Female Reproductive System Inflammation and Infections Overview
Explore information on inflammation and infections of the female reproductive system, including common conditions like Bartholinitis, vaginitis, vulvovaginitis, and more. Learn about the causes, clinical features, and management strategies for various bacterial, fungal, and viral infections affecting the female genital area.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
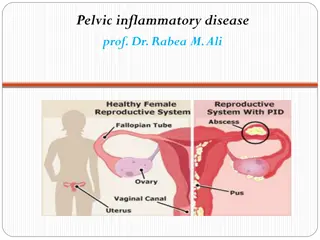
INFLAMATION AND INFECTIONS OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
COMMON INFECTIOUS CONDITION Bartholinitis, Bartholin abscess and Bartholin cysts Vaginitis : Bacterial,viral,monilial and atrophic (postmenopausal) Vulvovaginitis
ETIOLOGY Specific organisms or non-infective dermatitis Irritation from vaginal discharge or menses Lack of vulvar hygiene Glycouria
CAUSATIVE ORGANISMS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATION BACTERIAL INFECTIONS CAUSES caused by sexually transmitted organisms CLINICAL FEATURES Increased vaginal discharge Musty or fleshy odour of discharge following sexual intercourse Homogeneous, gray white discharge MANAGEMENT Local antiseptics Systemic antibiotics
CAUSATIVE ORGANISMS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATION MONILIASL INFECTION CAUSES Candida albicans CLINICAL FEATURES Itching and burning Thick curd like discharge Dyspareunia Vulvar or vaginal erythema Edematous cervix MANAGEMENT Local fungicidal preparation (nistatin,clotrimazole,miconazole or econazole or fluconazole)
CAUSATIVE ORGANISMS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATION VULVAL INFECTIONS CAUSES Varicella zoster virus CLINICAL FEATURES Painful eruptions of group of vesicles MANAGEMENT Analgesics Antiviral - Acyclovir Antibiotic
CLINICAL FEATURES Dryness and soreness Itching and burning Vulvar and vaginal atrophy Pale,thin, friable vaginal mucosa Sparse pubic hair Dyspareunia Yellowish or blood stained discharge
TREATMENT Intravaginal applications of estrogen cream Systemic estrogen if there is no contraindication Treatment of local infection if present
BARTHOLINITIS Infection of the major vestibular glands
CAUSES Staphylococcus E.Coli Streptococcus Enterococcus Gonococcus Chlamydia trachomatis Polymicrobial infection is common.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION Local pain and discomfort Difficulty in walking or sitting Tenderness and induration of the posterior half of the labia when palpated between thumb outside and the index finger inside the vagina Tenderness and induration of the posterior half of the labia Duct opening looks congested and secretion comes out
TREATMENT Hot compress and analgesics Antibiotics (Ampicillin) in the early stage Drain the abscess (excision of an elliptical piece of skin)
Bartholins Cyst Marsupialization for preservation of the gland function Excision for recurrent cases
BARTHOLINS ABCESS Bartholin s abscess is the end result of acute bartholinitis Bartholinitis Fibrosis Ducts get blocked Exudates pent up inside Abscess
BARTHOLINS ABCESS CLINICAL FEATURES Pain and discomfort Patient cannot walk or even sit Fever Tenderness Swelling beneath the posterior half of the labium majus
BARTHOLINS ABCESS TREATMENT Rest Analgesics Sitz bath Antibiotic Ampicillin or Tetracycline Abscess should be drained Marsupialisation
VAGINAL INFECTION (VAGINITIS)
VULVO VAGINITIS IN CHILDHOOD Inflammatory condition of the vulva and vagina Caused by lack of estrogen
VULVO VAGINITIS IN CHILDHOOD ETIOLOGY Non specific vulvovaginitis Presence of foregin body in the vagina Associated infection Infection caused by candida albicans and gonococcus
VULVO VAGINITIS IN CHILDHOOD CLINICAL FEATURES Pruritis Vaginal discharge scanty to copious Painful micturition Soreness of the vulva Minora may be swollen and red
VULVO VAGINITIS IN CHILDHOOD INVESTIGATION Two smears are taken One direct examination and the other for gram stain Culture to exclude intestinal infection Vaginoscopy to exclude foreign body
VULVO VAGINITIS IN CHILDHOOD TREATMENT Perineal hygiene Removal of foreign body Estrogen ointment Ethinyl estradiol vaginal cream
CANDIDA VAGINITIS(MONILIASIS)
CANDIDA VAGINITIS (MONILIASIS) ETIOLOGY Candida albicans Gram positive Yeast like fungus
CANDIDA VAGINITIS (MONILIASIS) CLINICAL FEATURES Vaginal discharge with intense vulvovaginal pruritis Discharge is thick,curdy white and in flakes ,often adherent to the vaginal wall Vulva may be red and swollen Vaginal examination may be tender Removal of white flakes reveals multiple oozing spots
CANDIDA VAGINITIS (MONILIASIS) TREATMENT Fungicidal preparation Nystatin,clotrimazole,miconazole,econazole are used in the form of vaginal cream or pessary Single dose oral therapy with fluconazole or itraconazole is also found effective
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS ETIOLOGY 1. Imbalance of normal vaginal flora Diminution of Doderlein lactobacillus and Increase in other bacteria, in particular, anaerobic bacteria. 2. Causative factors of the imbalance are unknown Gardnerella vaginalis
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS CLINICAL PICTURE Symptoms: 10-40% asymptomatic Mild pruritus or burning sensation Increased vaginal discharge and fishy odor Signs: Discharge: thin, greyish-white, homogenous, but not sticky No inflammation reaction (No epithelial edema or erythema)
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS TREATMENT Systemic therapy (oral) (80%) 1) Metronidazole 400mg, 2-3 times a day for 7 days 2) Clindamycin 300mg, twice a day for 7 days Topical therapy (80%) 1) Effervescent tablets of metronidazole 200mg/day, for 7-10 days 2) 2% Clindamycin cream, once a day for 7 days Vaginal washing 1-3% H2O2 , 1% lactic acid, 0.5% acetic acid
ATROPIC VAGINITIS(SENILE VAGINITIS) DEFINITION Vaginitis in postmenopausal women is called atrophic vaginitis
ATROPIC VAGINITIS(SENILE VAGINITIS) CLINICAL FEATURES Postmenopausal yellowish or blood stained vaginal discharge Discomfort,dryness,soreness in the vulva Dyspareunia Evidences of pruritis vulvae The character of discharge is yellowish or blood stained Vaginal examination is often painful and the walls are found inflamed
ATROPIC VAGINITIS(SENILE VAGINITIS) DIAGNOSIS Exclude carcinoma EUA Diagnostic curettage Cervical cytology or biopsy TREATMENT Improvement of general health and treatment Systemic estrogen therapy Intravaginal application of estrogen cream
ACUTE CERVICITIS It is an infection of the Endocervix including the glands and the stroma
ACUTE CERVICITIS ETIOLOGY Neisseria gonorrhoeae Chlamydia trachomatis Staphylococcus Streptococcus Enterococcus
ACUTE CERVICITIS CLINICAL FEATURES Symptoms Asymptomatic Mucopurulent vaginal discharge Vaginal irritation symptoms:pruritus, burning sensation Lumbosacral pain, Intermenstrual bleeding, postcoital bleeding Symptoms of the lower urinary tract Signs Inflammation of the cervix with mucopurulent discharge (MPC for mucopurulent cervicitis)
ACUTE CERVICITIS DIAGNOSIS Gram s stain of the cervical discharge for leukocyte Tests for gonococcus and chlamydia Wet mount microscopy for trichomonads
ACUTE CERVICITIS TREATMENT Systemic medication Choice of drugs depends on the pathogens,Examples: GONORRHEA INFECTION Third generation Cephalosporins Ceftriaxone Sodium Spectinomycin CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS Doxycycline Azithromycin Erythromycin Ofloxacin
CHRONIC CERVICITIS ETIOLOGY When the stratified epithelium which normally 1. covers the vaginal portion of the cervix is replaced by columnar epithelium which is continuous with that of the cervical canal. Most erosion are not infected, nor they are the result of 2. inflammation. Occurs in the newborns, pregnancy, oral contracepives 3.
CHRONIC CERVICITIS CLINICAL FEATURES Symptoms The only symptom is a mucoid discharge. A slight postcoital bleeding (but malignancy should be excluded) Signs A red area is seen around the external os.
CHRONIC CERVICITIS TREATMENT Erosion found on routine examination should not be treated unless it is causing troublesome discharge. A cervical smear is needed before the treatment, and if necessary, colposcopy and biopsy. Cervical ectropion PHYSICAL THERAPY Thermal cauterization, Cryotherapy, Laser therapy