Geometric Concepts and Algebraic Reasoning
Explore topics such as perimeter, area, volume, circles, quadratics, and graphing while enhancing skills in solving equations, proportions, and geometric calculations. Prepare for further studies in mathematics with this comprehensive learning guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
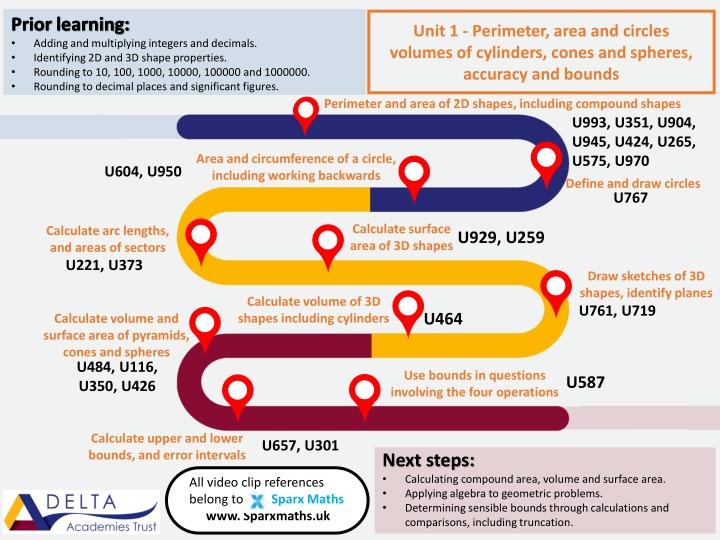
Prior learning: Prior learning: Adding and multiplying integers and decimals. Identifying 2D and 3D shape properties. Rounding to 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000 and 1000000. Rounding to decimal places and significant figures. Unit 1 - Perimeter, area and circles volumes of cylinders, cones and spheres, accuracy and bounds Perimeter and area of 2D shapes, including compound shapes U993, U351, U904, U945, U424, U265, U575, U970 Area and circumference of a circle, including working backwards U604, U950 Define and draw circles U767 Calculate surface area of 3D shapes Calculate arc lengths, and areas of sectors U221, U373 U929, U259 Draw sketches of 3D shapes, identify planes U761, U719 Calculate volume of 3D shapes including cylinders U464 Calculate volume and surface area of pyramids, cones and spheres U484, U116, U350, U426 Use bounds in questions involving the four operations U587 Calculate upper and lower bounds, and error intervals U657, U301 Next steps: Calculating compound area, volume and surface area. Applying algebra to geometric problems. Determining sensible bounds through calculations and comparisons, including truncation. All video clip references belong to Sparx Maths www. Sparxmaths.uk
Prior learning: Applications of fractions, decimals, percentages. Ratio, including 1:n and n:1. Linear graphs, including conversion and tariff graphs. Unit 2 - Multiplicative reasoning Simple and compound interest U533 , U332 Express a multiplicative relationship between two quantities U176 Solve proportion problems using the unitary method U610 Distance/velocity time graphs U914, U937 Rates of change and payU256 Understand and use compound measures, including speed, density and pressure U151, U910, U527 Calculate using direct and inverse proportion U721, U357 Solve worded problems involving indirect proportion Solve worded problems using direct proportion U407, U138 U238, U407 Next steps: Use graphs to represent direct and indirect proportion. You will re-visit proportionality again if you intend to take A Level Maths in year 12 and 13. All video clip references belong to Sparx Maths www. Sparxmaths.uk
Prior learning: Confidence in solving equations. Drawing linear graphs using a table of results or recognising gradient and y-intercept. Unit 3 Quadratics and Graphs Expanding trinomials (triple brackets) Factorise including finding the difference of two squares and with a coefficient U178, U963, U960 U606 Solving and interpreting quadratic equations graphically U667, U601 Graphing inequalities Solve linear inequalities Solving simultaneous equations using quadratics U547, U601, U875 U747 U509, U759, U738, U145 Solve simultaneous equations algebraically and graphically U760, U760, U836, U875 Solve quadratic inequalities U133, U747, U601 Equations of circles and tangents U567 Graphs of exponential functions, exponential growth and decay U229, U988 Graphs of cubic and reciprocal functions U980, U593 Next steps: Within AQA Further Maths GCSE you will be introduced to polynomial division and within A Level Maths you will solve cubic equations algebraically. All video clip references belong to Sparx Maths www. Sparxmaths.uk
Unit 4 - Collecting data, cumulative frequency & box plots and histograms Prior learning: Calculating averages and range from frequency tables. Reading scales on different axes. Plotting coordinates in the first quadrant. Frequency polygons U840 Two-way tables U120 Statistical vocabulary and sampling Scatter diagrams Capture and recapture Pie charts U508, U172 U322, U911, U162 U199 U328 Cumulative frequency diagrams, find the median, interquartile range, greater than or less than U182, U879, U642 Compare the mean, range, median and interquartile range of two distributions U507 Interpret and construct box plots U879, U837 Find range, median and interquartile range to draw conclusions from box plots U837 Construct and interpret histograms with unequal widths U185, U814 Estimate the median from a histogram with unequal widths Understand and use frequency density U267, U983 U814 Next steps: Apply and use these statistical analysis skills in other subjects (geography/biology/psychology) All video clip references belong to Sparx Maths www. Sparxmaths.uk
Prior learning: Basic probability, including simple vocabulary. Calculations with fractions, decimals and percentages. Construction of two-way tables. Unit 5 - Probability, Venn diagrams and tree diagrams Understand and use experimental and theoretical probability Draw and use a sample space diagram and product rule of counting U104, U369 U580 Draw and use a two-way table for probability, including solving algebraic problems U981 U476, U296, U748 Draw and use a Venn diagrams for probability and sets Use union and intersection notation Understand conditional probabilities and decide if two events are independent Draw and use a probability tree diagram. U729 U558 Use diagrams to calculate conditional probability U821, U246, U806 Compare experimental data and theoretical probabilities from samples of different sizes U580 Next steps: Comparing probability distribution tables (geography) Chi-squared test (biology) and T-Test (psychology) Venn diagrams for characterization (English) All video clip references belong to Sparx Maths www. Sparxmaths.uk
Prior learning: Applying Pythagoras theorem. Trigonometry basics (SOH CAH TOA) Recall exact Trig values for 0o, 30o, 45o and 60o and 90o. Unit 6 - Trigonometric functions Recognise, sketch and interpret graphs of sin, cos and tan. Know the exact values for common trigonometric angles. U450 U627 U450 Apply transformations to trigonometric graphs U455 Know and apply the general equation for the area of a non-right-angled triangle U592 Know and use the sine and cosine rules for non- right-angled triangles U591 U952 Know and use the sine and cosine rules to solve 3D problems Understand, recall and use trigonometric relationships and Pythagoras theorem and use them to solve problems in 3D U541 Next steps: Complex geometry questions involving multiple steps. Knowing and using trigonometric identities to solve equations in AQA Further Maths GCSE and A Level Maths. All video clip references belong to Sparx Maths www. Sparxmaths.uk
Prior learning: Recall geometry facts for angles and sides of 2D shapes. Using scale factors to enlarge 2D shapes. Ratio, including 1 : n and n : 1. Metric conversion, including mm2 to cm2 and others. Unit 7 Similarity and congruence Understand and use SSS, SAS, ASA and RHS conditions to prove congruence Understand similarity of triangles and other shapes U866, U551 U790, U187, U866 Use formal proof to show that two shapes are similar U578 Understand the effect of enlargement on angles, perimeter, area and volume U630, U110 Find missing lengths, areas and volumes in similar 3D shapes U110 Solve problems involving frustums of cones which involve similar triangles U334, U350 Next steps: More complex problems, involving geometric proof, appear with the vector geometry topic later in the year and within the AQA Further Maths GCSE. All video clip references belong to Sparx Maths www. Sparxmaths.uk