Field Capacity, PWP, and Water Holding Polymers in Soil and Plant Water Relations
Learn about Field Capacity (FC) and Permanent Wilting Point (PWP), their significance for plant growth, and the role of water holding polymers like hydrogels in soil moisture management.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
UNIT - 01 :- SOIL AND PLANT WATER RELATIONS LECTURE - 05 :- Concept of FC and PWP ;Water holding polymers and their relevance.
FIELD CAPACITY Field capacity (FC) is the amount of soil moisture or water content held in soil after excess water has drained away and the rate of downward movement has decreased, which takes place within 2-3 days after a rain or irrigation in previous soil. Weight of water retend in the soil after gravitational water has drained off that is the water exactly required by the plants for their growth.
Fig; Graph between soil texture class and volumetric soil moisture
CONCEPT OF PWP Critical value below which root cannot extract enough moisture due to increase in soil moisture surface tension. At this point water can t percolates out of soil because it is strictly adhere to the soil particles. It is the point when there is no water available to the plants. Permanent wilting point depends on the plant variety, but it is usually around 1500 kPa (15 bars). At this stage, the soil still contains some water, but it is difficult for the roots to extract from the soil particles . If water is less than permanent wilting point plants wilt and growth is stopped and plants die.
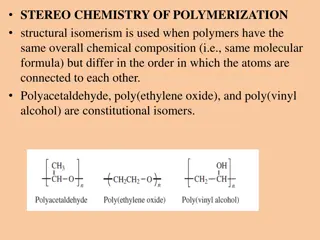
WATER HOLDING POLYMERS Water holding polymers potentially influence soil evaporation and infiltration rates of water through the soils. Particularly, the polymers reduce irrigation frequency and compaction tendency, stop erosion and water run off. Hydrogels are hydrophilic crosslinked polymers that form three-dimensional molecular networks which can absorb and hold great amounts of water.
HYDROGEL Moisture released by hydrogel close to root area helps reduce stress and increase growth and plant performance. Hydrogels can reduce fertilizer leaching and reduce application of pesticides. Hydrogel works as water reservoirs round the root mass zones of the plant. Fig; Hydrogel