Graphing Linear Equations: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Learn how to graph linear functions with detailed examples and step-by-step instructions. Understand slope-intercept form, finding solutions, and more to master graphing linear equations effectively.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
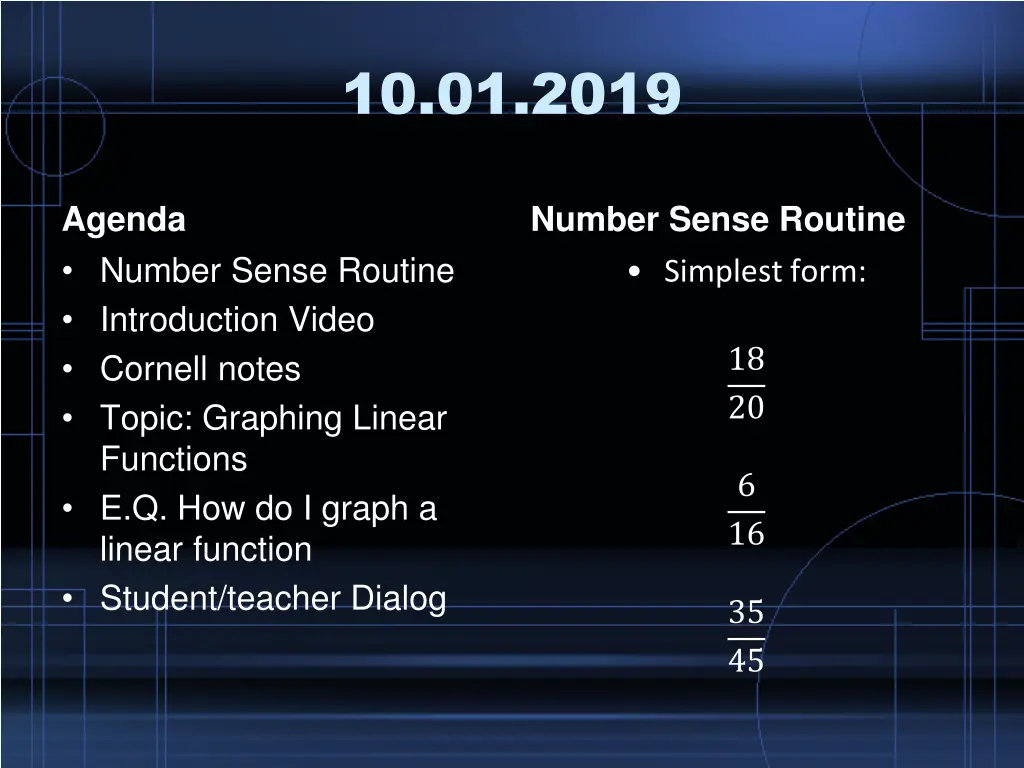
10.01.2019 Agenda Number Sense Routine Introduction Video Cornell notes Topic: Graphing Linear Functions E.Q. How do I graph a linear function Student/teacher Dialog Number Sense Routine Simplest form: 18 20 6 16 35 45
Graphing Linear Equations
Linear Equation An equation for which the graph is a line
Solution Any ordered pair of numbers that makes a linear equation true. (9,0) IS ONE SOLUTION FOR Y = X - 9
Linear Equation Example: y = x + 3
Graphing Step 1: ~ Three Point Method ~ Choose 3 values for x
Graphing Step 2: Find solutions using table y = x + 3 X | Y 0 1 2
Graphing Step 3: Graph the points from the table (0,3) (1,4) (2,5)
Graphing Step 4: Draw a line to connect them
Try These Graph using a table (3 point method) 1) y = x + 3 2) y = x - 4
Slope-Intercept y = mx + b m = slope b = y-intercept
Slope-Intercept The m in the slope-intercept form is ALWAYS attached to the X variable. The slope is NEVER including the X variable For example, if given y = 3x + 4 the slope is 3 NOT 3x.
Y-intercept Where the line crosses the y-axis
Y-intercept The y-intercept has an x-coordinate of ZERO
Y-intercept To find the y- intercept, plug in ZERO for x and solve
Y-Intercept Summary The y-intercept is the b in the slope intercept form. This b (y-intercept) is your starting point on the graph. To easily remember this, think of b as you Beginning point. For example, in y = 3x + 4 the Beginning point is at (0,4) {Remember: to find the y- intercept, plug on zero for the x.}
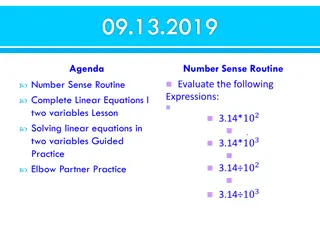
10.02.2019 Agenda Number Sense Routine Introduction Video Cornell notes Topic: Graphing Linear Functions E.Q. How do I graph a linear function Student/teacher Dialog Number Sense Routine Simplest form: Simplest form: 16 62 16 62 15 20 32 24 15 20 32 24
X-intercept Where the line crosses the x-axis
X-intercept The x-intercept has a y coordinate of ZERO
X-intercept To find the x- intercept, plug in ZERO for y and solve
Slope Describes the steepness of a line
Slope Equal to: Rise Run
Rise The change vertically, the change in y
Run The change horizontally or the change in x
Finding Slope Step 1: Find 2 points on a line (2, 3) (5, 4) (x1, y1) (x2, y2)
Finding Slope Step 2: Find the RISE between these 2 points Y2 - Y1 = 4 - 3 = 1
Finding Slope Step 3: Find the RUN between these 2 points X2 - X1 = 5 - 2 = 3
Finding Slope Step 4: Write the RISE over RUN as a ratio Y2 - Y1 = 1 X2 - X1 3
Step 1: Mark a point on the y-intercept
Step 2: Define slope as a fraction...
Step 3: Numerator is the vertical change (RISE)
Step 4: Denominator is the horizontal change (RUN)
Step 5: Graph at least 3 points and connect the dots
10.03.2019 Agenda Number Sense Routine Graphing linear Inequalities Video Graphing Equations Review Group Activity Student/teacher Dialog Number Sense Routine Make X the Subject Make X the Subject Simplest form: 7 ? ? 3 63 16 62 7 ? ? 3 63 5 ? ? 4 15 20 100 4 ? ? 2 40 32 24 5 ? ? 4 100 4 ? ? 2 40
Group Activity Write the linear equation on the top of the graphing paper Graph the linear equation Make a table with three points of the line Make sure all names from the group is on your graphing paper Decorate your Graph