Graphical Model Learning Schema and Bayesian Networks in Relational Data
Explore the process of learning graphical models and Bayesian networks for complex relational data, including structure learning, lattice search techniques, and upgrading IID Bayesian network learners. Enhance your understanding of Bayesian network learning with detailed insights and examples.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
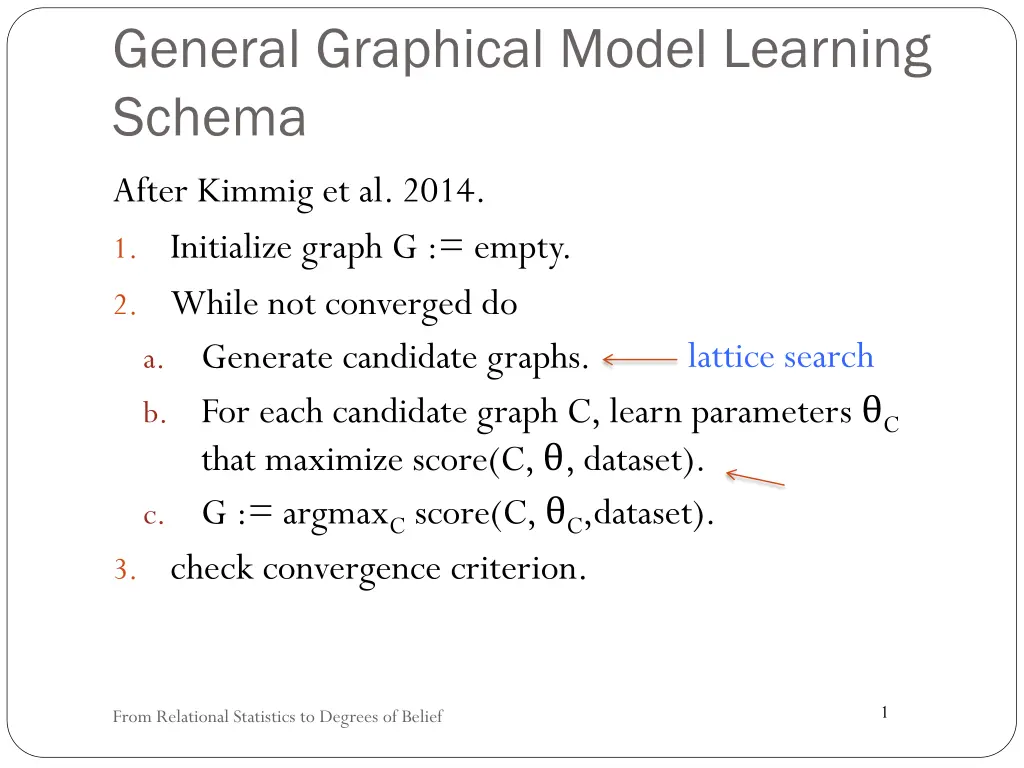
General Graphical Model Learning Schema After Kimmig et al. 2014. 1. Initialize graph G := empty. 2. While not converged do a. Generate candidate graphs. b. For each candidate graph C, learn parameters C that maximize score(C, , dataset). c. G := argmaxCscore(C, C,dataset). 3. check convergence criterion. lattice search 1 From Relational Statistics to Degrees of Belief
Structure Learning Lattice Search Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Upgrading IID Bayesian Network Learners The Learn and Join Algorithm Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Learning a Bayesian Multi-Net Learn a Bayesian network for each relationship chain using a single-table Bayesian network learner Nodes and edges are propagated from shorter chains to smaller chains ActsIn(A,M), HasRated(U,M) Lattice of Relationship Chains ActsIn(A,M) HasRated(U,M) Actors A Movies M Users U Khosravi, H.; Schulte, O.; Man, T.; Xu, X. & Bina, B. (2010), Structure Learning for Markov Logic Networks with Many Descriptive Attributes, in 'AAAI', pp. 487-493. Friedman, N.; Getoor, L.; Koller, D. & Pfeffer, A. (1999), Learning probabilistic relational models, in 'IJCAI', pp. 1300--1309. 4
Network View: Single Template Nodes Path length = 0 occupation, gender country, gender country, runtime Users U Actors A Movies M learn BN for attributes of random Movie learn BN for attributes of random User learn BN for attributes of random Actor 5 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Network View: Single Links Path length = 1 country, gender country, runtime country, runtime occupation, gender ActsIn(A,M) HasRated(U,M) Actors A Movies M Movies M Users U not ActsIn(A,M) not ActsIn(A,M) learn BN for attributes of random Actor, random Movie, existing link, absent link learn BN for attributes of random User, random Movie, existing link, absent link 6 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Network View: Two Links Path length = 2 country, gender country, runtime occupation, gender HasRated(U,M) ActsIn(A,M) Users U Actors A Movies M not ActsIn(A,M) not ActsIn(A,M) learn BN for attributes of random Actor, random Movie, random User, 4 combinations of existing/absent links 7 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Implementation of Lattice Search Example Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Contingency Table for Movies count Action Drama Horror 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 538 2504 845 9 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Learning a DAG for Movies Apply existing Bayesian network learning for IID data to Movies contingency table 10 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Contingency Table for Users COUNT(*) gender age 78 F 1 298 F 18 557 F 25 338 F 35 189 F 45 146 F 50 144 M 1 805 M 18 1538 M 25 855 M 35 361 M 45 350 M 50 11 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Learning a DAG for Users Apply existing Bayesian network learning to Users table 12 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Contingency Table for Users + Movies count Action Drama Horror Age Gender 1F 1M 18F 18M 25F 25M 35F 35M 45F 45M 1F 1M 18F 18M 25F 25M 35F 35M 45F 45M HasRated T T T T T T T T T T F F F F F F F F F F 929 2170 4552 14737 8126 32309 4568 16007 2156 6523 40723 74726 154580 415133 289312 788983 175924 440563 98770 186251 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 .... .... the full CT table contains 42 rows 13 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Learning a DAG for Users + Movies Apply existing Bayesian network learning to join of Users, Movie, Ratings tables 14 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Fast Structure Learning Dataset # Predicates # tuples RDN_Boost MLN_Boost 14 612 18 870 19 11,316 11 24,326 Lattice 1 0.0 102 6.9 286 2.9 1 0.0 UW Mondial Hepatitis Mutagenesis MovieLens(0.1M ) MovieLens(1M) Imdb(1.5M) Standard deviations are shown for cross-validation. Units are seconds/predicate or function 15 0.3 27 0.9 251 5.3 118 6.3 19 0.7 42 1.0 230 2.0 49 1.3 7 71,010,051 171,538,400 83,402 44 4.5 min 31 1.87 min >24 hours >24 hours 1 0.0 10 0.1 >24 hours >24 hours 549 15 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Learned Structure Example IMDB_3R UserID Occupation Age gender UserID MovieID Rating RDN-Boost MovieID Time Model Target Markov Blanket RDN- Boost gender(U) Occupation(U), Age(U) ActorID MovieID Learn- and-Join gender(U) Occupation(U), Age(U), Rating(U,M), RunningTime(M), CastMember(M,X), AGender(X) ActorID AGender 16 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data
Consistency Preservation Statistical Consistency: As the amount of available data increases, the graphical model learner converges to a graphical structure that is correct for the data generating mechanism. Theorem If a Bayesian network structure learner is consistent for IID data, then upgrading the learner with the learn-and-join algorithm is consistent for relational data. Schulte, O. and Gholami, S.(2016) Consistent Model Selection Scores for Multi-Relational Data . StarAI Workshop@IJCAI. 17
Conclusion Structure Learning: Structure search using the lattice of relationship chains Apply iid Bayes net learner to each point in the lattice Propagate correlations from lower levels to higher levels, dynamic programming style fast structure learning complex correlations along long relationship chains 18 Learning Bayesian Networks for Complex Relational Data