Histology of Digestive Glands: Pancreas and Liver
The histology of glands in the digestive system, focusing on the pancreas and liver. The pancreas serves as both an exocrine and endocrine gland, producing digestive enzymes and hormones. It consists of exocrine units called acini and endocrine units composed of islets of Langerhans. The liver, the largest gland in the body, is divided into lobes and lobules, with hepatocytes and sinusoids playing crucial roles in its function.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
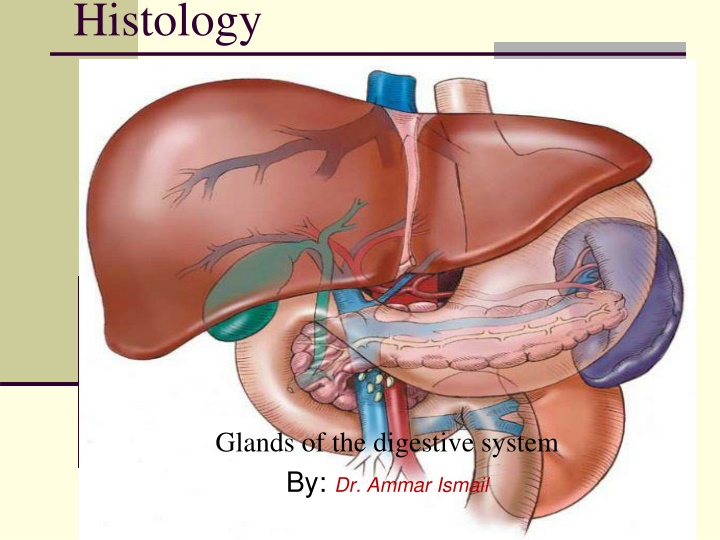
Histology Glands of the digestive system By: Dr. Ammar Ismail
Pancreas The pancreas is an exocrine gland that produces digestive juices( amylase, ,trypsin ) and an endocrine gland that hormones . lipase manufactures Its gland surrounded by capsule which gives trabiculi to divides the parenchyma into lobules which contain two types of secretary unit. compound tubuloacinar
Pancreas 1 Exocrine units : (acini ) The pancreatic acini is spherical shape formed from cuboidal cells have central nuclei . the acini of pancreas have no basket cells ( myoepithelial cells). The duct system of pancreas begins with in the center of acinus which open to the intercalated duct which composed of pale low cuboidal , intercalated ducts join each other to form larger intralobular ducts lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium and this lead to interlobular ducts , also these later duct connect into main pancreatic duct which join the common bile duct before opening in the duodenum .
Pancreas 2 Endocrine units : Its composed of spherical aggregates of cells , known as islets of langerhans, that are scattered among the acini .There are five cell types composing the islets of langerhans :Alpha , Beta , Delta , PP cells and G- cells These cells cannot be differentiated from each other by rotten histological examination . These five cells types responsible ,Glacogon , somatostatine , Gastrin , pancreatic polypeptide . for synthesis, Insulin
Liver : The liver is a largest gland in the body its surrounded by mesothelium .The connective tissue capsule extend into the gland and divided it into lobes and lobules . The parenchyma of liver is consist of epithelial cells of endodermal origin, the hepatocytes arranged in anastomosing rows separated by sinusoids converging on the central vein , the sinusoids are lined with fenestrated endothelial cells and macrophages (Kupffer cells ). The bile is secreted by each hepatocytes into the bile canaliculi , that are lined with the plasma membrane of the hepatocytes between adjacent liver cells . Its flows from there the bile ducts are lined with cuboidal epithelium in the portal areas . Note : The smallest functional unite of liver is acini .