Forces in Context
Exploring the concept of forces in context, this content covers topics such as resolving forces into i and j components, adding and subtracting forces, finding resultant forces, and using W=mg in problem-solving scenarios. It also delves into the concept of tension, defining it as a force on objects caused by a string pulling them in a given direction with a constant force. Additionally, it discusses weight as a force pulling objects towards the center of the Earth due to gravity. Examples and solutions are provided to aid in comprehension of these fundamental physics principles.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
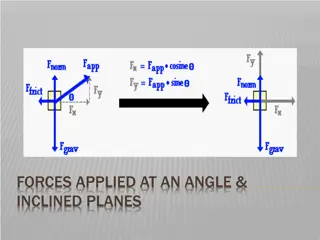
BAT resolve forces into i and j components BAT add and subtract forces, finding the resultant force in different situations BAT Use W=mg in problems Starter: The balloon is being pushed by resultant force 70 N at an angle of depression of 400 . What are the i and j components of the force ? 70 cos40 = 53.6 70 sin40 = 45.0 400 53.6i 45j 70
Tension What is Tension? Tension is a Force on objects caused by a string pulling them in a direction by a given amount. The string can be a rope or wire. Usually assumed to be inelastic, this means the Force is constant. i.e. the string does not stretch. Tension is usually given by T
WB8 A stone sphere is pulled by two horizontal ropes with Tension and directions shown Suggest a suitable model 10 8 Plan view 400 600 i) The Tension in the ropes is constant the ropes are inelastic ii) No resistant forces iii) The weight is modelled as a particle
WB8 solution A stone sphere is pulled by two horizontal ropes with Tension and directions shown. Find the size of the resultant force in the form xi + yj 10 ?????? ?????? ??????? ??????? 8 400 600 HORIZONTALLY 8cos60 10cos 40= -3.7 VERTICALLY 10sin40+ 8sin 60= 13.6 Resultant force = ?.? = ?.? ? + ??.? ? ??.?
What is weight? Weight is a Force on objects pulling them to the centre of the Earth caused by Gravity The Earth is modelled as a particle which gives objects a constant rate of acceleration g towards the center of the Earth W = mg Weight is given by Where g = 9.8 ms-2 and m is mass (kg)
WB9 A Sign hanging in space with mass 4 kg is pulled by two Cables with Tension and directions shown Suggest a suitable model j j i i i, j notation i, j notation 15 12 500 300 W i) The Weight (W) is constant / g is a constant ii) Cables are inelastic / Tension is constant in each iii) No other forces iv)Sign modelled as a particle
WB9 solution A Sign hanging in space with mass 4 kg is pulled by two Cables with Tension and directions in the same plane as shown Find the resultant force in the form xi+ yj ??????? ??????? ??????? ?? ????? 15 12 500 300 ? ?? W = HORIZONTALLY 15cos50 12cos30= -0.75 VERTICALLY15sin50+ 12sin 30 39.2 = -21.7 ?.?? ??.? Resultant force = - = ?.?? ? ??.? ?
Thrust What is Thrust? When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal to the surface is called thrust For example thrust can be the force caused by a car or plane engine. Or it could be the force exerted by a spring on a ball bearing
WB10 A pinball is at rest on a smooth slope. A spring exerts a thrust of 60 ? on the pinball. Where tan =3 4. Suggest a suitable model i) The Thrust is constant, and acts in a vertical plane ii) Weight (W) is constant / g is a constant iii) No other forces iv)Pinball modelled as a particle v) A smooth slope there are no resistance forces
WB10 A pinball is at rest on a smooth slope. A spring exerts a thrust of 60 ? on the pinball as shown. Where tan =3 Find the resultant force in the form xi+ yj 4. If the pinball has a mass of 0.3 kg ? ? ?? ? tan? =3 sin? =3 cos? =4 4 5 ?0 5 ?.? ??? ? ?.? ??? ? HORIZONTALLY 60 0.3 ??? ?= 59.76 VERTICALLYR = ?.? ??? ? = ?.?? ??.?? ? Resultant force = - = ??.?? ?
WB11 A trailer is being towed by a car up a rough slope, when the car brakes causing a thrust on the tow bar. Suggest a suitable model i) The towbar is inelastic, Thrust is constant, and acts in a vertical plane ii) Weight (W) is constant / g is a constant iii) Trailer modelled as a particle iv)A rough slope the resistance forces are constant and act in a vertical plane
A trailer is being towed by a car up a rough slope of 20 , WB11 when the car brakes causing a thrust on the tow bar of 10 N. The trailer has a mass of 120kg and the resistance force acting on the trailer are 30 N . Find the resultant force in the form xi+ yj ? ? ?? ? ?? ? ??? ??? ?? ??? ??? ?? HORIZONTALLY ?? ?? ?????? ?? = ??.? VERTICALLYR = ??? ??? ?? = ???.? ?? ? Resultant force = = ?? ?
BAT resolve forces into i and j components BAT add and subtract forces, finding the resultant force in different situations BAT Use W=mg in problems self-assess One thing learned is One thing to improve is