of sunlight in the winter. spherical Something spherical is like a sphere in being round, or more or less round, in three dimensions. orbit To move in a regular, repeating curved path around another object, due to the attraction of gravity. gravity A force that pulls things together. This pull is because objects have mass. The bigger the mass, the bigger the pull. satellite Any object (natural or man made) that orbits something else. How long is a year? Earth takes 365 and a quarter days to orbit the Sun. Every four years on Earth is a leap year (366 days) due to the extra quarter day it takes to orbit the Sun. It is the Earth s tilt that causes the seasons. eclipse An eclipse occurs when an astronomical object is temporarily obscured. A lunar eclipse is when the Earth moves between the Sun and the Moon, therefore blocking the Sun's rays from striking the Moon. The structure of the Solar System where the planets orbit around the Sun. heliocentric Other key facts The Sun, Earth and Moon are approximately spherical. Neil Armstrong was the first man to step on the moon in 1969. The structure of the Solar System people used to believe in where the other planets and the Sun orbit Earth. geocentric
Year 5: Forces Knowledge Mat Can you feel the force? Subject Specific Vocabulary Sticky Knowledge about Forces Prior Knowledge force A push or pull that causes an object to start or stop moving, change speed and change direction. You can t see forces but you can see how they affect things Know what a force is and able to explain that pushes and pulls are types of forces. When forces are applied to an object they allow them to move or stop moving. The strength of the force determines how far and fast an object moves. Friction is the resistance of motion when two surfaces make contact. Gravity is the force that causes objects to move downwards towards the ground. Magnets have poles, and opposite poles attract, while similar poles repel. What are forces? Forces are pushes and pulls which change the motion of an object. They will make it start to move or speed up, slow it down or even make it stop. Gravity is the force that pulls objects to the centre of the Earth. Friction is a force - it is the resistance of motion when one object rubs against another. It helps slow down a moving object friction A force between two surfaces or objects that are moving, or trying to move, across each other. It is a resistance of motion and slows down a moving object. gravity A force which tries to pull two objects towards each other. resistance A force which slows down a moving object. What types of friction are there? Air resistance is the friction created between air and an object moving through it. Water resistance is the friction created between water and an object moving through it or floating on it. Air and water resistance affects how fast or slowly objects move through the air or water. air resistance A type of friction between a moving object and the air around it. The air pushes against the object as it moves out of the way to let the object through. water resistance A type of friction between water and an object moving through the water. The water pushes against the object as it moves out of the way to let the object through. Up thrust A force where water or air push back against an object placed in them. Other key facts Isaac Newton developed the theory of gravity and made important investigations into motion. Galileo also made important discoveries about motion and machines. Investigate When an object has a smooth and sleek shape to reduce the friction caused by it moving through air or water. streamlined The measure of the force of gravity on an object, measured in newtons. Investigate the amount of friction created by different surfaces. Use measures (such as length and time) to show how far or fast and object travels. Explore the effects of friction on motion and find out how it slows or stops moving objects Make parachutes to investigate how air resistance works. Ensure that only one variable is changed while other variables stay the same. Explore resistance in water by making and testing boats of different shapes Design and make products that use levers, pulleys, gears and/or springs and explore their effects What are examples of mechanisms? weight Levers allow us to do heavy work with less effort . Using a lever to pick up or move a large heavy box makes it much easier to move it. How much matter (stuff) is inside an object, measured in kilograms. mass A system of moving parts designed to perform a task, working together in a machine. Pulleys also allow us to do heavy lifting with little effort- objects are attached to ropes which are pulled downwards and over pulley wheels, mechanism lever Anything long and rigid moved around a fixed point (fulcram) which can help lift or pull things. Used to make a small force lift or move a lighter load. Load Gears are toothed wheels. Their teeth can fit into each other so that when the first wheel turns, so does the next one. Using gears can change the force, speed or direction of a motion pulley A simple machine that makes lifting something easier. It has a wheel or set of wheels with grooves that a rope or chain can be pulled over. gear Two or more wheels with teeth (cogs) that fit together, move in opposite directions and are used in machines to change speed or direction. Springs can be stretched by pulling them or squashed by pushing them. The greater the force pulling or pushing, the greater the force the spring uses to move back to its original shape. A spiral of wire which returns to its original shape after it is pressed or pulled. Spring
Year 5: Life Cycles Knowledge Mat What is the circle of life? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about Life Cycles lifecycle Patterns in the way animals and plants grow, behave and change between birth and death. Some examples of life cycles Animals can be grouped into vertebrates (then further into fish, reptiles, birds, mammals and amphibians) and invertebrates. The structure of flowers and how they relate to reproduction and the process of pollination. Reproduction as one of the seven life processes The processes of dispersal, fertilisation and germination. The word metamorphic means a change of form (in the context of rocks) What are examples of life cycles? The life cycles of mammals, birds, amphibians and insects have similarities and differences. One difference is that amphibians and insects go through the process of metamorphosis. This is when the structure of their bodies changes significantly as they grow. In general, the life cycles of plants and animals have three basic stages. However, some organisms may have more than three and the exact names of each stage can slightly differ depending on the species. Many insects have four stages in their life cycle. Life processes M- movement R- respiration S sensitivity G- growth R- reproduction E- excretion N- nutrition The way different plants and animals make new plants and animals. The reproduction system differs in plants and animals. reproduction This form of reproduction requires only one parent that makes a copy of itself and happens mostly in plants. asexual reproduction This form of reproduction requires male and female parts and happens in both plants and animals. sexual reproduction pollen A substance made by flowering plants used for transferring male reproductive parts to other plants. Investigate stamen The male part of the flower that produces pollen. It has a stalk called a filament and a head called an anther. What is reproduction? Reproduction is when an animal or plant produces one or more individuals similar to itself. Sexual reproduction requires two parents with male and female gametes (cells) and will produce offspring that is similar to but not identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction will produce offspring that is identical to the parent (clones) and requires only one parent. carpel The female part of the flower that has a stalk called a style, a sticky tip called a stigma and an ovary that contains ovules. Dissect a flower, identify and label the different parts and explain their functions. Set up a simple experiment to investigate how to grow new plants from seeds, stem and root cuttings, tubers, bulbs. Observe life cycle changes in a variety of living things in local environments. Compare the life processes of reproduction in some animals. Compare the life cycles of plants and animals in the local environment with other plants and animals (in the rainforest, in the oceans, in desert areas etc) Observe changes in an animal over a period of time stigma Located at the end of the stalk and the area where pollen is received. pollination The way pollen is transferred from a stamen of one plant to a stigma of another plant. There are two types; insect and wind. How do plants reproduce? Male gametes are found in the pollen and female gametes in the ovary. Pollination occurs when pollen from the anther is transferred to the stigma by bees and other insects. The pollen then travels down and meets the ovule. When this happens, seeds are formed - this is called fertilisation. Seeds are then dispersed so that germination can begin again. Some plants, such as daffodils and potatoes, can also produce offspring using asexual reproduction germination When a seed starts growing. Seeds need oxygen, water and warmth to germinate. fertilisation When an egg and pollen join together to make new seeds. A dramatic change in the life cycle of an animal in which it ends up looking totally different. metamorphosis naturalist A scientist that observes and studies the relationships and patterns in nature. behaviourist A scientist that observes and studies animals, their behaviour and their environments.
Year 5: Animals including humans How does life begin? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about Animals including Humans growth Getting bigger. Some living things grow to a certain size then stop while others grow for their whole lives. Animals can be grouped into vertebrates (and then further into fish, reptiles, amphibians, birds and mammals). Animals have offspring that grow into adults. Know some examples of life cycles (including those of plants and humans) Reproduction and growth are two of the seven life processes. How to live a healthy lifestyle, including how animals move depending on their arrangement of bones, joints and muscles. What are the main stages of the human life cycle? development The gradual and progressive changes in size , shape and function during the life of a living thing. reproduction The way different plants and animals make new plants and animals that are similar to the parent. The reproduction system differs in plants and animals. sexual reproduction fertilisation This form of reproduction requires male and female parts and happens in both plants and animals. When a female egg and male sperm join together and create a new living thing, It happens in the female body. Foetus An unborn baby inside the mother s body that begins to develop all its organs and body parts. Baby After a 9 month gestation period, the baby will be born. Infancy - this is a period of rapid change. Many toddlers learn to walk and talk at this stage. Childhood - children learn new things as they grow. They become more independent. Adolescence over a few years many physical and emotional changes occur which will enable reproduction in adulthood. Much more independent. Early adulthood - this is when humans are usually at their fittest and strongest and they are able to reproduce. Middle adulthood - changes such as hair loss or hair turning grey may happen. There are also some hormonal changes again and the ability to reproduce decreases. Late adulthood - there is a decline in fitness and strength. gestation The time between conception and birth, during which the embryo is developing and growing inside the mother. The condition of a female animal when there is a baby growing inside her womb. pregnant embryo Fertilisation creates an embryo which is a new life in early development. Embryos develop and grow quickly. Investigate foetus An unborn baby inside the mother s body at a further stage of development where it has begun to develop all its organs and body parts. baby The earliest stage of development for a human after being born and before it can walk or talk. Research the gestation periods of other animals and comparing them with humans. Compare the growth pattern of humans to other animals. Consider why humans take so long to learn to walk in comparison to other animals. Create a Venn diagram to show what the similarities and differences are between children, adolescents and adults. infancy A period of your life when you are very young and there are rapid changes. Many toddlers learn to walk and talk during this stage. childhood A stage of life where young children continue growing and learning new skills, becoming more independent. Why is development important? The early years, especially the first three years of life, are very important for building the baby's brain. A child's brain develops rapidly during the first five years of life, especially the first three years. It is a time of rapid cognitive, linguistic, social, emotional and motor development. The years between 6 and 14 -middle childhood and early adolescence - are a time of important developmental advances that establish children's sense of identity. adolescence The time in a young person s life where physical and emotional changes occur to enable reproduction in adulthood. You are much more independent. adulthood The stage of development when a human is fully grown and mature, and able to reproduce. mature When a child or young animal matures, they become an adult. The length of time, on average, that humans or animals are expected to live. life expectancy
Year 5: Reversible and Irreversible Changes Knowledge Mat Can materials change? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about Reversible and Irreversible changes materials The substance something is made out of. Can be described as solid, liquid or gas. A variety of everyday materials and their physical properties. Compare and group materials on the basis of their properties Suitably of materials for use based on their properties. How magnets and electrical circuits work. Shapes of solid objects can be changed by squashing, bending, twisting and stretching. Materials that are solids, liquids and gases and their particle structure Some materials change state when they are heated or cooled and the temperature at which this happens. The roles of melting, evaporation and condensation in the water cycle and the role temperature has on the rate of evaporation. Some materials such as rocks are permeable How to group and classify materials based on their materials using more complex vocabulary. particles Solids, liquids and gases are made up of tiny particles. These are so small they are invisible without the strongest microscopes. magnetism transparency hardness flexibility solution A mixture made when a solid mixes completely into a liquid. The solid is the solute and the liquid is the solvent. permeable conductivity soluble insoluble soluble A material or substance that has the ability to completely dissolve in liquid. What are reversible and irreversible changes? Reversible changes are changes that can be undone. They are temporary and the material can easily be switched back to its original state. Examples include evaporating, dissolving, filtering, sieving and melting. Irreversible changes are permanent, extremely difficult to reverse and form new materials. Examples include rusting and burning and other reactions. dissolve When a material or substance becomes broken up or absorbed by something or to disappear into something else. reversible A temporary change that can be undone so the material can change back to its original state or condition. irreversible A permanent change and can t be easily undone. Usually results in forming new materials from the original ones. What is a solution? When solid particles mix with liquid particles , this is called dissolving The result is a solution. Materials that dissolve are soluble. Materials that do not dissolve are insoluble. Transparent materials let light pass through them so you can see through them. transparent Investigate evaporating The process of a substance in a liquid state changing to a gaseous state due to an increase in temperature and/or pressure. Find the best material to stop an ice cube from melting. Find out if thermal conductors also make good electrical conductors. Investigate which materials are soluble and insoluble. Design an experiment that investigates dissolving and consider which variables you could change. Create a variety of mixtures using different materials and use a variety of methods to separate them. Observe and compare the changes that take place when cakes are baked or bicarbonate of soda mixes with vinegar. Can mixtures be separated? Some materials can be separated after they have been mixed based on their properties - this is called a reversible change. Some methods of separation include the use of a magnet, a filter (for insoluble materials), a sieve (depends on the size of the solids) and evaporation. When a mixture cannot be separated back into the original components, this is called an irreversible change. filtering To pass a substance through a device that can filter or separate solid particles from liquids or gases. melting A physical process that results in the transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid through heat or pressure being applied. rusting A reaction that occurs when iron or steel are exposed to a certain liquid and gas. thermal Something that is thermal is hot, retains heat, or has a warming effect. What are thermal conductors and insulators? Materials which are good thermal conductors allow heat to move through them easily. Thermal conductors are used to make items that require heat to travel through them easily. Thermal insulators do not let heat travel through them easily. conductors Materials that allow heat or electricity to pass through them or along them easily. insulators Materials that do not conduct heat or electricity well, and instead keep the heat in.