Food Chains and Webs
Dive into the intricate relationships within food chains and webs, from producers to consumers and the flow of energy in ecosystems. Understand the vital roles each organism plays in sustaining life and maintaining balance in nature's delicate web.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Food Chains and Webs
Producers Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers Tertiary Consumers
Another Link in the Food Chain Everyone plays a specific role in the food chain of life. You might be a human thinking they are king of the hill or you might be a bacterium under the feet. You are very important to the survival of the system no matter what role you play.
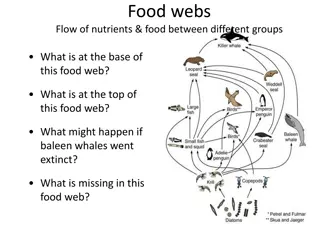
Food Chains and Webs You will see the terms food chains and food webs. They describe the same series of events that happen when one organism consumes another to survive.
Food web is a more accurate term since every organism is involved with several other organisms.
The Producers Producers are the beginning of a simple food chain. Producers are plants and vegetables.
The Producers All energy comes from the Sun and plants are the ones who make food with that energy. They use the process of photosynthesis. Plants also make loads of other nutrients for other organisms to eat.
The Consumers Consumers are the next link in a food chain. There are three levels of consumers.
Primary consumers (1st Order) Worms, insects, squirrels, mice: all eat plants (HERBIVORES) ex: squirrel eats acorns Secondary consumers (2nd Order) Eat the primary consumers (CARNIVORES) example: cat eats squirrel Tertiary consumers (3rd order) Eat the primary and secondary consumers (CARNIVORES) ex: wolf eats cat and squirrel
Omnivores eat both plants and meat They can be EITHER primary or secondary consumers.
Scavengers =They eat the remains of dead organisms left by the consumers - vultures, coyotes, hyenas
The Decomposers The last links in the chain are the decomposers. (They break things down) Like bacteria, mold, fungi, mushrooms If you die, they eat you. If you poop, they eat that. If you lose a leaf, they eat it. Whenever something that was alive dies, the decomposers get it.
Decomposers break down nutrients in the dead "stuff" and return it to the soil. The producers can then use the nutrients and elements once it's in the soil. The decomposers complete the system, returning essential molecules to the producers.
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.