Force and Its Effects in Engineering and Science
Explore the concepts of force, moment of force, and difference between weight and mass in engineering and science. Learn how to calculate forces, understand their effects on objects, and solve problems related to equilibrium and motion.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
dbs dbs 1012: 1012: ENGINEERING ENGINEERING SCIENCE SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3
OBJECTIVES: OBJECTIVES: Apply the concept of force define force and its unit state the effect of force differentiate between weight and mass define Newton s Second Law define forces in equilibrium solve problems involving forces in equilibrium calculate resultant force using resolution method
OBJECTIVES: OBJECTIVES: Use the concept of moment of force define moment of force and its unit describe principle of moment of force apply the concept and formula of moment of force in solving the related problems
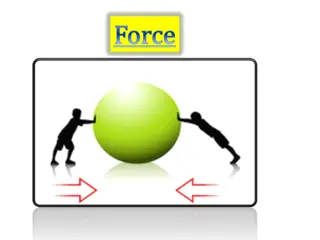
What is What is object become closer http://bodybalance4you.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/31.gif http://www.epicparent.tv/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/FORCE.gif object become distant FORCE FORCE A push or pull action
Calculating Force, F Calculating Force, F where F = force (N) m = mass (kg) a = acceleration (ms-2) SI Unit: Newton (N N)
The Effects of Force The Effects of Force http://www.oldschool.com.sg/modpub/56232851044ccbc4962704 http://lvp.lockyersmid.dorset.sch.uk/pluginfile.php/3230/mod_resource/content/0/content/pictures/physical/keyideas/phpkey0005.jpg http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_wLL4IEx-gB0/SZl_mX_6FNI/AAAAAAAAAB4/RGiDwSsQOAM/s400/img010.jpg
The Effects of Force The Effects of Force A force acting on an object may cause the object to change shape and size change direction start moving stop moving accelerate decelerate
Differences between Differences between WEIGHT, W WEIGHT, W MASS, m MASS, m Defined as the amount of matter in an object Defined as the force of gravity Vector quantity Scalar quantity Derived quantity Base quantity SI unit: Newton (N) SI unit: kilogram (kg)
Who is Who is Sir Isaac Newton?? Newton Newton formulated formulated: : the the laws laws of of motion, motion, and and universal universal gravitation gravitation
Physical Laws of Motion Physical Laws of Motion Newton s First Law Newton s First Law Newton s Second Law Newton s Second Law Newton s Third Law Newton s Third Law
Newtons Second Law Newton s Second Law States that when the net force acting on an object is not zero, the object will accelerate at the direction of the exerted force.
Newtons Second Law Newton s Second Law Acceleration is directly proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass F a m (Law of Acceleration)
Newtons Second Law Newton s Second Law F = ma F = force (N) m = mass (kg) a = acceleration (ms-2)
Exercises 1. How much force must a 35,000 kg jet plane develop to accelerate at a rate of 2.0 m/s2 ? (Answer : 70,000 N) 2. What acceleration will be produced by a force of 4000 N on a 1000 kg car ? (Answer : 4 m/s2) 3. A 0.145 kg baseball is hit from a tee with a bat so it leaves the tee at 40 m/s. If the ball was in contact with the bat for 0.0035 seconds, how much force was used to hit the ball ? (Answer : 1657 N)
Equilibrium Force Equilibrium Force Conditions for equilibrium : 1. The resultant of the forces must be zero. Fnet= 0 2. The resultant force along any two mutually perpendicular axes is zero. Fx= 0 and ??= 0
Equilibrium Force Equilibrium Force 7N 8N 8N Net force = 0 N 12N 20N 15N Object will stay at rest since there is no movement All forces which act upon an object are balance
Resultant Force Resultant Force Y y-axis Fy F2 force Fy F1 force Fx Fx horizontal component Fx = F cos X x-axis Fx Fy vertical component Fy = F sin F3 force
Solving Resultant Force, F Solving Resultant Force, FR R 1. Draw the table Angle, Angle, F Fx x = F = F cos F1 cos 1 = ___ F1 sin 1 = ___ F2 cos 2 = ___ F2 sin 2 = ___ F3 cos 3 = ___ F3 sin 3 = ___ Fx cos F Fy y = F sin = F sin Force, F Force, F F1 F2 F3 1 2 3 Fy http://victimsupporteurope.eu/activeapp/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/iStock_000011957632XSmall2.jpg Angle, is measured anticlockwise from x-axis
2. Calculate the magnitude of FR = + 2 2 ( ) ( ) F F F R x y 3. Calculate the direction of FR F y = 1 tan F x
4. Draw the vector diagram of FR + Vy FR F FR R - Vx + Vx FR FR - Vy
Exercises 1. Find the resultant force and its direction for the figure below. Sketch the resultant force diagram. y 12 N 24 N 65 30 x 50 20 N (Answer : FR = 19.25 N, = 47.52 )
Exercises 2. Calculate the resultant force and its direction for the figure below. Sketch the resultant force diagram. y 50 kN 20 75 kN 20 35 x 60 kN 40 100 kN 80 kN (Answer : FR = 161.86 kN, = 6.17 )
Moment of Force Moment of Force A force can cause many things to move or stop. When a force causes an object to turn, this turning effect is called moments https://encrypted-tbn2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSPEtT8wlH0qR50yFFD4CrtwMuhsN7D_65aPgSva4LS34pRKjJypA Example:
Moment of Force Moment of Force Is defined as the turning effect of force the turning effect of force. . 2 types of moments: https://encrypted-tbn2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSPEtT8wlH0qR50yFFD4CrtwMuhsN7D_65aPgSva4LS34pRKjJypA clockwise moment anticlockwise moment
Calculating Moments, M Calculating Moments, M where M = moment F = force (N) d = perpendicular distance of force from pivot (m) SI Unit: Newton meter (Nm Nm)
http://thumbs.dreamstime.com/z/fat-cat-smiling-14603634.jpg d Weight = F What will happen to the beam?? Explain briefly how to ensure the beam is in equilibrium.
Example 1 Example 1 A cat of weight 20 N stands on one end of a see-saw and the distance between the cat and the pivot is 3 m. Find the moment. http://thumbs.dreamstime.com/z/fat-cat-smiling-14603634.jpg d = 3 m F = 20 N M = 60 Nm
Example 2 Example 2 A duck stands on one end of a see-saw, 5 m away from the pivot. If the mass of the duck is 1.5 kg, find the moment. http://us.cdn4.123rf.com/168nwm/tigatelu/tigatelu1304/tigatelu130400017/18879158-cute-baby-duck-cartoon.jpg d = 5 m m = 1.5 kg M = 73.58 Nm
Application of Moments Application of Moments http://www.tacklejp.com/Portals/1/dreamstime_15223957.jpg http://dailyserving.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/open-door.jpg https://encrypted-tbn3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcS-c57Ct__4BUFEgcnMMJLvKK_iDfJgLTUqLO105fPz8Ys8ScKw-g http://steroidjunkie.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/how-to-arm-wrestle.jpg
Principle of Moments Principle of Moments An object will be in equilibrium (stable) if the total clockwise moment is equal to the anticlockwise moment at the same pivot http://us.cdn4.123rf.com/168nwm/tigatelu/tigatelu1304/tigatelu130400017/18879158-cute-baby-duck-cartoon.jpg http://us.cdn4.123rf.com/168nwm/tigatelu/tigatelu1304/tigatelu130400017/18879158-cute-baby-duck-cartoon.jpg weight weight
Solving Problems Solving Problems Related to Principle of Related to Principle of Moments Moments Finding the center of gravity, x F4 F1 F2 Resultant moment method Force moment method x F3
Resultant Moment Method Resultant Moment Method Take the beginning of the beam as fulcrum Step 1 Step 1 Identify whether the forces are clockwise (+) or anticlockwise ( ) moment Step 2 Step 2 Step 3 Step 3 Apply the formula http://victimsupporteurope.eu/activeapp/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/iStock_000011957632XSmall2.jpg Distance,d is measured from the force to the fulcrum
Resultant Moment Method Resultant Moment Method F3(-) F1(+) d1 d2 d3 x F2(+) + + + + ( ) ( ) ( ) F d F d d F d d d = 1 1 2 1 F 2 F 3 1 2 3 x + F 1 2 3
Exercises Find the center of gravity from point P for figure below by using resultant moment method. 100 N 50 N 25 N 1 m 5 m P Q x (Answer : x = 3.57 m)
Force Moment Method Force Moment Method Take any point on the beam as fulcrum except except on the force Step 1 Step 1 Identify whether the forces are clockwise or anticlockwise moment Step 2 Step 2 Step 3 Step 3 Equate both moments http://victimsupporteurope.eu/activeapp/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/iStock_000011957632XSmall2.jpg Distance,d is measured from the force to the fulcrum
Force Moment Method Force Moment Method F3 F1 d1 d2 d3 x F2
Force Moment Method Force Moment Method F3 F1 d1 d2 d3 x F2 Total of acw moment = Total of cw moment F1x d1 + F3d1+ d2+ d3 x = F2d1+ d2 x
Exercises Find the center of gravity from point P for figure below by using force moment method. 100 N 50 N 25 N 1 m 5 m P Q x (Answer : x = 3.57 m)
Exercises Calculate the center of gravity from point B for figure below by using a) resultant moment method b) force moment method 70 N 40 N 30 N 20 A B 2m 1m 1m 6m 1m 20 N (Answer : x = 7.11m)