Female Reproductive Unit -Introduction
Sexual reproduction involves the union of ovum and sperm cells, known as gametes, each carrying half of the normal body cell's chromosomes. This process plays a crucial role in the female reproductive unit. Through the introduction of sex cells, a new organism's genetic material is formed, ensuring genetic diversity and continuation of species. Understanding the intricacies of this fundamental biological process is essential in comprehending the complexity of life's creation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Female Reproductive Unit -Introduction Sexual reproduction This is the union of the nuclei of ovum and sperm cell. Ovum and sperm cells are called gametes. Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of a normal body cell. Gametes (ovum and sperm cell) Gametes are produced in the gonads. Female gonads are the ovaries; male gonads are the testes.
Introduction Fertilization An ovum leaves the ovaries and travels through the fallopian tube. Fertilization takes place if sperm cells are present and unite with the ovum. The fertilized egg implants then divides to form a ball of cells, called a zygote (and later an embryo and then a fetus).
Organs of the Female Reproductive System Organs of the female reproductive system (lateral view)
Organs of the Female Reproduction System Organs of the female reproductive system (anterior view)
Menstruation and Pregnancy Menstrual cycle Day 1-5 Blood cells, endometrial cells, and glandular secretions discharge from the body. Day 6-12 Estrogen aids repair of endometrium. The ovum grows in the follicle. Day 13-14 The egg leaves the ovary and passes through the fallopian tube. Day 15-28 The corpus luteum secretes progesterone; the uterus lining builds up.
Menstruation and Pregnancy Pregnancy If fertilization occurs, the egg implants in the uterine endometrium. The placenta forms, attaches to the uterine wall. Amnion holds the fetus in an amniotic cavity. Nutrients, oxygen, and wastes exchange between the fetus and mother. The placenta produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Menstruation and Pregnancy Pregnancy Progesterone maintains placenta development. The uterus expands as the fetus grows. Normal delivery fetal position is cephalic presentation (head first). Pregnancy Three phases of labor 1. Dilation and thinning of the cervix 2. Birth of the infant 3. Delivery of the placenta
Hormonal Interactions The pituitary secretes: Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) The pituitary stops producing FSH and LH During pregnancy With oral contraceptives Menopause Gradual ending of the menstrual cycle Normally begins between ages 45 and 55 Falling estrogen levels Option for estrogen replacement therapy
Abnormal Conditions Endometriosis Endometrial tissue located outside the uterus Fibroids Benign tumors of the uterus Figure shows location of uterine fibroids
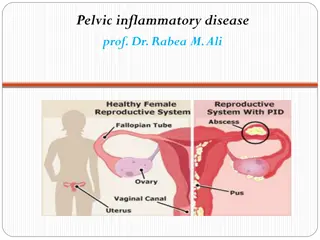
Pathology: Gynecological & Breast Breast Carcinoma of the breast Ovaries Ovarian cysts Collections of fluid within a sac in the ovary Fallopian tubes Pelvic inflammatory disease Leading causes of PID are sexually transmitted diseases
Pathology: Pregnancy Placenta previa- placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb & covers all or part of the opening to the cervix. Preeclampsia-occurrence of elevated blood pressure (hypertension) & significant amounts of protein in urine. Abruptio placentae Premature separation of the normally implanted placenta Ectopic pregnancy Misplaced implantation of egg
Clinical Tests and Procedures Clinical tests Pap test (Pap smear) Pregnancy test Amniocentesis Needle placement guided by ultrasound images Procedures X-rays Ultrasound Gynecological procedures Procedures during pregnancy