Groundwater Modeling Methods
This content delves into various aspects of groundwater modeling using the MODFLOW software, covering topics such as specified heads, extraction and injection wells, Darcy's Law, river-aquifer interaction, and more. Detailed explanations with images are provided to enhance learning on key concepts in groundwater management and analysis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHB Time Variant Specified Head DRN Drain DRT Drain Return Flow ETS Evapotranspiration Segments EVT Evapotranspiration GAGE Gage GHB General Head HFB Horizontal Flow Barrier LAK Lake MNW Multinode Well MNW2 Multinode Well 2 RCH Recharge RIV River SFR Stream Flow Routing STR Stream-Aquifer Interaction SUB Subsidence WEL Well UZF Unsaturated Zone Flow
Assigned to individual cells Q can be steady state or transient Extraction well (neg Q) Injection well (pos Q)
Assigned to individual cells Used to simulate Agricultural drains Springs Creek beds Required parameters Elevation Conductance
Hijk CD Delev When the head is above the drain elevation: Q = CD (Hijk - Delev) or Q = CD (Delev - Hijk) for proper sign on Q
CD Delev Hijk When the head is below the drain elevation: Q = 0
Darcys Law: h = q k A L Where: q = flow rate k = hydraulic conductivity Dh = head difference L = flow length A = gross cross-sectional area
Darcys law can be rewritten as: = q C h Where: kA C = L The appropriate values for k, A, and L must be determined on a case-by-case basis
Length of overlap of river on cell L = length of reach Direction of Flow M = KA KLW K = Hydraulic Conductivity of River Bed Material Thickness of River Bed = = Ccell M M W = Width of River
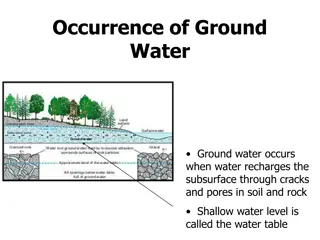
One value assigned to each vertical column (one per each cell in the top layer) Represents recharge due to precipitation Can be steady state or transient Infiltration rate must be assigned in correct units [L/T]