Fluid Composition and Transport Modeling
Explore a detailed simulation of fluid composition and transport, incorporating factors like ferric iron and lead concentrations. Configure reaction intervals, define inlet fluid properties, specify domain size, flow rates, and mass transport properties. Utilize sorbing surfaces for complexation processes and iteratively analyze Pb++ distribution. Understand the dynamics of Pb++ sorption and transport in aquifer sediments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Specify domains starting fluid composition on the Initial pane Negligible ferric iron (HFO) in initial system Considerable Pb++ in initial system
Define the reaction intervals. Specify what fluids flow into the domain, and when. A single inlet fluid flows into the domain for 10 years. Click to add a new reaction interval
The inlet fluid is defined on the Fluids pane Inlet fluid carries ferric hydroxide colloid into the domain Negligible Pb++ in inlet fluid
Specify domain size and gridding on the Domain pane. Domain is 1 km long, divided into 100 nodal blocks
Specify flow rate on the Flow pane. Set specific discharge or hydraulic head/ potential drop
Set various mass transport properties on the Medium pane. Colloid migrates by advection and dispersion
File Open Sorbing Surfaces Surface complexation dataset for hydrous ferric oxide. Set mobility in the domain to 1 to make HFO and its sorbate a mobile colloid. Kd describes distribution coefficient between Pb++ and immobile aquifer sediments You can add any number of sorbing surfaces.
Config Iteration If you check to include sorbate , the total Pb++ concentration defined for each fluid (Initial and Fluids panes) is distributed between solution and surfaces. Run Go traces the model
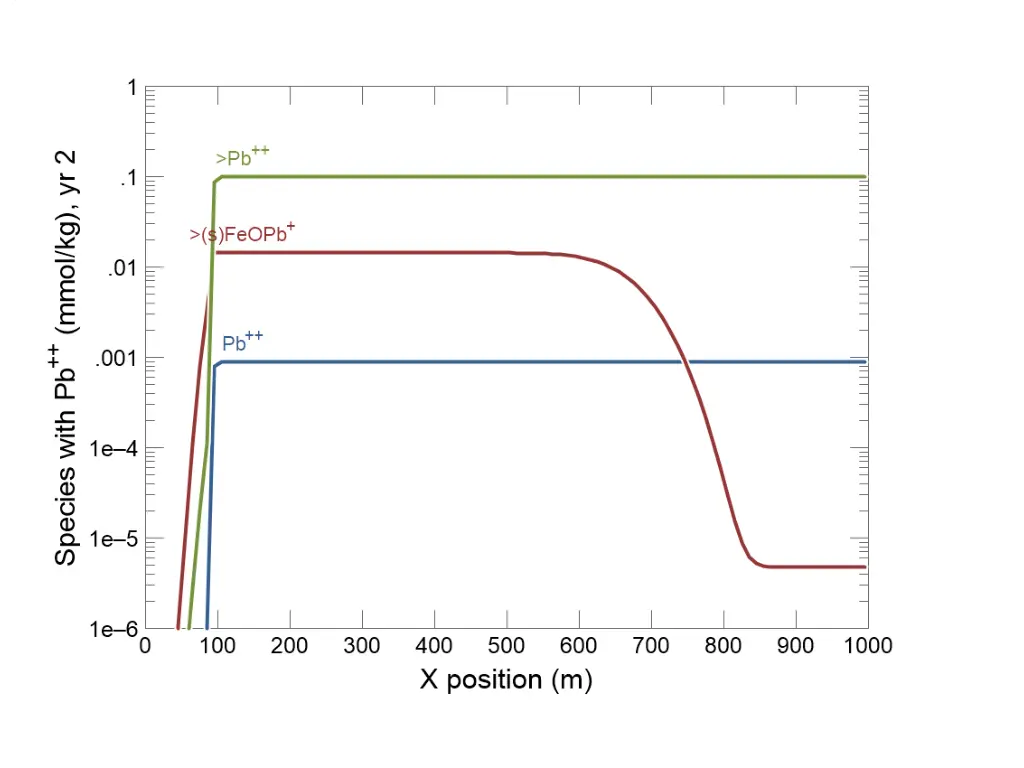
Initially Pb++ almost entirely sorbed to immobile aquifer sediments (>Pb++). Pb++ scavenged from aquifer sediments (>Pb++) onto mobile colloid surface (>(s)FeOPb+). Fluid transports ferric hydroxide colloid through aquifer.
