Fasciola Hepatica: Transmission, Life Cycle, and Clinical Manifestations
Fasciola hepatica, a parasitic trematode, is transmitted through ingestion of metacercariae in aquatic plants or water. Its life cycle involves stages in the liver and bile ducts, leading to clinical manifestations such as fever and abdominal pain. Diagnosis typically involves identifying eggs in stool samples.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
4. Fasciola hepatica : Mode of transmission is by ingestion of metacercariae found in edible aquatic plants or by drinking water with floating metacercariae Metacercariae excsts in the duodenum or jejunum and liberate the juvenile fluke Juvenile fluke penetrates the intestinal wall and reaches the liver capsule The parasite burrows into the liver parenchyma where it grows and develops It becomes sexually mature in the bile ducts
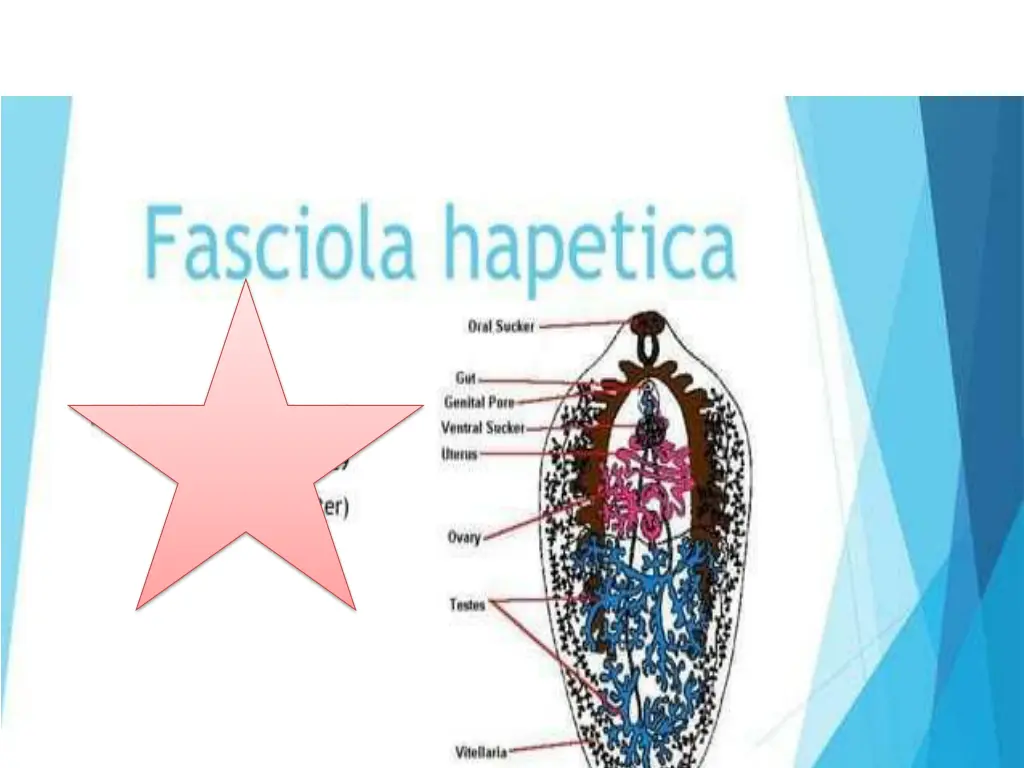
5. Fasciola hepatica Adult Worm Large, broad, flat body Leaf shaped Anterior end forms a prominent cephalic cone Small oral and ventral suckers Long and highly branched intestinal caeca
7. Fasciola hepatica and gigantica Definitive host: Sheep Cattle Humans (Accidental) Other Mammals Intermediate host Fresh Water Snail 8. Fasciola hepatica Ova .Large ,Hen s egg shaped ,Ovoid ,Operculated ,Bile stained ,Unsegmented
9. Life cycle of F.hepatica The life cycle of Fasciola hepatica starts when a female lays eggs in the liver of an infected human. Immature eggs are discharged in the biliary ducts and taken out in the feces. If landed in water, the eggs become embryonated and develop larvae called miracidia. A miracidium invades an aquatic snail and develops into cercaria, a larva that is capable of swimming with its large tail. 10. Cycle of events in infection The cercaria exits and finds aquatic vegetation where it forms a cyst called Metacercariae. A human eats the raw freshwater plant containing the cyst. The Metacercariae excysts in the first part of the small intestine, duodenum. It then penetrates the intestinal wall and gets into the peritoneal cavity.
12. Fasciola species Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestations - Fascioliasis -Asymptomatic - Can produce fever - - Right upper quadrant abdominal pain - -Hypereosinophilia - - Acute or invasive phase - Migration from intestine to liver in liver parenchyma Chronic or latent phase Asymptomatic - Parasite has reached the bile ducts - Obstruction - Stimulates inflammation in the biliary epithelium leading to fibrosis - Obstruction causes Biliary sepsis Traumatic and necrotic lesions
13. Fasciola species Diagnosis Microscopy -demonstration of eggs in the Stool Samples Yellow-Brown Eggs Eggs Don t Show for 4 Months Duodenal or Biliary Aspirate Antibody Test Can detect 2 Weeks After Infection Ultrasound Visualize Adults in Bile Duct Reveals Burrows in Liver CT Scan
14. Fasciola species Treatment Bithionol 20-50 mg/kg body weight on alternate days to complete 10 to 5 doses Triclabendazole Also a recommended drug of choice due to: Efficacy 15. Control : Education Effective Way Wash Aquatic Vegetables in 6% Vinegar for 5-10 minutes Better herding practices , Moluskicide Controls Intermediate Snail Host Safety Cheapest and Most Cost Ease of use
