IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Channel State Estimation
Explore the innovative approach proposed by Bo Li et al. from Northwestern Polytechnical University to improve transmission reliability in IEEE 802.11 networks by enhancing channel state estimation and bidirectional initialized random access techniques. Discover how this advancement addresses issues of real-time channel state reflection between senders and receivers, leading to a more reliable data transmission process.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
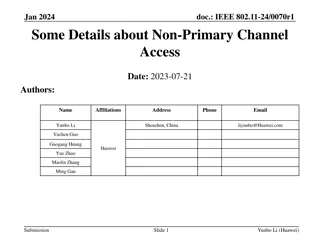
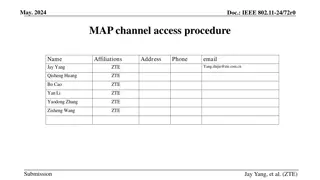
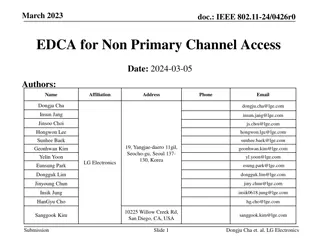
May 2016 doc.: IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Channel State Estimation based Bidirectional Initialized Random Access Date: 2016-05-12 Authors: Name Affiliation Address Phone Email Bo Li libo.npu@nwpu.edu.cn Mao Yang yangmao@nwpu.edu.cn Zhongjiang Yan zhjyan@nwpu.edu.cn Xiaoya Zuo zuoxy@nwpu.edu.cn Run Zhou zhourun_xsy@163.com Northwestern Polytechnical University 127 West Youyi Road, Xi an Shaanxi,710072, P.R.China +86-18192187626 Submission Slide 1 Bo Li, et al. (NWPU)
May 2016 doc.: IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Background In the current 802.11 WLAN, it is always the sender node that initializes the transmission through CSMA/CA. BUT, the channel state, e.g. idle or busy, detected by the sender can hardly precisely reflects the real-time channel state of the receiver. This results in low transmission reliability. e.g. the sender believes that the channel is idle and transmits data after backoff but, actually, the receiver is now experiencing severe interference. Submission Slide 2 Bo Li, et al. (NWPU)
May 2016 doc.: IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Motivation To improve the transmission reliability, two possible methods: the sender is able to estimate the receiver s channel state the receiver can initialize the transmission rather than just the sender does it. Submission Slide 3 Bo Li, et al. (NWPU)
May 2016 doc.: IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Channel State Estimation based Random Access The sender maintains the average interference difference Isd between the sender and the receiver through the historic transmission. The sender and the receiver can exchange their average interference information during RTS/CTS. During the sender s backoff period, the sender detects the RSSI, and estimates the interference at the receiver Ide = RSSI - Isd. If Ide > CCA, backoff suspend If Ide < CCA, backoff counter decreases by 1 and backoff continues The sender sends Data or RTS when the backkoff period completes. Submission Slide 4 Bo Li, et al. (NWPU)
May 2016 doc.: IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Bidirectional Initialized Random Access Step 1: At the end of the TXOP initialized by the sender, if the sender still has large enough data to send, it fills one bit Rq in the last data frame to ask the receiver to directly initialize the following TXOP from the sender to the receiver. Step 2: If the receiver receives the last data frame with Rq, it responds with ACK with one bit named Rs filling in. TXOP Sender RTS Data Data Data Rq CTS ACK ACK ACK Rs=1 Receiver Submission Slide 5 Bo Li, et al. (NWPU)
May 2016 doc.: IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Bidirectional Initialized Random Access Step 3: the receiver runs backoff period according to itself s channel state. Step 4: if the receive finishes its backoff period, it directly sends CTS to the sender to initialize the transmission. Sender Data backoff CTS ACK Receiver Submission Slide 6 Bo Li, et al. (NWPU)
May 2016 doc.: IEEE 802.11-16-0588-00-00ax Conclusion In this presentation, in order to improve the transmission reliability, we introduce channel state estimation and bidirectional initialized, i.e. both the sender and the receiver, based random access. Submission Slide 7 Bo Li, et al. (NWPU)