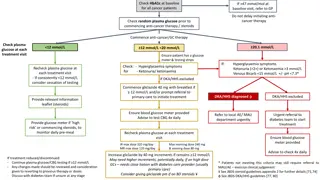
Glucose Metabolism: An In-depth Look
Importance of gluconeogenesis in glucose production, its main reactions, rate-limiting enzymes, and substrates. Learn about the gluconeogenic pathway, substrates like glycerol and glucogenic amino acids. The process of dephosphorylation, carboxylation, and transport involved in gluconeogenesis. Dive into the energy-consuming, anabolic pathway key for maintaining glucose levels in the body.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Comparison of RTV vs Cobi GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Design Randomisation* 1 : 1 Double-blind W48 W192 COBI + RTV placebo + ATV 300 mg + FTC/TDF QD > 18 years ARV-na ve N = 344 HIV RNA > 5,000 c/mL Any CD4 cell count eGFR > 70 mL/min Sensitivity to ATV, FTC And TDF on genotype COBI placebo + RTV + ATV 300 mg + FTC/TDF QD N = 348 * Randomisation was stratified by HIV RNA (< or > 100,000 c/mL) at screening Objective Non inferiority of COBI compared with RTV at W48: % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL by intention to treat, snapshot analysis (lower limit for the 95% CI for the difference = -12%, 95% power) Gallant JE. JID 2013;208:32-9 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Baseline characteristics and patient disposition COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF N = 344 RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF N = 348 Mean age, years 37 38 Female 17% 18% HIV RNA (log10c/mL), median HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL 4.78 4.84 38.4% 41.1% CD4 cell count (/mm3), mean 353 351 CD4 < 200 per mm3 12% 16% Hepatitis B / hepatitis C coinfection 5% / 6% 3% / 5% Discontinuation by W48 17% 11% For lack of efficacy N = 2 N = 0 For adverse event N = 25 N = 25 Lost to follow-up N = 11 N = 4 Non-compliance N = 4 3 Gallant JE. JID 2013;208:32-9 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Response to treatment at week 48 HIV RNA < 50 c/mL COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF % Primary analysis 98.0 98.0 100 87.4 85.2 Viral suppression was high in both treatment arms, for various subgroups, including patients with HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL at baseline 75 50 25 Mean CD4/mm3increase at W48 : + 213 COBI vs + 219 RTV 0 ITT, snapshot Per protocol Adjusted difference (95% CI) = -2.2%( - 7.4 ; 3.0) Adjusted difference (95% CI) = -0.1 % ( - 2.5 ; 2.3) Gallant JE. JID 2013;208:32-9 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Response to treatment at week 144 (ITT, snapshot) HIV RNA < 50 c/mL % 100 COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF 87 85 80 74 72 60 40 20 21 20 9 9 6 8 5 4 0 W48 W144 W48 W144 W48 W144 Virologic success Adjusted difference (95% CI) = -2.1%( -8.7 ; 4.5) Virologic failure No data Gallant JE. JAIDS 2015;69:338-40 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Criteria for resistance testing : confirmed HIV-1 RNA load rebound of 400 c/mL or not obtaining HIV RNA < 400 c/mL by or after week 8 Resistance data up to week 144 COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF N = 344 N = 348 At W48 W48-W144 At W48 W48-W144 Analysed for the development of resistance 12 (3.5%) 9 (2.6%) 12 (3.4%) 7 (2.1%) Available data 10 - 12 - Emergent reverse transcriptase resistance 2 2 0 1 M184V 2 1 1 V118I 0 1 0 Emergent mutations to protease inhibitors 0 0 0 0 Gallant JE. JID 2013;208:32-9 ; Gallant JE. JAIDS 2015;69:338-40 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Adverse events occurring in > 10% of patients in either group (W48) COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF 20.9% 17.7% 17.7% 15.4% 11.0% 10.8% 11.3% RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF 15.5% 18.4% 16.4% 20.4% 15.5% 15.2% 9.8% p Jaundice Scleral icterus Nausea Diarrhea Headache Nasopharyngitis Hyperbiluribinemia 0.076 - - 0.093 0.093 0.09 Laboratory abnormalities at W48 COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF Median increase of creatinine (mg/dL) at W48 + 0.13 + 0.09 (P < 0.001) Grade 3-4 hyperbilirubinemia 65.3% 56.6% Grade 3-4 elevation of ALT / AST 3.2% / 2.9% 2.0% / 2.0% Increase in total cholesterol (mg/dL) at week 48 + 5 + 9 (NS) Increase in triglycerides (mg/dL) at week 48 + 19 + 32 (NS) Gallant JE. JID 2013;208:32-9 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Adverse events leading to discontinuation of study drug COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF N = 344 RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF N = 348 W48 W48-W144 W48 W48-W144 Total number of patients (%) 25 (7.3%) 9 25 (7.2%) 8 Scleral icterus 8 4 4 1 Jaundice 9 1 7 0 Hyperbilirubinemia 1 0 2 1 Rash 1 0 0 0 Allergic dermatitis 2 0 0 0 Renal AEs 6 4 5 6 Proximal renal tubulopathy 7 in each group In 5 of the 7 patients in the COBI group and 6 of the 7 patients in the RTV group, PRT occurred after week 48 Gallant JE. JID 2013;208:32-9 ; Gallant JE. JAIDS 2015;69:338-40 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Serum Creatinine and eGFR Change in serum creatinine (mg/dL), median [IQR] Change in eGFR (mL/min), median [IQR] 0.4 20 0.3 10 -7.5 0.12 -9.1 0.13 0.13 -8.3 0.2 0 0.1 -10 0.0 -20 0.09 0.08 0.07 -13.7 -12.9 -15.1 -0.1 -30 -0.2 -40 BL 24 48 72 96 120 144 BL 24 48 72 96 120 144 Week Week COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF Gallant JE. JAIDS 2015;69:338-40 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Median change in fasting lipids at week 144 (mg/dL) COBI + ATV + FTC/TDF RTV + ATV + FTC/TDF 20 p = 0.49 p = 0.11 p = 0.11 p = 0.35 16 15 15 14 12 11 10 9 7 5 5 0 Triglycerides Total cholesterol LDL-c HDL-c No difference in TC:HDL ratio changes between arms (- 0.3 vs -0.2) Gallant JE. JAIDS 2015;69:338-40 GS-US-216-0114
Study GS-US-216-0114: ATV + ritonavir + FTC/TDF QD vs ATV + cobicistat + FTC/TDF Summary COBI was non inferior to RTV in combination with ATV plus FTC/TDF up to week 144 Both regimens achieved high rates of virologic success Safety and tolerability profiles of the 2 regimens were comparable Once-daily COBI is a safe and effective pharmaco-enhancer of the protease inhibitor ATV Renal safety was comparable between treatment arms Discontinuation due to renal events was 2.9% in the COBI group and 3.2% in the RTV group at W144 Proximal renal tubulopathy occurred in 7 vs 7 patients (2.0%) A small, but significantly higher with COBI, increase in creatinine was seen in both groups, as early as week 2, with peak at week 8, and stabilization through 144 weeks Gallant JE. JID 2013;208:32-9 ; Gallant JE. JAIDS 2015;69:338-40 GS-US-216-0114