Extreme Programming (XP) Methodology: Enhancing Software Quality and Responsiveness
Extreme Programming (XP) is an agile software development methodology focused on improving software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. It advocates frequent releases and emphasizes paired programming, code reviews, unit testing, and clear communication with customers. Despite its benefits, XP has potential drawbacks like unstable requirements and lack of overall design specification.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
COMP 3663 DANIEL L. SILVER, PHD IMPLEMENTATION 2
XP = EXTREME PROGRAMMING An agile method intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements Advocates frequent "releases" in short development cycles Recognizes that requirements will change Intended to improve SE productivity Name is derived from the idea that the beneficial elements of traditional software engineering practices are taken to "extreme" levels. Originally - Newly tested code every day!
XP = EXTREME PROGRAMMING Features: Paired programming Extensive code reviews Unit testing Organic flat structure Simplicity and clarity in code Frequent communication with the customer / among programmers Potential drawbacks: Unstable requirements Compromises of user conflicts are lost No overall design specification
XP = EXTREME PROGRAMMING Four basic activities: Coding - only truly important product; code should always be clear and concise and have one interpretation Testing - unit, integration, acceptance testing Listening - to what the customer really needs Designing - creating a design structure that organizes the logic in the system; cohension and coupling Four or more values: Communication, Simplicity, Feedback, Courage, Respect Darn near a religion !!
XP = EXTREME PROGRAMMING What we wish it meant: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ytu1Hxzr_Bs Strengths and Weaknesses of XP https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LkhLZ7_KZ5w
PAIRED PROGAMMING An agile software development technique Two programmers work together at one workstation Driver - writes code Observer, pointer or navigator reviews code as typed The two programmers switch roles frequently Observer also considers the "strategic" direction of the work Considers improvements and likely future problems Driver can focus on the "tactical" aspects of current task
PAIRED PROGAMMING Economics: Pairs spend about 15% more time versus individuals Results in 15% fewer defects, from 70%-85% (which cost $ as well) Quality: Greater potential to generate more diverse solutions Different experience / knowledge Different search for relevant information Different roles = different perspective Satisfaction: 96% of programmer/ analysts who try it like it 95% more confident in solutions Education: Show me and I may remember, Involve me and I will understand Knowledge shared between paired individuals (logic, coding methods, style) Promiscuous pairing - each programmer can work / share with many others
PAIRED PROGAMMING Teamwork: Sharing problems / solutions less chance for hidden agendas Raises communication bandwidth / frequency within the project Increases information flow within the team Watch-out-fors: Silence = lack of collaboration Watch the master = junior person side-lined by senior Withdrawl = down one member most of the time Pairing Combinations: Expert Expert - high productivity, great results / may yield little insight into solutions and practicses Expert Novice - many opportunities for mentoring, leads new solutions and ideas / may lead to "watch the master Novice Novice low productivity, quality / but significantly better than individuals
PAIRED PROGAMMING Video - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ET3Q6zNK3Io
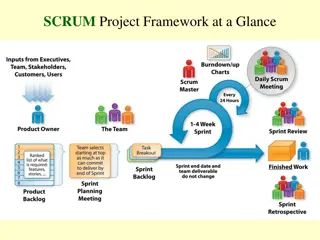
SCRUM An iterative and incremental agile SE framework A flexible, holistic product development strategy where a development team works as a unit to reach a common goal [Takeuchi and Nonaka] Enables teams to self-organize by: Encouraging physical co-location or close online collaboration Daily face-to-face communication among all team members A key principle is recognition that change happens Called "requirements churn Accepts that problem cannot be fully understood or defined Focuses is on: Maximizing the team's ability to deliver quickly on what they know Responding to emerging requirements
SCRUM Where does the word scrum come from? Three core roles: Product Owner , Development Team, Scrum Master Product Owner Communicates between team and steakholders Voice of the customer Face of the team to the stakeholders Ensures that the team delivers value to the business Responsible for user stories capturing requirements Empathetic, good at negotiations and collaboration
SCRUM Where does the word scrum come from? Three core roles: Product Owner , Development Team, Scrum Master Development Team Deliver potentially shippable increments (PSIs) at the end of each Sprint 3 9 individuals with cross-functional SE skills Self-organizing group Scrum Master Ensures team delivers the product Acts as buffer between the team and any distracting influences Enforces Scrum rules, chairs key meetings, challenges team Not a Project Manager does not manage people
SCRUM Sprint Iteration = basic unit of development in Scrum Time-boxed one to four weeks, two weeks typical Emphasizes working product at end of Sprint integrated, fully tested, end-user documented, and potentially shippable Started by a planning meeting Tasks for the sprint are identified Goal of sprint estimated Ends with review-and-retrospective meeting Progress is reviewed / lessons identified
SCRUM Daily scrum meeting Occurs each day a project team communication meeting All members of team come prepared with the updates Starts precisely on time even if members are missing Same location and same time every day Length is set to 15 minutes All are welcome, but normally only the core roles speak During the meeting, each team member answers three questions: What have you done since yesterday? What are you planning to do today? Any impediments/stumbling blocks? Problems are documented by the Scrum Master. Work towards resolution happens outside meeting. No discussions.
SCRUM Scrum of Scrums Technique to scale Scrum up to large development groups (12+) Allows Scrum team reps (ambassadors) to discuss work Focus on areas of overlap and integration Each daily scrum selects a member as "ambassador The SofS asks four questions: What has your team done since we last met? What will your team do before we meet again? Is anything slowing your team down or getting in their way? Are you about to put something in another team's way?
SCRUM Video - Scrum in Under 10 Minutes: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XU0llRltyFM&list=PLutqk bLkswNsTZipUX4oF4AKfsblDOuLR Video - Scrum in only 8 Minutes: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QfFu-YQfK4 Video - Scrum in only 2 Minutes:-- Wow !! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WxiuE-1ujCM