Higher Biology
Animals adapt to extreme heat, cold, drought or food scarcity by entering dormancy. Learn about predictive and consequential dormancy, hibernation, and aestivation as survival strategies in challenging environments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Higher Biology Metabolism & Adverse Conditions
Adverse Conditions There are many environments where conditions may be extreme and beyond the tolerable limits for normal metabolism, e.g. Extreme heat Extreme cold Drought Lack of food Animals either need to adapt to these conditions or avoid them if they are to survive. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 2
Surviving Adverse Conditions Organisms can lower their metabolic rate in order to conserve energy. We call this dormancy. Dormancy is a part of the life cycle of the organism where growth & development are halted on a temporary basis. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 3
Predictive Dormancy Predictive dormancy happens when the organism becomes dormant before the adverse conditions arrive. It is generally genetically controlled. If the seasons are predictable, the organism can use certain factors to respond, e.g. trees shedding their leaves in winter. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 4
Consequential Dormancy Consequential dormancy occurs after the adverse conditions have started. It is found in regions where the climate is more unpredictable. The biggest advantage is that the organism can remain active for longer. The disadvantage is that if the climate suddenly worsens, many organism may die before they can become dormant. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 5
Hibernation Hibernation is a type of dormancy employed by animals to survive harsh winter conditions. The animal will normally increase its consumption of food before hibernation and store it as fat. https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/236x/a4/28/52/a428521a490ae791aea909a4c883fed2.jpg Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 6
Hibernation It will then lower its metabolic rate which will result in a drop in body temperature, heart rate and breathing rate. These steps allow the animal to survive long periods of low temperatures as its energy expenditure is lowered also. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 7
Aestivation Aestivation is like hibernation but in the heat or drought. In some environments the temperature can become so hot that the animal needs to find somewhere to shelter away from the intense conditions. This can be an underground burrow where it is cooler and damper. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 8
Daily Torpor Daily torpor is a very short term kind of hibernation. The animal s metabolic rate becomes reduced for a part of the day as the animal rests. It is common among small birds and small mammals because they have such a high surface area : volume ratio. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 9
Daily Torpor This means they require much more energy to survive. Therefore, a period of torpor allows the organism to conserve energy. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 10
Avoiding Adverse Conditions Firstly, it is important to remember that there is a difference between surviving and avoiding adverse conditions. Migration is a technique used by a lot of animals to avoid extreme conditions. It involves the movement of a population from one area to another over a fairly long distance. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 11
Migration http://cdn2.kidsdiscover.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/1.jpg Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 12
Innate Behaviour An organism s migratory behaviour is thought to be inherited. Innate behaviour is inherited and inflexible and therefore the entire species performs the same migratory behaviour each year. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 13
Learned Behaviour Learned behaviour develops with the organism and is based on experience. It is generally flexible and is the result of watching others or trial and error. Migration is a result of both innate and learned behaviour. Scientists have a number of techniques used to study migration including ringing birds legs, attaching transmitters, marking animals, etc. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 14
Behaviour Learned Innate https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQ-nLXzueHTtmq3m4Go3lKWvCE3JfK5VabgvZKbDAdYhlo5W-lwwg http://www.tokresource.org/tok_classes/biobiobio/biomenu/options_folder/E3_innate_learned/geese-imprinting.jpg Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 15
Extremophiles Most extremophiles belong to the group archaea but some are bacteria. Extreme thermophiles can survive in temperatures up to 80oC in places like hot springs and volcanic vents. http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/extremophile.jpg Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 16
Extremophiles Extremophiles are organisms which live under extreme conditions that most other organisms would find lethal. Examples include: Extreme heat (>40oC) Extreme cold (<5oC) pH Salinity Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 17
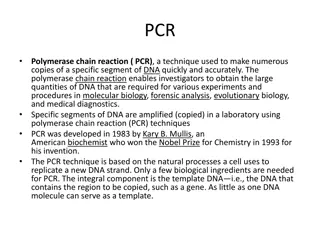
Extremophiles Extreme cryophiles can survive for long periods of time in ice in places such as the Arctic and Antarctica. These organisms have the ability to survive in extreme conditions due to the fact that they possess unusual enzymes capable of functioning at extreme temperatures, e.g. taq polymerase which is heat tolerant and used in the PCR. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 18
Extremophiles Some extremophiles can make use of substances like hydrogen sulphide by using high energy electrons to regenerate ATP. This results in the production of sulphuric acid. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 19
Extremophiles Methanogens are anaerobic microbes which can generate hydrogen and ATP and produce methane which is a by- product. These organisms cannot live in the presence of oxygen. Monday, 24 February 2025 G R Davidson 20


![❤[READ]❤ Cosmic Biology: How Life Could Evolve on Other Worlds (Springer Praxis](/thumb/21556/read-cosmic-biology-how-life-could-evolve-on-other-worlds-springer-praxis.jpg)