Gas Exchange in Fish and Insects: Adaptations and Mechanisms
Explore the specialized adaptations for efficient gas exchange in fish gills and insect tracheal systems. Understand the ventilation mechanisms in fish and insects, along with the graph analysis of oxygen concentration for different gas exchange methods.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
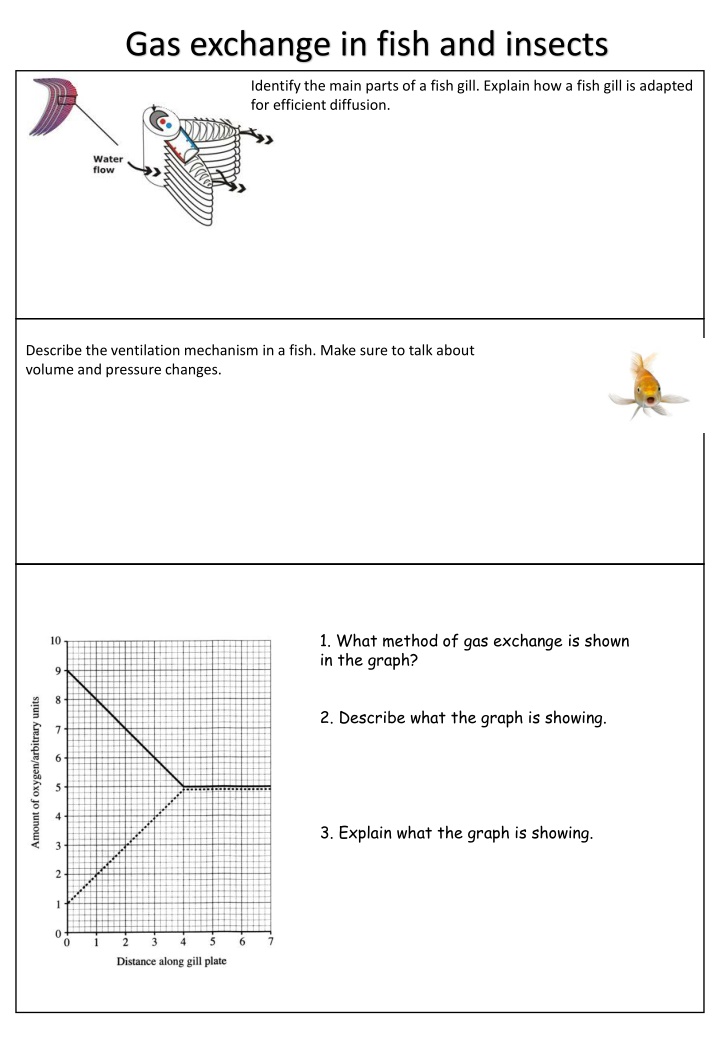
Gas exchange in fish and insects Identify the main parts of a fish gill. Explain how a fish gill is adapted for efficient diffusion. Describe the ventilation mechanism in a fish. Make sure to talk about volume and pressure changes. 1. What method of gas exchange is shown in the graph? 2. Describe what the graph is showing. 3. Explain what the graph is showing.
1. What method of gas exchange is shown in the graph? 2. Describe what the graph is showing. 3. Explain what the graph is showing. Describe the ventilation mechanism in an insect. Describe the ventilation mechanism in a human. Make sure to talk about pressure changes, the pleural membranes and the pressure changes in the pleural cavity.
Gas exchange in fish and insects Identify the main parts of a fish gill. Explain how a fish gill is adapted for efficient diffusion. Gill arch has gill filaments on them. Gill filaments have lamellae at 90o angle to increase surface area. The gills have an extensive capillary network to provide an excellent blood supply. Describe the ventilation mechanism in a fish. Make sure to talk about volume and pressure changes. Fish opens mouth and lowers buccal cavity floor. This increases volume and lowers pressure in buccal cavity. Water rushes in. Fish closes mouth, and raises buccal cavity floor. This decreases volume and increases pressure. Water is forced out through operculum over the gills allowing gas exchange to take place. 1. What method of gas exchange is shown in the graph? Parallel flow. 2. Describe what the graph is showing. As the distance along the gill plate increases,the concentration of oxygen in the blood increases until a distance of 4 along the gill plate and then remains constant. As the distance along the gill plate increases the amount of oxygen in the water decreases until a distance of 4 along the gill plate. It then remains constant There is a higher concentration of oxygen in the water compared with the blood, so oxygen diffuses into the blood, through the semi-permeable membrane until the concentrations are equal and equilibrium is 3. Explain what the graph is showing.
1. What method of gas exchange is shown in the graph? Counter current flow. 2. Describe what the graph is showing. As the distance along the gill plate increasesthe concentration of oxygen in the blood increases. As the distance along the gill plate decreasesthe concentration of oxygen in the water decreases. The water has a higher concentration of oxygen than the blood along the entire gill plate as the water and blood flow in opposite directions. This allows oxygen to diffuse into the blood down a concentration gradient. Equilibrium will not be reached. 3. Explain what the graph is showing. Describe the ventilation mechanism in an insect. Abdomen expands. Air rushes into tracheal system through spiracles of thorax. Abdomen starts to compress. This causes spiracles of thorax to close and compression of abdomen also causes spiracles of abdomen to open and forces air out of these spiracles. Describe the ventilation mechanism in a human. Make sure to talk about pressure changes, the pleural membranes and the pressure changes in the pleural cavity. oThe external intercostal muscles contract, moving the ribs up and out. oThe outer pleural membrane is pulled outwards due to the ribs moving up and out. oThe diaphragm contracts and flattens. oThis causes pressure to drop in the pleural cavity and the inner pleural membrane moves outwards (which is attached to the lungs). oThe inner plural membrane pulls on the surface of the lungs and causes the alveoli to expand.