Group Norms and Roles in Social Group Work
Explore the importance of group norms, roles, and culture in social group work. Discover how norms shape behavior, foster predictability and stability, and influence leadership development. Learn about the emergence of norms, managing conflicts, and interventions to change group norms effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dr. Jaimon Varghese Social Group Work 1 4/4/2025
Norms Roles Culture Subgroup formation (unit 3.3) Conflict management (unit 3.3) Leadership development (unit 3.3) Social Group Work 2 4/4/2025
Shared expectations & beliefs about appropriate ways to act in a social situation such as group By providing guidelines for acceptable & appropriate behaviour, norms increase predictability, stability, and security for members Norms are overt and covert Social Group Work 3 4/4/2025
Emergence of norms as the group progresses reduces the need for structure and control by the worker Norms discourage the capricious use of power by the leader Deviations from norms are not necessarily harmful, sometimes help groups move in new directions or challenge the old ways of accomplishing the tasks Social Group Work 4 4/4/2025
Discussing, diagnosing, & making explicit decisions about group norms Directly intervening in the group to change a norm Deviating from a norm & helping a group to adapt a new response Helping the group become aware of external influences and their effect on the group s norms Social Group Work 5 4/4/2025
Hiring a consultant to work with the group to change its norms 3 Stages of norm change 1947) Disequilibrium or unfreezing caused by a crisis that demonstrates dysfunction of old norm Return to equilibrium accepting new norm or freezing Refreezing: stabilizing the new norm 3 Stages of norm change (Lewin, 1947) (Lewin, Social Group Work 6 4/4/2025
Roles are shared expectations about the functions of individuals in the group Roles define behaviour in relation to a specific function or task that the group member is expected to perform Roles ensure that vital group functions are taken care of. Social Group Work 7 4/4/2025
Discussion on each members role Clarifying the responsibilities & the privileges of existing roles Asking members to assume new roles Adding new roles according to preferences expressed during the group s discussion Social Group Work 8 4/4/2025
Group culture emerges from the mix of values that members bring to the group. Worker helps members examine, compare and respect each other s value systems Group culture is also affected by the agency, community and society where the group is situated. Members need to identify and understand them Social Group Work 9 4/4/2025
Worker helps members to identify their own stereotypes and eliminate stereotyped ways of relating with each other Value conflicts reduce group cohesion and lead to sudden demise of the group. Worker mediates value conflicts among members & between members and the larger society Social Group Work 10 4/4/2025
A culture that emphasizes values of self-determination, openness, fairness, diversity of opinions and acceptance of differences facilitates the achievement of group & individual goals. Groups are most satisfying when they meet members socioemotional & instrumental needs. Worker balances members emotional needs with their needs for task accomplishment Social Group Work 11 4/4/2025
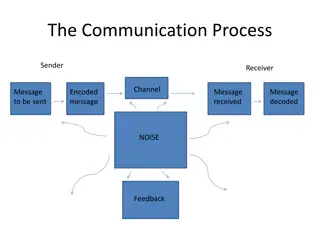
Communication involves the transmission of a message from a sender to a receiver. communication includes: i) encoding of perception, thoughts and feelings into language and other symbols by a sender; ii) transmission of language and symbols verbally, non-verbally or virtually; and iii) decoding of the message by the receiver ( (IGNOU, 2020: Unit 2, p.5) IGNOU, 2020: Unit 2, p.5)
Patterns of Group interaction (Ronald W Toseland and Robert F Rivas, 2012:74) (1) Maypole: leader communicates from the centre to each memberand members communicate with the leader (2) Round robin: members take turn (3) Hot seat: extended back & forth between leader and a member while other members watch (4) Free floating: members contribute according to their ability and need of the group Social Group Work 13 4/4/2025
Factors affecting communication patterns (Ronald W Toseland and Robert F Rivas, 2012:74) (1) Cues & reinforcement that members receive for specific interactional exchanges (2) Emotional bonds that develop between group members (3) Subgroups that develop (4) Size & physical arrangements (5) Power & status relationships Social Group Work 14 4/4/2025
Principles for practice of effective communication patterns (Ronald W Toseland and Robert F Rivas, 2012:74) (1) Members in group are always communicating (2) Communication patterns can be changed (3) Members communicate for a purpose (4) There is meaning in all communications (5) Messages are often perceived selectively Social Group Work 15 4/4/2025
(6) Messages may be distorted in transmission (7) Feedback & clarification enhance accurate understanding of communication (8) Open, group-centred communications are often, but not always, the preferred pattern of interactions. Help the groups develop interaction patterns that meet members socioemotional needs while accomplishing the group purposes Social Group Work 16 4/4/2025
IGNOU (2020) MSW 008 - Social Group Work: Working with Groups (rev. ed.). New Delhi: School of Social Work, Indira Gandhi National Open University Lewin Kurt (1947) Frontiers in group dynamics. Human Relations, 1, 2-38 Pallassana R. Balgopal & Vassil V. Thomas (1983) Groups in Social Work An ecological perspective, New York: Macmillan Publishing Co. Toseland W. Ronald & Rivas F. Robert (2012) An Introduction to Group Work Practice (7th Ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon Social Group Work 17 4/4/2025
Social Group Work 18 4/4/2025