Genetic Information Transfer: Transcription Process Explained
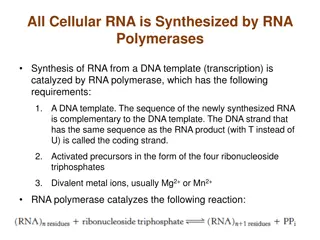
The process of transcription involves copying genetic information from DNA to RNA, utilizing complementarity to guide the process. It differs from replication as only a segment of DNA is transcribed, necessitating clear boundaries. A transcription unit in DNA comprises a promoter, structural gene, and terminator, each playing a crucial role in gene expression. Understanding the conventions of defining template and coding strands is essential for successful transcription. Explore the intricacies of genetic information transfer through transcription here.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Predicting the Secondary Structure of RNA Mitra Shokat Spring 2017
Optimizing RNA Secondary Structure Goal - Given a sequence of RNA, determine most probable secondary structure What determines secondary structure? Base pairings Thermodynamics
Nussinov Algorithm Dynamic programming approach to predicting RNA secondary structure Input sequence of RNA (string) Output graphical representation of base pairings in optimal secondary structure Simplifying assumptions: Optimal structure is one that contains maximum number of base pairings Pseudoknots not allowed
Pseudocode Initialize matrix: Fill main diagonal and diagonal below it with zeros Fill matrix: For each index, choose option that yields max score - 4 options: 1. pair rna[i] and rna[j] and attach to best structure for rna[i+1:j-1] 2. add rna[i] to best structure of rna[i+1:j] 3. add rna[j] to best structure of rna[i:j-1] 4. combine two optimal structures for rna[i:k] and rna[k+1:j] https://bibiserv.cebitec.unibielefeld.de/sadr2/rnasecondarystructure/secondarystr uctureprediction/index.html Backtrack: For each index in matrix, backtrack to source of maximum score S.Will. RNA Structure and RNA Structure Prediction MIT.2011
Results Input - 'GACACGACGA Predicted Output - Actual Output -
Results Input alanine tRNA sequence Predicted Output - Actual Output -