Exploring Organisms and Ecosystems
Learners will delve into how organisms interact and depend on one another in various ecosystems and habitats. They will also examine the adaptations of different species and the impacts of human actions on these environments. Key vocabulary includes ecosystem, species, habitat, biodiversity, and more. The focus is on fostering respect, readiness to learn, and being in the right place, while promoting characteristics of effective learners such as respect, positivity, motivation, persistence, and goal-setting.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
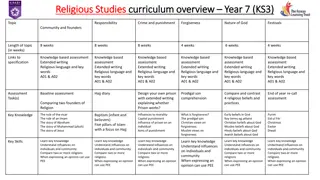
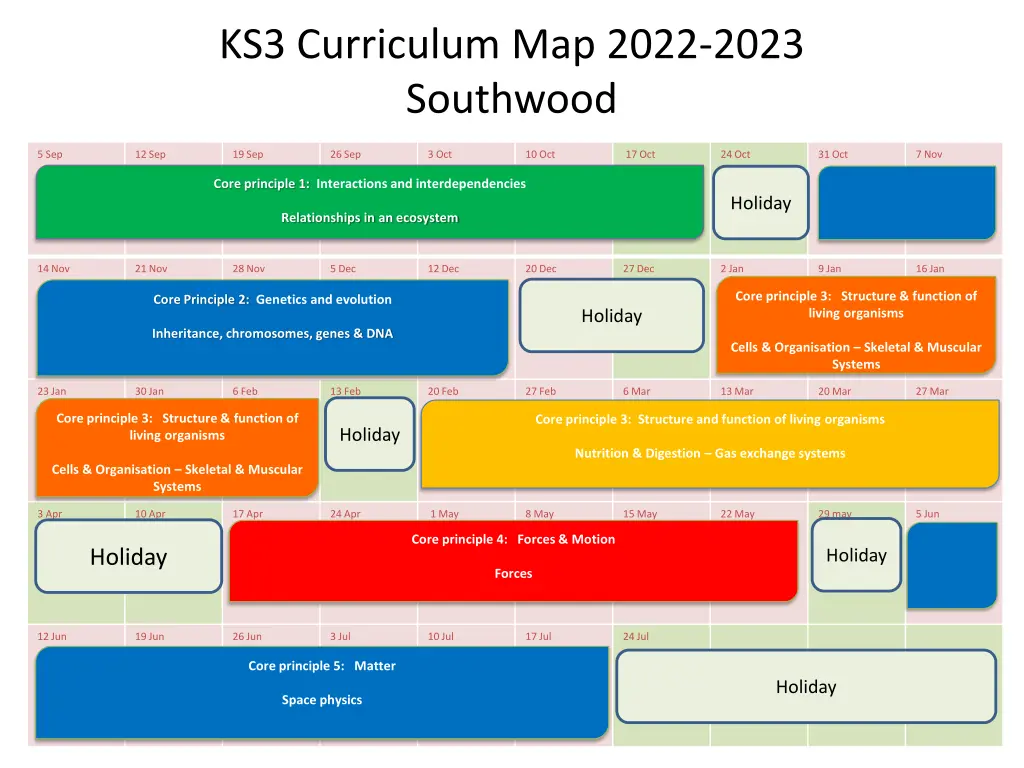
KS3 Curriculum Map 2022-2023 Southwood 5 Sep 12 Sep 19 Sep 26 Sep 3 Oct 10 Oct 17Oct 24Oct 31 Oct 7 Nov Integers Baseline Shape and Angles Mental Methods Representing Data Representing Data Number Patterns Core principle 1: Interactions and interdependencies DTT Holiday Relationships in an ecosystem 14 Nov 21 Nov 28 Nov 5 Dec 12 Dec 20 Dec 27 Dec 2 Jan 9 Jan 16 Jan Decimals Core principle 3: Structure & function of living organisms Square Roots Ratio And Proportion Ratio And Proportion Mental methods 2 Doddle Assessment DTT Assessment Core Principle 2: Genetics and evolution Averages Holiday Averages Inheritance, chromosomes, genes & DNA Cells & Organisation Skeletal & Muscular Systems 23 Jan 30 Jan 6 Feb 13 Feb 20 Feb 27 Feb 6 Mar 13 Mar 20 Mar 27 Mar Core principle 3: Structure & function of Assessment Core principle 3: Structure and function of living organisms Negative Numbers Doddle Assessment living organisms Doddle assessment DTT DTT Holiday DTT 3D Solids Fractions Problem Solving Tasks Fractions Nutrition & Digestion Gas exchange systems DTT Cells & Organisation Skeletal & Muscular Systems 3 Apr 10 Apr 17Apr 24Apr Probability 1May 8 May 15 May 22May 29 may 5 Jun Time and scales Core principle 4: Forces & Motion Equations Doddle assessment DTT DTT Doddle quiz/ 25 questions Holiday Holiday Forces Substitution & Formulae 12 Jun 19 Jun 26Jun 3 Jul 10 Jul 17 Jul 24Jul Fractions decimals and percent Using percentages Metric Measures Perimeter, area and volume Doddle assessment Mini Maths Projects Core principle 5: Matter Holiday Space physics
KS3 Science: Interactions and Interdependencies E M P O W E R How does learning relate to whole school intent? Learning about relationships in ecosystems is important for all to understand and appreciate so that student of all abilities and all aspirations are able to make informed decisions with regards looking after the environment to achieve global goals for the future. How does learning relate to subject intent? Explain everyday and technological applications of Science; evaluate associated personal, social, economic and environmental implications; and make decisions based on the evaluation of evidence and arguments. Overview: Learners will explore how organisms interact and depend on one and other within different ecosystems and habitats and measure their distribution/population trends. They will also study how different species adapt to their environments for food, protection or to find a mate whilst being challenged to think about how these environments are changing due to human impacts and the effect this may have on their populations RESPECT READY TO LEARN RIGHT PLACE Key Vocabulary: Ecosystem, Species, Community, Habitat, Organism, Population, Biodiversity, Biome, Competition, Decomposer, Producer, Consumer, Adaptation, Pollination, Photosynthesis. L E A R N Characteristics of effective learners: Skills Knowledge 1. Levels of organisation within an ecosystem, 1. 2. Respectful to others and their surroundings Positive attitude and commitment to their education Motivated and persistent even if you face difficulty Consistently behaves well Sets goals and achieves High attendance 1. Read, interpret and create food chains and webs. A C H I E V E 2. Abiotic and biotic factors, 2. Mathematical skills: Using data to draw graphs and predict population trends. 3. Material cycles, 3. 4. How organisms are interdependent and are 3. Practical skills: use quadrats to observe and collect data around population sizes. 4. 5. 6. adapted to their environment, 4. Use observation to critically think, make predictions and draw conclusions. 5. Methods of identifying species and measuring distribution, frequency and 5. Use critical thinking skills to make sense of the world around us and find solutions to global environmental issues. abundance of species in a habitat Reading: Exploring Science 7 (7C Pages 35-48) Exploring science 8 (8D Pages 49-62) Additional Practical's: Practical 1 - Data collection, handling and analysis by using quadrats (Investigate the number of plants/species using quadrats, 7Ca Page 36) Practical 2 In which solution of PH will cress grow best? Practical 3 Do plants follow light?
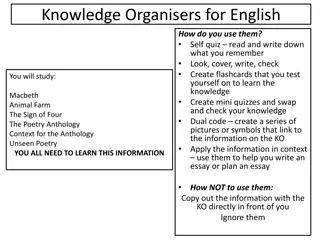
Knowledge Organiser KS3 Science Term 1
Topic: Interactions & Interdependencies Topic: Interactions & Interdependencies Skills and Knowledge Vocabulary Independence Knowledge: Key Vocabulary: Check out my free science class on Seneca using the details or QR code below: 1. Levels of organisation within an ecosystem. 2. Abiotic and biotic factors. 3. Material cycles. 4. How organisms are interdependent and are adapted to their environment. 5. Methods of identifying species and measuring distribution, frequency and abundance of species in a habitat. Ecosystem Species Community Habitat Organism Population Biodiversity Biome Competition Decomposer Producer Consumer Adaptation Pollination Photosynthesis Skills: 1. Read, interpret and create food chains and webs. 2. Mathematical skills: Using data to draw graphs and predict population trends. 3. Practical skills: use quadrats to observe and collect data around population sizes. 4. Use observation to critically think, make predictions and draw conclusions. 5. Use critical thinking skills to make sense of the world around us and find solutions to global environmental issues. Access great learning opportunities on: https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zng4d 2p
Knowledge Organiser: Interactions and Interdependencies
KS3 Science: Genetics and Evolution E M P O W E R How does learning relate to whole school intent? Learning about genetics and evolution is an integral knowledge. Learners should all be aware of the world around them and understand the complexities of how it all came to be in order to gain an empowered, appreciation for all life. How does learning relate to subject intent? Explain everyday and technological applications of Science; evaluate associated personal, social, economic and environmental implications; and make decisions based on the evaluation of evidence and arguments. Overview: Learners will be able to identify and classify different living organisms. They will discover how variation occurs and why it is important for the survival of species. They will also think about what we can do to maintain biodiversity by recognising the changes to environments due to human impacts. RESPECT READY TO LEARN RIGHT PLACE Key Vocabulary: Organism, variation, relationship, correlation, offspring, inherit, environment, classification, kingdom, vertebrate, invertebrate, species, characteristic, nuclei, chromosome, DNA, gene, genetics, gamete, fertilisation, embryo, fusion, mutation, dominant, recessive, breed, breeding, resistant, cloning, pollination, asexual, allele. L E A R N Characteristics of effective learners: Skills Knowledge 1. 2. Respectful to others and their surroundings Positive attitude and commitment to their education Motivated and persistent even if you face difficulty Consistently behaves well Sets goals and achieves High attendance 1. Identify heredity as the process by which genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next 1. Cultural Skills: identify and classify a number of different living organisms. A C H I E V E 2. Recognise a simple model of chromosomes, genes and DNA in heredity. 2. Mathematical skills: Use data to plot graphs and identify/interpret, trends and correlations. 3. 3. Identify differences between species 4. 5. 6. 3. Practical skills: Use PH scale, universal indicators and knowledge of carbon dioxide to test acidity. 4. An understanding of how and why variation between individuals within a species is important for some organisms to compete more successfully, which can drive natural selection 4. Use observation to critically think, make predictions and draw conclusions. 5. Recognise how changes in the environment may leave individuals within a species, and some entire species, less well adapted to compete successfully and reproduce, which in turn may lead to extinction 5. Use critical thinking skills to make sense of the world around us and find solutions to global ethical and environmental issues. 6. Realise the importance of maintaining biodiversity and the use of gene banks to preserve hereditary material Reading: Exploring Science 7 (7D Pages 49-62) Exploring Science 9 (9A Pages 7-18) Additional Practical s: Ocean Acidification in a cup experiments, Dissolving seashells and blowing bubbles in water to turn it acidic (PH) Jelly baby DNA models Traits investigation (Earlobes)
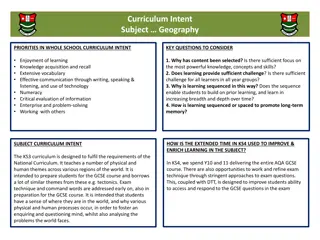
Knowledge Organiser KS3 Science Term 2
Topic: Genetics & Evolution Topic: Genetics & Evolution Skills and Knowledge Independence Vocabulary Knowledge: 1. Identify heredity as the process by which genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next 2. Recognise a simple model of chromosomes, genes and DNA in heredity. 3. Identify differences between species 4. An understanding of how and why variation between individuals within a species is important for some organisms to compete more successfully, which can drive natural selection 5. Recognise how changes in the environment may leave individuals within a species, and some entire species, less well adapted to compete successfully and reproduce, which in turn may lead to extinction 6. Realise the importance of maintaining biodiversity and the use of gene banks to preserve hereditary material Key Vocabulary: Check out my free science class on Seneca using the details or QR code below: Organism Variation Relationship Correlation Inherit Environment Classification Kingdom Vertebrate Invertebrate Species Characteristic Nuclei /Nucleus Chromosome DNA Gene Genetics Gamete Fertilisation Embryo Fusion Mutation Dominant Recessive Breeding Resistant Cloning Pollination Asexual Skills: 1. Cultural Skills: identify and classify a number of different living organisms. Mathematical skills: Use data to plot graphs and identify/interpret, trends and correlations. Practical skills: Use PH scale, universal indicators and knowledge of carbon dioxide to test acidity. Use observation to critically think, make predictions and draw conclusions. Use critical thinking skills to make sense of the world around us and find solutions to global ethical and environmental issues. 2. 3. 4. Access great learning opportunities on: https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zng4d 2p 5.
Knowledge Organiser: Genetics & Evolution
Knowledge Organiser: Genetics & Evolution
Knowledge Organiser KS3 Science Term 3
KS3 Science: Structure and functions of living organisms E M P O W E R How does learning relate to whole school intent? Learning about genetics and evolution is an integral knowledge. Learners should all be aware of the world around them and understand the complexities of how it all came to be in order to gain an empowered, appreciation for all life. How does learning relate to subject intent? Explain everyday and technological applications of Science; evaluate associated personal, social, economic and environmental implications; and make decisions based on the evaluation of evidence and arguments. Overview: Learners will be able to order, identify and describe functions of different organelles, cells, tissues and organs within organisms. They will make observations using light microscopes and by preparing slides. They will also be able to identify major bones and muscles and describe how they work together in pairs for movement. RESPECT READY TO LEARN RIGHT PLACE Key Vocabulary: Organ, brain, gullet/foodpipe, trachea/windpipe, lungs, heart, skin, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines, flower, leaf, stem, root, function, tissues, microscope, stage, focusing wheel, objective/eyepiece lenses, magnification, resolution, specimen, slide, coverslip, stain, cell, membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, chlorophyll, vacuole, cell wall, adapted, specialised cells, excrete, nutrition, cell division/mitosis, body/plant systems, graft, skeleton, vertebrae/backbone, skull, bones, muscles, contract, relax, biceps, triceps, joints, tendons, antagonistic pairs. L E A R N Characteristics of effective learners: Skills Knowledge 1. 2. Respectful to others and their surroundings Positive attitude and commitment to their education Motivated and persistent even if you face difficulty Consistently behaves well Sets goals and achieves High attendance cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe, interpret and record cell structure using a light microscope 1. Cultural Skills: identifying organelles, cells, tissues and organs of living organisms. A C H I E V E the functions of the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, mitochondria and chloroplasts 2. Mathematical skills: making scientific calculations using formulae . 3. the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells 4. 5. 6. the role of diffusion in the movement of materials in and between cells 3. Practical skills: Using microscopes and creating slides to make observations the structural adaptations of some unicellular organisms the hierarchical organisation of multicellular organisms: from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. 4. Use observation to critically think, make predictions and draw conclusions. the structure and functions of the human skeleton, to include support, protection, movement and making blood cells 5. Use critical thinking skills to make sense of the our bodies and how they are broken down into different parts that all work together. biomechanics the interaction between skeleton and muscles, including the measurement of force exerted by different muscles the function of muscles and examples of antagonistic muscles. Reading: Exploring Science 7 (7A Pages 8-19) Exploring Science 9 (9B Pages 28-29) Additional Practical s: Using light microscopes, Creating slides with specimens Chicken wing antagonistic pairs practical