HIV Treatment Comparison Study: FPV/r vs. LPV/r in KLEAN Study
Explore the comparison of PI medications FPV/r and LPV/r in the KLEAN study, focusing on efficacy, patient characteristics, and virologic outcomes at week 48. Analyzing factors such as HIV RNA levels, CD4 counts, and treatment discontinuations provides valuable insights for ARV-naïve individuals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
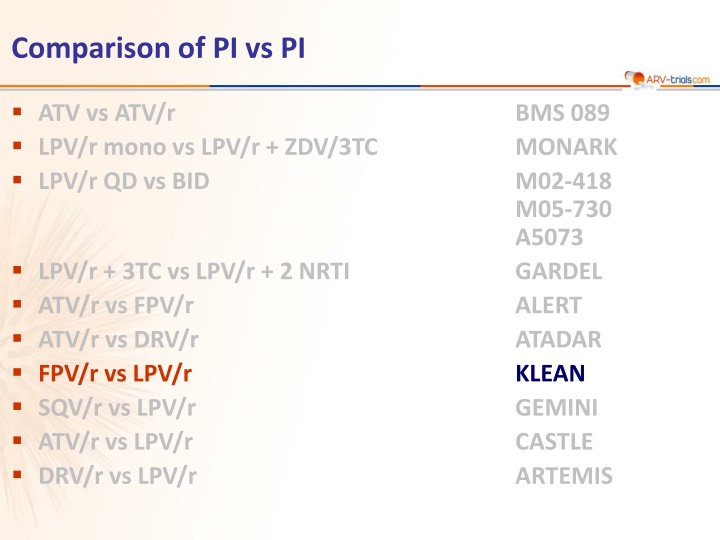
Comparison of PI vs PI ATV vs ATV/r LPV/r mono vs LPV/r + ZDV/3TC LPV/r QD vs BID BMS 089 MONARK M02-418 M05-730 A5073 GARDEL ALERT ATADAR KLEAN GEMINI CASTLE ARTEMIS LPV/r + 3TC vs LPV/r + 2 NRTI ATV/r vs FPV/r ATV/r vs DRV/r FPV/r vs LPV/r SQV/r vs LPV/r ATV/r vs LPV/r DRV/r vs LPV/r
KLEAN Study: FPV/r BID vs LPV/r BID, in combination with ABC/3TC Design Randomisation* 1:1 Open-label W48 FPV/r 700/100 mg BID N = 434 > 18 years ARV-na ve ABC/3TC fdc QD HIV RNA > 1,000 c/mL Any CD4 cell count LPV/r 400/100 mg BID N = 444 ABC/3TC fdc QD *Randomisation was stratified on HIV RNA < or > 100,000 c/mL Objective Non inferiority of FPV/r vs LPV/r at W48: % HIV RNA < 400 c/mL, ITT, TLOVR algorithm (lower margin of the 95% CI for the difference = - 12%, 90% power) Eron J. Lancet 2006;368:467-82 KLEAN
KLEAN Study: FPV/r BID vs LPV/r BID, in combination with ABC/3TC Baseline characteristics and patient disposition FPV/r LPV/r Randomized, N 443 444 Treated eligible patients, N 434 444 Median age, years 38 37 Female 22% 22% White/Black/Other 61% / 29% / 10% 56% / 33% / 11% HIV RNA (log10c/mL), median 5.1 5.1 HIV RNA > 100,000 c/mL 55% 53% CD4 cell count (/mm3), median 188 194 CD4 < 50/mm3 15% 18% Hepatitis B and/or C positive 15% 12% Discontinuation before W48 21% 22% Substitution of any NRTI for ABC in case of suspected hypersensitivity; no other ARV substitutions allowed Eron J. Lancet 2006;368:467-82 KLEAN
KLEAN Study: FPV/r BID vs LPV/r BID, in combination with ABC/3TC HIV RNA < cut-off at week 48 FPV/r LPV/r % 100 % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL (ITT-E, TLOVR) was similar between FPV/r and LPV/r across baseline subgroups (low or high HIV RNA, low or high CD4) < 400 c/mL < 50 c/mL < 50 c/mL < 50 c/mL Primary efficacy endpoint 73 89 88 80 71 67 67 66 65 60 Median CD4 increase at W48: 176/mm3(FPV/r) vs 191/mm3(LPV/r) 40 20 N = 434 444 434 444 328 341 Virologic failures at W48 (TLOVR analysis): 26 (FPV/r) vs 30 (LPV/r), including unconfirmed HIV RNA > 400 c/mL on final visit 0 ITT-E, TLOVR ITT-E, TLOVR ITT, M/D = F Observed analysis, ITT-E 95% CI for the difference = - 4.8; 7.05 ITT-E : ITT-exposed ITT, M/D = F : ITT missing/discontinuation = failure Eron J. Lancet 2006;368:467-82 KLEAN
KLEAN Study: FPV/r BID vs LPV/r BID, in combination with ABC/3TC Resistance data Genotypic and phenotypic resistance testing was done at virologic failure: 1) Viral rebound (2 consecutives HIV RNA > 400 c/mL after achieving < 400 c/mL 2) HIV RNA > 400 c/mL at W24 FPV/r N = 434 LPV/r N = 444 Protocol-defined confirmed virologic failure 16 (4%) 24 (5%) Confirmed rebound after achieving < 400 c/mL 10 20 Failure to achieve < 400 c/mL by week 24 6 4 Assessed for treatment-emergent resistance mutations 14 21 No treatment-emergent mutation 10 14 M41L 0 1 M184I/V 3 4 NNRTI resistance mutation (V106A) 0 2 PI resistance mutation (K20R = 1, I54L = 2, I62V = 1) 2* 2* * No reduced phenotypic susceptibility, no acquisition of major PI mutations Eron J. Lancet 2006;368:467-82 KLEAN
KLEAN Study: FPV/r BID vs LPV/r BID, in combination with ABC/3TC Safety and tolerability: FPV/r vs LPV/r Similar frequency of premature discontinuations for adverse events: 12% vs 10% Similar frequency of clinical adverse events grade 2 to 4 and laboratory abnormalities grade 3 to 4 in both groups Diarrhoea was the most common adverse event, and led to treatment discontinuation in 1% and 2%, respectively Similar frequency of suspected abacavir HSR: 7% vs 5% Similar frequency of grade 3-4 alanine transaminase (ALT): 12% of patients with hepatitis B and/or C co-infection vs 1% in the absence of co-infection Similar changes in fasting lipids at W48, including triglycerides. Use of lipid-lowering agents during the study period: 11% in both groups Eron J. Lancet 2006;368:467-82 KLEAN
KLEAN Study: FPV/r BID vs LPV/r BID, in combination with ABC/3TC Summary - Conclusion In combination with ABC/3TC QD, FPV/r BID was non inferior to LPV/r BID Virologic and immunologic outcomes at W48 were similar with FPV/r and LPV/r In patients with high baseline HIV RNA and those with low baseline CD4, similar antiviral potency of the 2 PI/r was evidenced Tolerability and safety, numbers of treatment discontinuations, and increases in fasting lipids were similar for FPV/r and LPV/r Confirmed virologic failure was uncommon in both groups with no emergence of major protease inhibitor-associated resistance mutation in either group In antiretroviral-na ve patients, FPV/r BID provides similar antiviral efficacy, immunologic response, safety and tolerability as LPV/r, both in combination with fixed dose ABC/3TC QD Eron J. Lancet 2006;368:467-82 KLEAN
