Fetal Anomalies in Pregnancy
Explore fetal congenital anomalies, associated USG features, preventive measures, high-risk factors in pregnancy planning, complications, and preconception advice. Dive into GDM risks, maternal complications, syndromes presenting with amenorrhea, and genetic mutations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
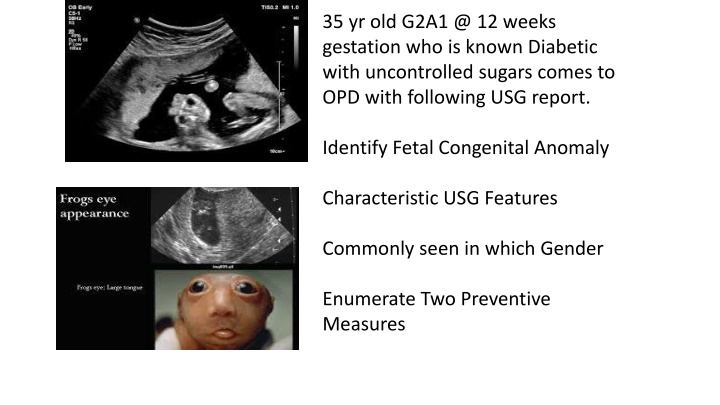
35 yr old G2A1 @ 12 weeks gestation who is known Diabetic with uncontrolled sugars comes to OPD with following USG report. Identify Fetal Congenital Anomaly Characteristic USG Features Commonly seen in which Gender Enumerate Two Preventive Measures
O OSCE 2 30 yr old lady married for 1 yr with a BMI of 34 is planning to conceive. Identify high risk factor in this case Enlist two possible complications which can occur during pregnancy What preconceptional advise should be given to her
OSCE 3 Enumerate Four High Risk Features for GDM Enumerate Four Maternal Complications resulting from hyperglycaemia in pregnancy
OSCE 4 Name two syndromes which present as primary amenorrhoea with absent secondary sexual Characteristics First Line Investigation Investigation of choice for diagnosis
OSCE 5 1. Swyers syndrome A. Mutation in Kal 1 Gene 2. Kallman Syndrome B. Mutaion in FMR 1 Gene 3. Fragile X Syndrome C. Mutation in SRY Gene 4. Turner s Syndrome D. 45 XO
OSCE 1 KEY Anencephaly Total or partial absence of Calvarium with absent cranial bones Bulging Orbits Frog Eye /Mickey Mouse appearance Female Preconceptional Folic Acid Supplementation Optimal sugar control both
OSCE 2 KEY Obesity Hyperglycemia in Pregnancy,Macrosomia,Sepsis,Increased LSCS Lifestyle modification Weight Reduction Investigation for timely Diagnosis of DM,HTN,Thyroid Dysfunction And their optimisation
OSCE 3 KEY Preeclampsia Polyhydramnios Infection PPH Advanced Maternal Age Family History of Diabetes Mellitus Obesity PCOS
OSCE 4 KEY Swyer ssyndrome/Turner s Syndrome Serum FSH/LH Karyotype
OSCE 5 KEY 1 C 2A 3B 4 D