Hemorrhagic Diatheses and Approach to Bleeding Disorders
Group of disorders that cause abnormal bleeding due to defects in hemostasis. This includes vascular abnormalities, platelet dysfunction, coagulation factor disorders, and DIC. Understanding the mechanisms of hemostasis, such as clotting and fibrinolysis, is essential for managing bleeding disorders. Physiological anticoagulants like serine protease inhibitors and components of the protein C system play a crucial role in maintaining hemostatic balance. This presentation provides an insightful overview of hemorrhagic diatheses and the approach to bleeding disorders.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
HEMORRHAGIC DIATHESES AND APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS Dr. B.V.Vydehi M.D PROFESSOR OF PATHOLOGY NARAYANA MEDICAL COLLEGE,NELLORE
Hemostasis Natural ability to arrest bleeding at the site of injury by vascular spasm, platelet plug formation & active participation of coagulation factors Co-ordinated activity of vascular endothelium, platelet function & activation of coagulation cascade
Hemostatic balance Clotting process is modified by lytic activity to prevent excessive or continuedclotting Injury Fibrinolytic mechanism Coagulation mechanism Plasminogen Prothrombin (F II) Activators (Blood & tissues) Thromboplastin (From blood-F III & tissue) Fibrinogen (F I) Fibrin Plasmin Thrombin Fibrin Degradation Products
Hemorrhagic Diatheses (Bleeding Disorders) Group of disorders characterized by defective hemostasis with abnormal bleeding Broad Classification : 1. Related to vascular abnormalities 2. Related to platelet abnormalities 3. Disorders of coagulation factors 4. Combination of all these as occurs in DIC
Physiological anticoagulants 1.Serine protease inhibitors : inhibit the coagulation cascade. 2.Neutralizers of activated coagulation factors (components of protein C system) HEMOSTASIS
1-Serine protease inhibitors: 1-Antithrombin (III) 2-Heparin and heparin like substance 3-Alpha 1 antitypsin 4-Alpha 2 macroglobulin HEMOSTASIS
2-Neutralizers of activated coagulation factors Components of protein C system 1-Protein C: synthesized in the liver, vit. K dependent, activated by thrombin 2-Thrombomodulin 3-Protein S and C4b-binding HEMOSTASIS
Approach to Bleeding Disorders - Purpuric spots (capillary or platelets defect not characteristic of hemophilia) - Hematoma, hemarthrosis or large ecchymoses at the site of trauma : suggests hemophilia (coagulation defect) - Sudden severe bleeding from multiple sites after prolonged surgery or during obstetric procedures suggests acquired fibrinogen defect HEMOSTASIS
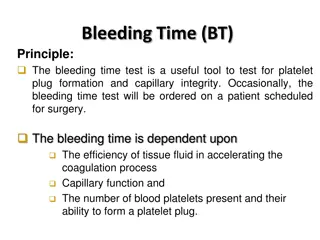
Screening Tests for Hemostasis LABORATORY TEST FACTOR MEASURED ASSOCIATED DISOREDRS 1. Bleeding time Platelet function/ i) Qualitative disorders vascular integrity 2. Platelet count Quantification of platelets i) Thrombocytopenia of platelets ii) Quantitative disorders of platelets iii) Acquired vascular disorders iv) Von Willebrand ds ii) Thrombocytosis
Screening Tests for Haemostasis LABORATORY TEST FACTOR/ MEASURED ASSOCIATED DISOREDRS 3. Prothrombin time Evaluation of extrinsic and i) Oral anticoagulant common pathway ( deficiency therapy of factors I, II, V, VII, X) ii) DIC iii) Liver disease 4. APTT Evaluation of intrinsic &common i) Parenteral heparin pathway (Def. of factors I, II, V,VIII, therapy IX, X,XI,XII ) ii) DIC iii) Liver disease 5. Thrombin time Evaluation of (i) Afibrinogenaemia common pathway iii) Parenteral heparin therapy ii) DIC
Bleeding disorders due to vascular abnormalities Inherited disorders : Hereditary Telangiectasia Ehler s Danlos syndrome Marfan syndrome Osteogenesis imperfecta
Bleeding disorders due to vascular abnormalities Acquired A.Purpura due to decreased connective tissue Eg: Senile Purpura Cushing syndrome Corticosteroid therapy Scurvy B.Purpura due to paraproteinemia
Bleeding disorders due to vascular abnormalities C. Purpura due to vasculitis Eg: Infections D. Mechanical Purpura Eg: self abuse E. Purpura Simplex Immunologic Drugs
Bleeding disorders due to vascular abnormalities Non thrombocytopenic purpuras Usually mild confined to skin & mucous membranes, characterized by petechiae, purpuras or ecchymoses Platelet count, BT, PT, APTT Usually normal Skin biopsy - May be diagnostic