Genetic Disorders Overview: Trisomies & Monosomy in Human Genetics
Explore the characteristics and impacts of genetic disorders like Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13, Monosomy X, and XYY Syndrome in this comprehensive overview. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and frequencies of these conditions affecting chromosomes, with insights on associated physical and intellectual disabilities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
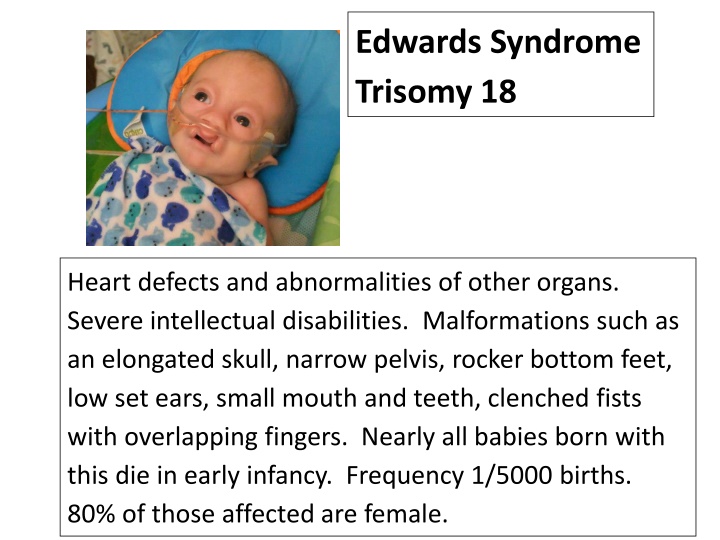
Edwards Syndrome Trisomy 18 Heart defects and abnormalities of other organs. Severe intellectual disabilities. Malformations such as an elongated skull, narrow pelvis, rocker bottom feet, low set ears, small mouth and teeth, clenched fists with overlapping fingers. Nearly all babies born with this die in early infancy. Frequency 1/5000 births. 80% of those affected are female.
Trisomy 13 - Patau syndrome Caused by extra 13th chromosome Severe intellectual disability Physical abnormalities in many parts of body Heart defects Brain/spinal cord abnormalities Small or non functional eyes Extra fingers or toes (polydactaly) Opening in lip (cleft lip) Opening in roof of mouth (cleft palate) Weak muscle Most infants born with this die in 1st week of life 5-10% of children live to 1 year.
Monosomy X Turners Syndrome Caused by missing X chromosome Affects females Short stature Early loss of ovarian function Ovaries develop but egg cells die Many unable to conceive (infertile) 30% of extra folds of skin on the neck puffiness of hands and feet Skeletal abnormalities Normal intellectual ability Kidney problems - 1/3 have heart defects Occurs in 1/2500 births
XYY Jacobs Syndrome Caused by an extra Y chromosome Affects males Very tall Normal sexual development and able to father children Increased risk of learning disabilities Increased risk of behavior problems Delayed motor skills Possible hand tremors or motor tics http://mrsloughsp4class.wikispaces.com/file/view/imagesCABQD8ER.jpg/310258468/imagesCABQD8ER.jpg Was thought that the extra Y chromosome makes males more aggressive and prone to criminal activity this has been shown not to be the case Most go on to lead normal/healthy lives Occurs in 1/1000 males many don t know they have it
Trisomy 21- Down Syndrome Caused by extra 21st chromosome Delays in intellectual development Delays in physical development Single crease across palm of hand Slightly flattened facial profile Upward slant to the eyes Occurs 1 in every 691 births Chances increase as age of mother increases 40% have heart defects Many adults with Down syndrome are capable of working in the community, but some require a more structured environment http://www.arlingtonheritagegroup.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/Down-syndrome-little-girl-NIH.jpg
XXY Klinefelters Syndrome Affects males Affects physical and cognitive development Individuals have small testes and don t produce as much testosterone Breast enlargement Delayed or incomplete puberty Infertility Intellectual disability Skeletal abnormalities Problems with speech Poor coordination As number of extra chromosomes increases so do health probs. 1/500 to 1000
XXX Triple- X Syndrome Affects females Taller than normal Usually no unusual physical features Normal sexual development Increased risk of learning disabilities Speech problems Weak muscle tone poor coordination Motor coordination problems Occurs in 1/1000 females
Cri-du-Chat (Cats Cry)Syndrome A piece of chromosome 5 is missing Infants have high-pitched cry that sounds like a cat Intellectual disability Delayed development many don t walk or talk Small head size Some with heart defects Distinctive facial features Widely set eyes Low set ears Small jaw Rounded face 1/20,000-50,000 newborns http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRDWFmTGcCiRZCWqmxuhZCTpIPoUe8ZMRRZ_t-4FRl7R6hXu5iFpQ:www.newhealthguide.org/images/10442619/image001.jpg
Cri-du-Chat (Cats Cry)Syndrome Video about what children CAN do when they have Cri-du-chat https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=La1D4cN Q5kQ