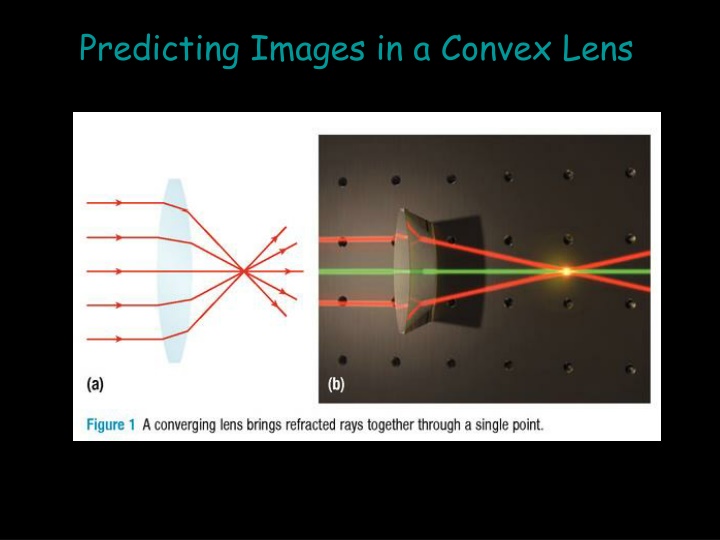
Image Formation in Convex and Concave Lenses
Explore the principles of image formation in convex and concave lenses through detailed ray diagrams and characteristic rays. Discover how rays behave in different scenarios such as when the object is beyond 2F, at 2F, between 2F and F, or when the image is at F or between F and O. See how rays refract through these lenses to predict the resulting images accurately.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Principal rays A ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted through the principal focus (F ).
The Principal rays A ray through the optical centre (O) continues straight through without being refracted.
http://www.physics-chemistry-interactive- flash- animation.com/optics_interactive/convergin g_lens_convex_positive.htm
Concave Lens Characteristic Rays Any incident ray parallel to the principal axis will refract as if it had passed through the principal Focus.
Concave Lens Characteristic Rays Any incident ray passing through the Optical Centre will pass undeviated (straight through).
Homework Pg. 561 #2, 3, 5, 6