Hepatic Encephalopathy and Associated Pathways
Explore the intricate mechanisms underlying hepatic encephalopathy, from inflammatory cytokines to ammonia metabolism, and their impact on astrocytic/neuronal dysfunction, synaptic plasticity, and cognitive impairment. Discover the connection between altered microbiome, neuroinflammation, and cognitive deficits in liver damage, providing insights into assessment and treatment strategies for patients with cirrhosis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
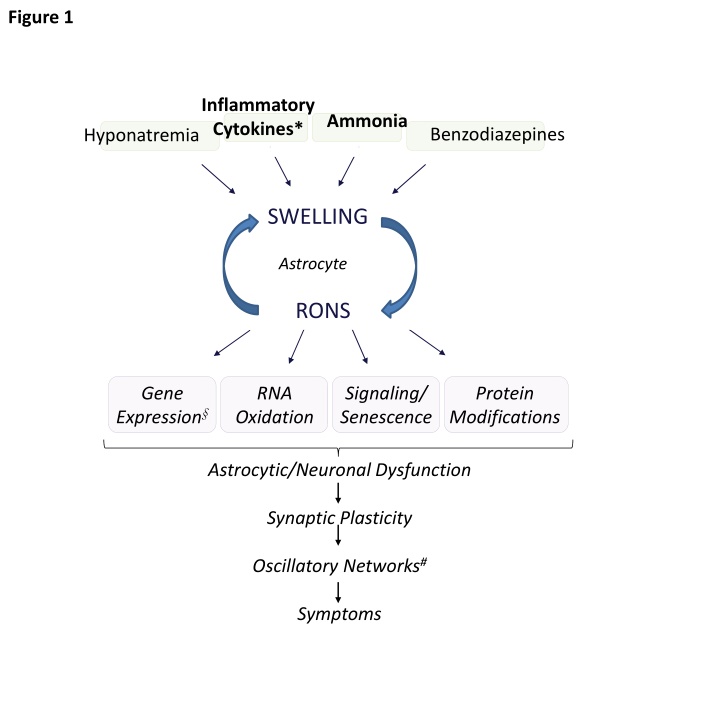
Figure 1 Inflammatory Cytokines* Ammonia Benzodiazepines Hyponatremia SWELLING Astrocyte RONS Gene RNA Signaling/ Senescence Protein Modifications Expression Oxidation Astrocytic/Neuronal Dysfunction Synaptic Plasticity Oscillatory Networks# Symptoms
Figure 2 HE-precipitating factors (e.g. ammonia, inflammatory cytokines) Mg2+ Glu 1 Extracellular NMDAR MRP4 TGR5 Cytosol GS Membrane stretch cPLA2 AC Arachidonic acid Ca2+ Neurosteroids Prostanoids 2 PBR GLS Glu + NH4+ Gln cAMP Mitochondrium iNOS 3 nNOS NOX2 Phagosomes Inactivation 4 4 NO O2- Proteasome Activation SOD 6 NOX4 ONOO- H2O2 4 PPAR MTF1 SP1 8 Fe(II) HO1 7 4, 5 P53 OH Protein Tyrosine Nitration PBR TGR5 MRP4 MT1/2 4 p21 RNA GADD45 18S-rRNA-8-OHG Translation inhibition? Oxidation Senescence GLAST-mRNA-8-OHG Degradation? GS-NO2Tyr Inactivation NKCC1-NO2Tyr Activation GLAST Cytosol Extracellular NH4+ Glu
Figure 3 Ammonia GS Glutamine Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway UDP-GlcNAc OGT Protein O-GlcNAcylation pri-miR326-3p miR326-3p HO1 Nox4 Fe(II) H2O2 Fenton Reaction OH RNA Oxidation Senescence
Fig. 4 Liver damage Liver damage Altered microbiome Altered microbiome Peripheral Peripheral inflammation inflammation Hyperammonemia Hyperammonemia Changes in: Changes in: Immunophenotype Immunophenotype Extracellular vesicles Extracellular vesicles Transmission to brain Transmission to brain Neuroinflammation Neuroinflammation Altered neurotransmission Altered neurotransmission Cognitive and motor Cognitive and motor impairment impairment
Fig. 5 Westhaven criteria and clinical description HE 0 MHE HE 1 HE 2 HE 3 HE 4 Recognizable clinical signs Disorientation Somnolence but arousable confusion No clinical signs Abnormal psychometry no Coma-like abnormalities overt HE covert HE low grade HE high grade HE (hospitalization required) (no hospitalization required) (sub-gradation by CFF or PHES) CFF (Hz) Glasgow coma scale PHES pts.
Fig 6 A Assessment for hepatic encephalopathy and treatment of stable out-patient with cirrhosis No history of overt HE History of overt HE Neurologic Examination Search and treat risk factors for HE Nutrition, Lactulose +/- Rifaximin Secondary Prophylaxis Normal Abnormal CT Head Test for mHE ?PHES, CFF, EEG, other Stable Recurrent Persistent normal abnormal Follow up Normal Abnormal Neurological Disease Refer Neurology Large Shunts Embolise Reduce TIPSS No mHE Follow up Consider liver transplantation ?Grade 1 / 2 HE mHE Search and treat risk factors of HE Nutrition, Lactulose +/- Rifaximin Primary Prophylaxis
Fig 6B Assessment for hepatic encephalopathy and treatment of hospitalized patients with cirrhosis Airway, Breathing, Circulation Neurological Examination Abnormal Normal CT Scan Manage Complications Normal Abnormal Ammonia Refer Neurology Abnormal Normal Hepatic Encephalopathy Grade 1-2 Monitor Search and treat precipitating events Nutritional Support adequate protein: enteral/parenteral 3-4 Admit ICU / protect airway / Intubate Specific Rx 1st Line 2ndLine 3rdLine 4thLine Lactulose/Rifaximin Polyethylene Glycol/*LOLA **Albumin Dialysis/Check ***PSS, consider occlusion Liver Transplantation *LOLA: L-ornithine L-aspartate (where available) **where available ***PSS: spontaneous or TIPSS