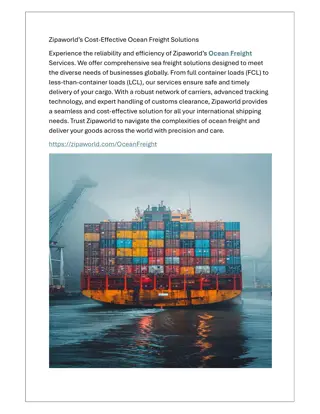
- "Funding and Support for Urban Freight Transition
- This guide explores EU and international funding programs supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation. It details the European Green Deal, sustainable industry practices, and initiatives for climate neutrality. Discover opportunities for courier and delivery operations in sustainable urban logistics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Module A: Governance Topic 2: Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 1
Introduction (3.) Session 1. - Overview of EU and other international funding programmes to support the green shift of urban logistics and last-mile freight transport. (4-8.) Session 2. - Overview of EU and other international institutional instruments to support and consult on the green shift of courier/postal/delivery operations. (9-13.) Session 3. - Overview of EU and other international career advancement opportunities in the green urban logistics sector. (14-16.) Session 4. - Assessment of digital tools and guides to greening courier/postal/delivery operations. (17-23.) Contents A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 2
INTRODUCTION This topic serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the variety of European Union and international initiatives aimed at supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation. It meticulously outlines the various funding programs, strategic frameworks, and educational opportunities designed to promote sustainable logistics and last-mile freight transport. The document delves into the European Green Deal and its ambitious targets for climate neutrality, sustainable industry practices, and the enhancement of the EU's natural capital. Additionally, it explores the role of the EIT Urban Mobility Framework in transforming urban mobility, details on significant EU funding programs through 2027, and the implications of these initiatives for courier, postal, and delivery operations. It is an essential resource for stakeholders interested in the intersection of policy, innovation, and sustainability in urban logistics. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 3
SESSION 1. Overview of EU and other international funding programmes to support the green shift of urban logistics and last-mile freight transport The European Union (EU) offers various funding programmes aimed at supporting the green shift in urban logistics and last-mile freight transport, as part of its broader objectives to achieve sustainable and smart mobility. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 4
1.1. European Green Deal and Transport The European Green Deal sets an ambitious blueprint to make the EU's economy sustainable. By turning climate and environmental challenges into opportunities across all policy areas, it aims to achieve no net emissions of greenhouse gases by 2050, decouple economic growth from resource use, and leave no person and no place behind. Overview: Climate Neutrality by 2050: Achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions through a socially fair transition. Sustainable Industry: Decarbonizing industries and implementing a circular economy action plan. Renovation Wave: Doubling building renovations for energy efficiency. Biodiversity and Farm to Fork Strategy: Protecting biodiversity and reducing pesticide use. Sustainable Transport: Aiming for a 90% reduction in transport emissions by 2050. Strategies: Increasing the EU s renewable energy share to 32% by 2030. Implementing the Circular Economy Action Plan to promote sustainability. Mobilizing 1 trillion in sustainable investments through public-private collaboration. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 5
1.2. EIT Urban Mobility Framework EIT Urban Mobility, an initiative by the European Institute of Innovation and Technology, seeks to improve urban life by accelerating the transition towards more sustainable and efficient urban transport systems. It brings together cities, universities, research organizations, and industry to innovate and educate in urban mobility, supported by a substantial EU funding commitment of up to 400 million from 2020 to 2026. Purpose: Improve urban mobility and reduce congestion. Key Programs: Innovation Hub: Develop sustainable urban transport solutions. Academy: Train future leaders in urban mobility. Business Creation and Factory: Support startups and innovations in urban mobility. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 6
1.3. EU Funding Programmes (2021-2027) The European Union's funding programs for the 2021-2027 period represent a strategic framework designed to support various sectors across member states, reinforcing economic growth, sustainability, and cohesion within the EU. These programs are pivotal in addressing contemporary challenges such as climate change, digital transformation, and social inclusion. Key Programs: Horizon Europe: 95.5 billion for research and innovation, focusing on global challenges and industrial competitiveness. Connecting Europe Facility (CEF): 33.71 billion for sustainable, interconnected transport networks. European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and Cohesion Fund (CF): Over 240 billion for regional development and cohesion. Programme for the Environment and Climate Action (LIFE): 5.43 billion focusing on environmental and climate action. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 7
1.4. Interreg 2021-2027 Initiatives Interreg 2021-2027 supports strategic regional cooperation across EU borders to address shared challenges and promote sustainable development. This initiative enhances connectivity, environmental resilience, and socio-economic integration by funding projects that encourage innovative solutions for regional and urban transportation challenges. Objective: Enhance regional integration and cooperation. Key Programs: Interreg Europe has supported various projects that impact the logistics sector, focusing on improving sustainability, efficiency, and technological integration. Interreg Danube Region supports various projects within the logistics sector, aiming to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness across the region. Interreg Central Europe (Interreg CE) is a European Union funding program that supports cooperation across Central European regions to tackle shared regional challenges. The program funds projects that enhance resilience and address transnational issues, focusing on innovation, environmental sustainability, and regional connectivity. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 8
SESSION 2. Overview of EU and other international institutional instruments to support and consult on the green shift of courier/postal/delivery operations. The green shift in courier, postal, and delivery operations is a global priority, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving market dynamics. This transition towards more sustainable practices in the delivery industry is supported and consulted by various international and EU institutions, through a mix of regulatory frameworks, technological innovations, and market- oriented reforms. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 9
2.1. UN and OECD Strategies on Sustainable Transport The UN's guide to climate action for transportation emphasizes a holistic and inclusive approach to decarbonizing the transport sector, crucial for aligning with the Paris Agreement and achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It outlines the imperative of shifting towards more sustainable, efficient, and inclusive transportation systems that cater to all, including the most vulnerable populations. Key Points: Decarbonization Efforts Inclusivity and Safety Economic and Job Opportunities Resilience and Adaptation Technology and Innovation Digital Integration A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 10
2.2. OECD's strategy for sustainable transportation The OECD's strategy for sustainable transportation, endorsed by Environment Ministers of OECD member countries in May 2001, focuses on moving towards Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST). It aims to support economic development and individual welfare without causing undue health and environmental impacts or depleting finite resources. The guidelines encourage governments to develop and implement strategies that consider their unique geographic and socio-economic conditions, offering a desirable approach for the transport sector that could also benefit other sectors in sustainable development. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 11
2.3. International Support and Consultation The World Trade Organization (WTO) outlines how the postal and courier services sector, which plays a crucial role in the global communications infrastructure, has undergone significant changes over recent decades. These changes include market-oriented reforms such as the corporatization and privatization of public postal operators and the reduction in the scope of postal monopolies. The WTO's General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) applies to postal and courier services, encouraging liberalization and improved market access. Technological advancements have also driven increased demand for parcel delivery, pivotal for e-commerce and just-in-time supply chain management . A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 12
2.4. EU Support and Consultation The European Union (EU), through its environmental and transport policies, significantly influences the green shift in courier, postal, and delivery operations. While specific EU-wide programs directly targeting courier/postal operations' sustainability were not identified in the provided materials, the EU's comprehensive environmental strategies, including the European Green Deal, likely encompass measures that indirectly support this sector's greening. The EU has historically emphasized reducing emissions, promoting energy efficiency, and fostering innovation in transport and logistics, which would include courier and postal services as part of the broader transport sector. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 13
SESSION 3. Overview of EU and other international career advancement opportunities in the green urban logistics sector. The green urban logistics sector is a rapidly growing field with various quickly developing areas such as sustainable supply chain management, transportation planning, renewable energy integration, data analytics, or last-mile delivery management, all of which are eqally important areas of sustainable freight logistics in optimizing logistics networks to minimize environmental impact. Europe is implementing ambitious policies and regulations to promote sustainable urban logistic shaping policies related to emissions reduction, congestion management, and alternative transportation. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 14
3.1. Institutions in career advancement in the green urban logistics sector 1. Academic institutions, research centers and think tanks: The Fraunhofer Institute for Material Flow and Logistics (Germany) The Institute for Transport Studies at the University of Leeds (UK) 2. Professional development courses, events, conferences and workshops: European Conference on Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMPs) Green Logistics Expo 3. Industry associations and networks: European Logistics Association The International Federation of Purchasing and Supply Management (IFPSM) International Society for Inventory Research A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 15
3.2. Areas in career advancement in the green urban logistics sector Companies can adopt to enhance sustainability across their operations by strategies that emphasize collaboration with internal teams, external partners, and technology vendors to pilot and scale innovative solutions that improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Key components of the strategies: 1. Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Focuses on reducing the carbon footprint through optimized network strategies, engagement with suppliers on sustainability initiatives, and tracking and reporting environmental performance indicators. Practices include efficient inventory management, packaging optimization, and waste reduction. 2. Green Fleet Management: Utilizes technologies to enhance the management and optimization of vehicle fleets to minimize environmental impacts and emissions. This involves implementing efficient routing and scheduling systems and adopting sustainable maintenance practices. 3. Last-Mile Delivery Management: Explores innovative approaches like electric vehicles, cargo bikes, and delivery consolidation schemes to optimize urban delivery operations, which requires cooperation with local actors. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 16
SESSION 4. Assessment of digital tools and guides to greening courier/postal/delivery operations. To enhance the greening of courier, postal and delivery operations through digital tools and guides, several initiatives and solutions have been identified, promoting sustainability and efficiency. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 17
4.1. Route Optimization Softwares Route optimization softwares play a crucial role in minimizing the environmental impact of delivery operations. By efficiently planning delivery routes, these tools significantly reduce mileage and, consequently, fuel consumption and carbon emissions. The optimization not only includes the shortest path but also considers traffic conditions, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity, ensuring the most efficient use of resources. Examples: Routific, Upper Route Planner Benefits: These tools help in reducing fuel consumption and vehicle emissions by optimizing delivery routes. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 18
4.2. Carbon Footprint Calculators Carbon footprint calculators enable businesses to measure their emissions across various activities, including logistics and transportation. By quantifying their carbon footprint, companies can identify high-emission areas and strategize on reduction initiatives. These tools often adhere to international standards, providing a reliable methodology for tracking and reporting emissions. Example: Carbon Trust Calculator Benefits: Enables businesses to measure their carbon emissions, focusing on transportation and logistics operations. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 19
4.3. Electric Vehicles (EVs) and E-Bikes The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) and e-bikes for deliveries is a significant step toward greening courier and postal operations. Companies like DHL and UPS are leading the way by incorporating electric vehicles into their fleets, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and pollution, especially in urban areas. E-bikes offer an efficient alternative for smaller, local deliveries, navigating city streets more effectively than traditional vehicles. Examples: DHL s corporate site UPS s corporate site Benefits: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and urban pollution. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 20
4.4. Sustainability Guides and Best Practices Guides and best practices from organizations like the Universal Postal Union (UPU) and insights from consultancy firms such as Boston Consulting Group (BCG) provide a framework for implementing sustainable practices in courier and postal operations. These resources cover a broad range of topics, from digital transformation to adopting green logistics strategies, offering valuable guidance for companies looking to reduce their environmental impact. Examples: Universal Postal Union (UPU) Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Benefits: Offer frameworks for reducing environmental impact while maintaining service quality. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 21
4.5. Packaging Innovation Sustainable packaging solutions are critical for reducing waste and promoting a circular economy. Innovations in packaging, including the use of biodegradable or recyclable materials, are essential in minimizing the environmental footprint of shipping and delivery. Companies like Packhelp are at the forefront of this movement, offering sustainable packaging options that meet the needs of modern e-commerce and delivery services. Example: Packhelp Benefits: Promotes a reduction in waste production and supports a circular economy. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 22
4.6. Digital Mail and E-Commerce Platforms The rise of digital mail and e-commerce platforms has the potential to significantly reduce the need for physical mail, cutting down on paper use and the associated logistics of mail delivery. By transitioning to digital invoices, bills, and communications, companies can decrease their paper consumption, contributing to forest conservation and reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional mail. Benefits: Reduces paper usage and the logistics demand for delivering mail and handling product returns. A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 23
https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en https://www.eiturbanmobility.eu/about-us/ https://www.eiturbanmobility.eu/horizon-lab/ https://www.eiturbanmobility.eu/academy/masterschool/ https://research-and-innovation.ec.europa.eu/funding/funding-opportunities/funding-programmes-and-open-calls/horizon-europe_en https://netzerocities.eu/the-nzc-project/ https://cinea.ec.europa.eu/news-events/news/connecting-europe-facility-2021-2027-adopted-2021-07-20_en https://cinea.ec.europa.eu/news-events/news/connecting-europe-facility-2021-2027-adopted-2021-07-20_en https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/find-funding/eu-funding-programmes/programme-environment-and-climate-action-life_en https://www.interregeurope.eu/find-policy-solutions/policy-briefs/sustainable-urban-logistics https://www.interregeurope.eu/good-practices/bouwhub-smart-building-logistics https://projects2014-2020.interregeurope.eu/recreate/ https://www.interregeurope.eu/spotlog https://interreg-baltic.eu/project/emma/ https://interreg-baltic.eu/project/cocoblog/ https://programme2014-20.interreg-central.eu/Content.Node/SOLEZ.html https://programme2014-20.interreg-central.eu/Content.Node/TalkNET.html https://www.interreg-central.eu/event/regional-food-logistics-free-webinar-organized-by-fh-bfi-vienna-and-econsult-as-part-of-the-food4ce-project/ https://unfccc.int/ https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/oecd-guidelines-towards-environmentally-sustainable-transport_9789264199293-en https://www.wto.org/english/tratop_e/serv_e/postal_courier_e/postal_courier_e.htm https://www.iml.fraunhofer.de/en.html https://environment.leeds.ac.uk/transport https://civitas.eu/thematic-areas/urban-logistics https://www.urbane-horizoneurope.eu/about/what-is-urbane/ https://www.polisnetwork.eu/what-we-do/working-groups/urban-freight/ https://www.routific.com/v3 https://www.upperinc.com/ https://www.carbontrust.com/en-eu https://www.upu.int/en/Home https://www.bcg.com/ https://packhelp.com/ References: A. Governance 2. Opportunities for funding and supporting the green transition of urban freight transportation 24
A. Governance 1. European Unions policy and legislative framework on green city logistics Thank you for your attention! 25