How Lexical Analysis Works
Learn about the process of lexical analysis in programming, where characters of the source program are scanned to identify tokens using input buffering and look-ahead pointers. Explore the role of the lexical analyzer as an interface between the source program and the compiler, aiding in syntax analysis and error handling.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
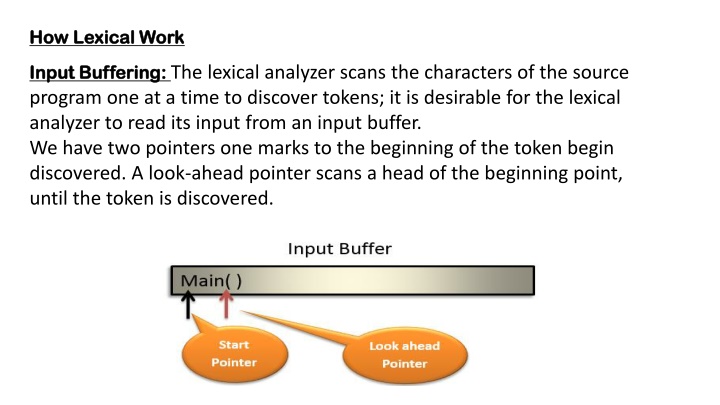
How Lexical Work How Lexical Work Input Buffering Input Buffering: : The lexical analyzer scans the characters of the source program one at a time to discover tokens; it is desirable for the lexical analyzer to read its input from an input buffer. We have two pointers one marks to the beginning of the token begin discovered. A look-ahead pointer scans a head of the beginning point, until the token is discovered.
Sometimes lexical analyzer needs to look ahead some symbols to decide about the token to return. In C language: we need to look after , = or < to decide what token to return.
Lexical Analyzer Lexical Analyzer The Role of the Lexical Analyzer Lexical Analyzer is the interface between the source program and the compiler. The main task of lexical Analyzer is to read the input characters and produce a sequence of tokens that the parser uses for syntax analysis. Interaction of lexical analyzer with parser
The Role of the Lexical Analyzer Upon receiving a "get next token" command from the parser, the Lexical Analyzer reads input characters until it can identify the next token.. Interaction of lexical analyzer with parser
The Secondary Tasks of Lexical Analyzer: The Secondary Tasks of Lexical Analyzer: 1. Removal of white space and the comments. White space (blanks, tabs, and newline characters). 2. Correlating error messages from the compiler with the source program. For example, the lexical analyzer may keep track of the number of newline characters seen, so that a line number can be associated with an error message. Note: Regular Expressions are used to define the tokens recognized by lexical analyzer. The lexical analyzer is implemented as Finite Automata (DFA).






















