Flow in Unsaturated Soil: Summary and Examples
Explore the concept of flow in unsaturated soil, focusing on continuity, Darcy's law, suction head, and moisture content. Examples and images help clarify key points such as determining vertical flux and hydraulic conductivity ratios for different soils. This comprehensive resource covers equations representing soil water characteristics and hysteresis in hydrology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
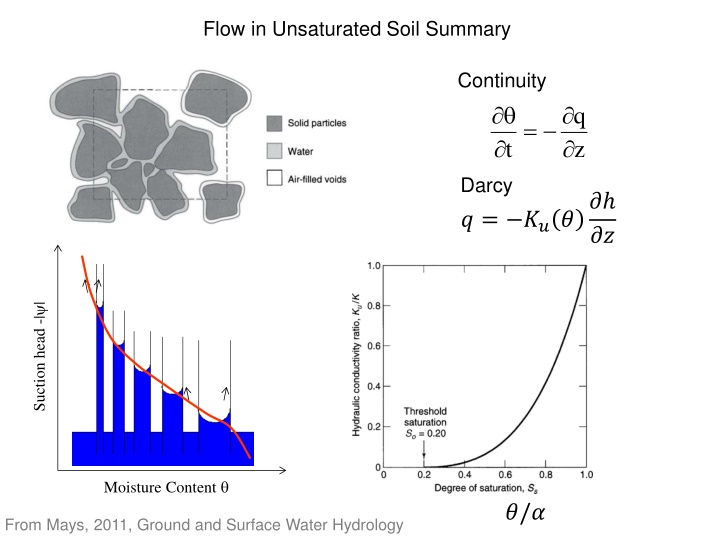
Flow in Unsaturated Soil Summary Continuity q = t z Darcy ? ?? ? = ??? Suction head -| | Moisture Content ?/? From Mays, 2011, Ground and Surface Water Hydrology
Example 3.7.1 Determine the vertical flux for a soil in which the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity is expressed as a function of the suction head as K=250( )-2.11 in cm/d. At depth z1 =80 cm, 1=-65 cm and at depth z2=100 cm, 2=-60 cm. Is the direction of flow up or down
Hydraulic Conductivity Ratio for different soils From Mays, 2011, Ground and Surface Water Hydrology
Equations to representing soil water characteristic functions
Residual moisture content r =5% Characteristic curve relating moisture content to pressure head (from Freeze and Cherry, 1979).
Basis for Hysteresis See http://hydrology.usu.edu/rrp/ hysteresis animation
Steady flow in a confined aquifer If the distance and the observed piezometric surface drop between two adjacent wells are 1000 m and 3 m respectively, find an estimate of the time it takes for a molecule of water to move from one well to the other. K is 3.5 m/day and effective porosity is 0.35 From Mays, 2011, Ground and Surface Water Hydrology
Steady flow in an unconfined aquifer A stratum of clean sand and gravel between two channels has K=0.1 cm/s and is supplied from a ditch ho=6.5 m that penetrates to the bottom. If the water in the second channel is h1=4 m deep above the bottom of the stratum, estimate the flow rate From Mays, 2011, Ground and Surface Water Hydrology
Unconfined aquifer between two rivers An unconfined aquifer of clean sand and gravel is located between two fully penetrating rivers. K=10-2 cm/s. L=460 m, W=1.6 m/yr, h1=10 m, h2=8.5 m, ne=0.35 Estimate - Maximum elevation of the water table - Daily discharge per km from the aquifers into each river - Travel times from groundwater divide to the rivers From Mays, 2011, Ground and Surface Water Hydrology
Unconfined aquifer flow equation with recharge 2 2 ? = ? ? ??= ?? ?? ??? ? +?? ? ???? ?? ??= ? ?2 ??2 2 2 = ? ?
