General Chemistry II - Course Overview and Grading Details
Explore the details of General Chemistry II course for Spring 2020, including the course overview, grade composition, exam schedule, important notes, and policies. Ensure to pass both laboratory and lecture portions separately.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
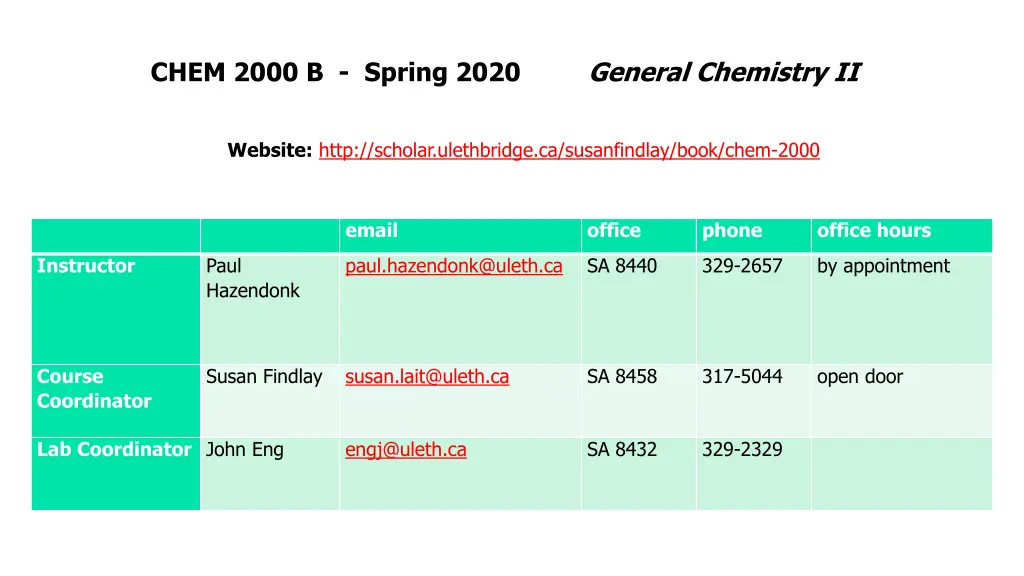
CHEM 2000 B - Spring 2020 General Chemistry II Website: http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/susanfindlay/book/chem-2000 email office phone office hours Instructor Paul Hazendonk paul.hazendonk@uleth.ca SA 8440 329-2657 by appointment Course Coordinator Susan Findlay susan.lait@uleth.ca SA 8458 317-5044 open door Lab Coordinator John Eng engj@uleth.ca SA 8432 329-2329
Textbook Chemistry : The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Third Canadian Edition M.S. Silberberg, P. Amaties, R. Venkateswaran and L Chen. Course Overview: CHEM 2000 is the second half of a full year course in general chemistry. As such, it should ideally be taken within one year of completing CHEM 1000. The goal of these courses is to introduce you to university-level chemistry and to give you an appreciation for the diversity of the field. In CHEM 2000, we will continue our study of matter at the atomic level by learning how atoms bond to make molecules. We then will learn how thermochemistry and electrochemistry dictate the extent to which reactions are favoured. Finally, we will introduce some key concepts from organic chemistry stereochemistry, typical organic reaction types and the role of acid-base chemistry in this discipline. functional groups, 2
Grade Composition: Dates Method 1 Method 2 1 Laboratory Assignments 2 see laboratory schedule due each Tuesday at 11:59 pm 3 25% 10% 25% 10% Midterm Tests 4 Final Exam 6 Mon. Feb. 13th and Mon. Mar. 20th from 6:30 - 8:00 pm 5 2 15% = 30% 35% 100% 0% scheduled by Registrar s Office after Add/Drop deadline 65% 100% Total YOU MUST PASS BOTH THE LABORATORY (12.5/25) AND LECTURE(37.5/75) PORTIONS OF THE COURSE SEPARATELY IN ORDER TO PASS THE COURSE. *Both midterms are on Monday evenings. If you have a direct conflict with either time, you must contact the course coordinator (Susan Findlay) at least one week before the test to arrange to write at an alternative time. The online assignments are a required course component. In order to complete these assignments, you will need to register with the Sapling Learning website (http://saplinglearning.ca), at a cost of $42. 3
Some General Notes The final exam is cumulative Practice Problems: The website has a list of recommended practice questions from our text as well as some supplementary practice problems. Allergy Alert: Latex balloons are used in some demonstrations. If you have any relevant allergy please inform your instructors (lab and lecture). Calculator Policy: scientific calculators with trigonometric and logarithmic functions as well as multiple brackets and/or data memories are allowed. Storing/downloading text to your calculator is strictly forbidden. Violation of these policies during a test will result in confiscation, regarded as cheating and will be dealt with accordinlgly. CALCULATORS WITH WIRELESS COMMUNICATION CAPABILITIES ARE STRICTLY FORBIDDEN. Attendance Policy: Attending the lab is mandatory, and you will be assigned a grade of 0 for any lab missed without a valid reason. Please see your lab manual for the correct protocol to make up a lab that was missed due to illness, etc. Special Needs Students: Please contact the Disabilities Resource Office to arrange for accommodations. Also, feel free to inform your instructor of your special needs in order for you to have a productive learning experience 4
Cheating and/or plagiarism: If you are caught cheating on any lab report or quiz, the minimum penalty is a grade of 0 for that report/quiz. If you are caught cheating on an exam, you will be assigned a grade of F for the course. In either case, a letter describing your offense will also be placed in your student file. Repeated offenses trigger progressively more severe forms of discipline. Two letters result in suspension or expulsion from the University. COPYING HOMEWORK IS CHEATING. If you are caught cheating on your homework, the minimum penalty is a grade of 0 for ALL homework in the course. A letter describing your offense will also be placed in your student file. STUDENTS WHO CHEAT CHEAT THEIR FELLOW STUDENTS. If you see someone cheating during an exam, inform the instructor in the following way. Write a message on your exam paper indicating what is happening and where. Put your hand up, and the instructor will come over. Point out your note, and the instructor will take it from there. This includes situations where someone may be cheating off you. If you allow someone to look at your work, you are also at fault and you will be disciplined. Recognize that it is often pointless to report cheating after the event. 5
Topics Covered & Approximate Schedule Topic Approx. Week 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Molecular Orbital Theory of Diatomic Molecules LCAO Theory for Molecules Larger than Two Atoms Multiple Bonds and Electron Delocalization Spectroscopy Band Theory Valence Bond Terminology Bonding: 1 5 1. Entropy and Free Energy (Enthalpy is pre-requisite knowledge) Free Energy and Equilibrium Phase Diagrams Redox Reactions Electrochemistry Drawing Organic Molecules Functional Groups Isomers and Stereochemistry Classes of Organic Reactions Organic Acids and Bases Thermochemistry: 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 5 - 9 9 - 12 Organic Chemistry 6
What have we already learned? The Atom i) Plum pudding model - Discovery of the fundamental particles : p, n & e. - Rutherford s famous experiment 8
What have we already learned? ii) Bohr Model Spectrum of Hydrogen - Nuclear atom - quantized energy and momentum The electron remains in a stable trajectory around the nucleus A photon is emitted (absorbed) when the electron changes from higher (lower) orbit to lower (higher) orbit Energy Problem!! Frequency
iii) Quantum mechanical model - Quantum Numbers - Electron configurations - The Periodic Table H( (n, l, m, s) ) = E(n) (n, l, m, s) n - Principle Quantum Number Determines which shell the electron is in and the energy of the electron, E(n) l l- Angular momentum Quantum Number Subshells exist for each shell differing in the angular momentum value. m - Magnetic Quantum Number Related to the orientation in space that of the orbital. s - Spin Quantum Number
Electron Configurations & Periodic Table It consists of: NUMBER (shell i.d.) LETTER (subshell) SUPERSCRIPT (occupancy) = 2 2 Be 1 2 s s
Orbitals Important Concepts: 1. Valence & Core electrons 2. Lewis Diagrams: Lone pair & Bonding pair electrons 3. Structure of Central Atom - VSEPR
Structure Shape Families Bonding: 1. Ionic 2. Metallic 3. Covalent 13