Exploring the Fascinating World of Mollusks
Mollusks, with around 200,000 species, are diverse soft-bodied invertebrates usually enclosed in calcium carbonate shells. This phylum includes various forms like chitons, snails, clams, octopuses, and more, each exhibiting unique features. Mollusks have bilateral symmetry and a ventral muscular foot for movement. They occupy diverse marine environments, from rocky shores to hydrothermal vents. Gastropods have a stomach-foot and use a radula to scrape algae, while bivalves like clams filter food particles from water using expanded gills.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
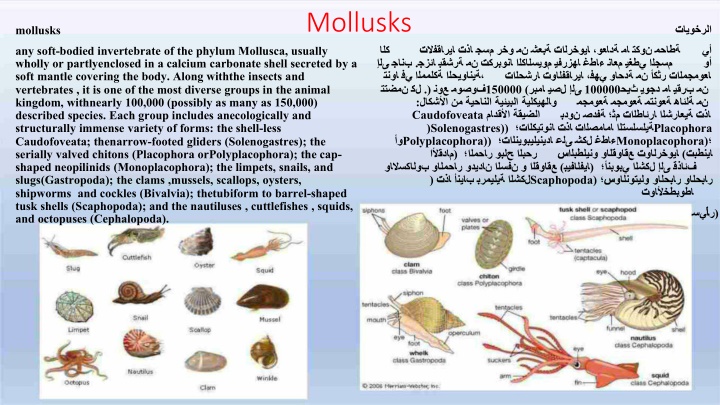
Mollusks mollusks . .) 150000 ( 100000 : Caudofoveata )Solenogastres)) Placophora Polyplacophora)) Monoplacophora) ) ( ) ) Scaphopoda) any soft-bodied invertebrate of the phylum Mollusca, usually wholly or partlyenclosed in a calcium carbonate shell secreted by a soft mantle covering the body. Along withthe insects and vertebrates , it is one of the most diverse groups in the animal kingdom, withnearly 100,000 (possibly as many as 150,000) described species. Each group includes anecologically and structurally immense variety of forms: the shell-less Caudofoveata; thenarrow-footed gliders (Solenogastres); the serially valved chitons (Placophora orPolyplacophora); the cap- shaped neopilinids (Monoplacophora); the limpets, snails, and slugs(Gastropoda); the clams ,mussels, scallops, oysters, shipworms and cockles (Bivalvia); thetubiform to barrel-shaped tusk shells (Scaphopoda); and the nautiluses , cuttlefishes , squids, and octopuses (Cephalopoda). ( )
Phylum Mollusca 200,000 species More species in ocean than any other ani mal group Soft body enclosed by calcium carbonate shell Body covered by mant le Thin layer of tissue that secretes t he shell Displays Bilateral Symmetr y Ventral muscular foot used for locomotion Most had have that includes eyes and other sens ory organs
Essentially, Essentially, a a mollusc s s of of vital vital organs organs wrapped wrapped in in a a dorsal dorsal shell. mollusc is is a a coiled coiled mas mas shell.
Phylum Mollusca Some have radula Ribbon of small teeth used to ra sp food from surfaces Made of chiti n Have paired gill s Portion of body may be coiled and asymetrical Occupy all marine environments rocky shores to hydrothermal vents
Class Gastropod Stomach Footed Coiled mass of vital organs enclosed by a dorsal shell re sting on a foot Most use radula to scrape algae Mud snails are deposit fee ders Whelks, oyster drills, and cone shells are carnivores that prey on clams, oysters, worms, and small fishes Modified Radula to drill and rasp prey
ClassBivalvia Clams, mussels, and oyst ers Body laterally compressed and encl osed with two parts (valves) No head or rad ula Gills expanded and folded used to o btain oxygen, and filter and sort food particles fro m water
Class Bivalvia Inner surface of shell lined w/ m antle so whole body lies in mantle cavity Strong muscles used to close valves Clams burrow in sand or mud and wa ter drawn in and out of mantle by siphons Allow clam to feed and obtain oxygen whi le buried
Class Bivalvia Mussels secrete byssal threads that attach them to rock s and other surfaces
Class Bivalvia Oysters cement their left shell t o hard surface and other to another oyster are lodged within the mantle cavity and Pearls occur when irritating particles covered by secretions (CaCO3) from oyster
Class Bivalvia Some scallops can swim by rapidly ejecting water from mantle cavity with siphon Shipworm bores in mangroves, driftwood, and pilings Have symbiotic relationship w/ bacteria in the gut that digests wood Valves lie at the inner end of tunnel lined w/ calcium carbona te and siphon protrudes from entrance Fouling organism = settles on bottoms of boats, pilings, and ot her submerged surfaces