Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Key Functions
Learn about the key functions of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) which include capturing, storing, updating, manipulating, and analyzing geographically referenced data. GIS helps in spatial data management and analysis for various applications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
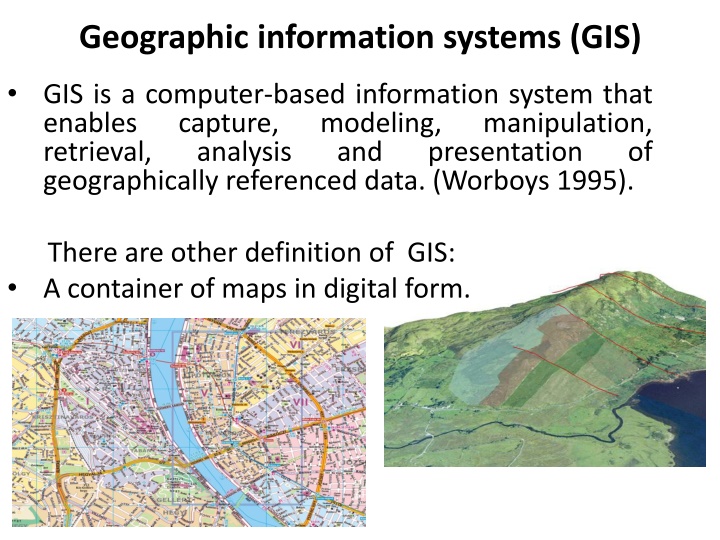
Geographic information systems (GIS) GIS is a computer-based information system that enables capture, modeling, retrieval, analysis geographically referenced data. (Worboys 1995). manipulation, presentation and of There are other definition of GIS: A container of maps in digital form.
Spatial is special Spatial refers to any space. relating to, occupying, or having the character of space, or involved in the perception of relationships (as of objects) in space. Spatial data can be referred to as geographic data or geospatial data. Spatial data provides the information that identifies the location of features and boundaries on Earth. geospatial implying a subset of spatial applied specifically to the Earth s surface and near- surface
What is an Information System? SYSTEM USED FOR: capturing storing updating manipulating analyzing
Data vs. Information Data, by itself, generally differs from information. Data is of little use unless it is transformed into information. Information is an answer to a question based on raw data. We transform data into information through the use of an Information System.
What is a GIS? Information System A means of storing, retrieving, sorting, and comparing spatial data to support some analytic process. + Geographic Position
What is a GIS? GEOGRAPHIC Information System GIS links graphical features (entities) to tabular data (attributes)
GIS Definition A GIS is a system (hardware + database) that is designed to efficiently, assemble, store, update, analyze, manipulate, and display geographically referenced information (data identified by their locations). A GIS also includes the people operating the system and the data that go into the system.
Key Functions of a GIS Data can be: 1. Positioned by its known spatial coordinates. 2. Input and organized (generally in layers). 3. Stored and retrieved. 4. Analyzed (usually via a Relational DBMS). 5. Modified and displayed
Geographic Information Systems Define Define problem problem Decision Decision GIS GIS Process Process Define GIS Define GIS criteria criteria Output Output Import or Import or build datasets build datasets GIS GIS analysis analysis
Reference Rolf A. de, Principles of Geographic Information Systems (2001), ITC ( International Training Center) Educational, textbook series1, Twenty University, Netherlands. Michael F. Worboys (1995), GIS Computing perspective, UK, follow http://books.google.iq/books?id=duT2fcnQeJMC&printsec=fron tcover&dq=GIS:+A+Computing+Perspective+1997+pdf&hl=en&s a=X&ei=RZJGUqCoN4fIsgbb_YGADA&ved=0CD0Q6AEwBA#v=on epage&q&f=false link: Paul A. Longley, et al (2005),Geographical Information Systems and Science, 2nd Edition, UK. Lectures GIS of Center GIS and Physical Geography and Ecosystem analysis department, Lund University.






















