Immuno-modulatory Factors and Glucocorticoid-Insensitive Proteins in Asthma
Explore the role of immuno-modulatory factors and glucocorticoid-insensitive proteins produced in asthma pathogenesis, affecting airway remodeling, hyper-responsiveness, and immune cell interactions in ASM tissues of asthmatic patients.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
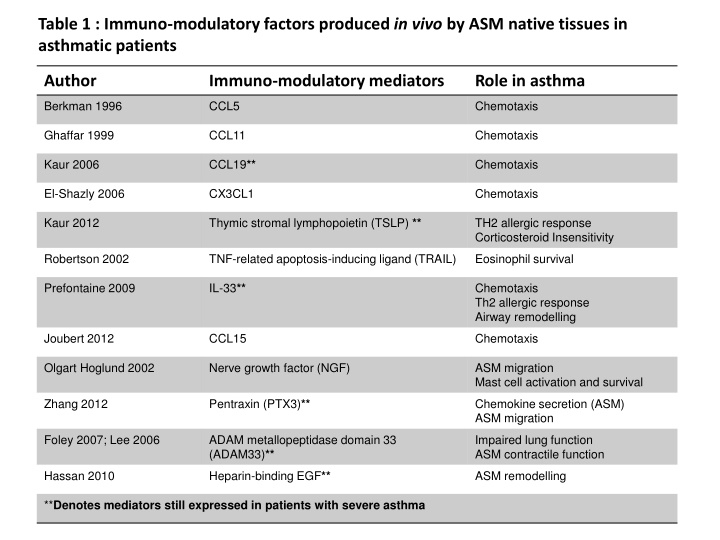
Table 1 : Immuno-modulatory factors produced in vivo by ASM native tissues in asthmatic patients Author Immuno-modulatory mediators Role in asthma Berkman 1996 CCL5 Chemotaxis Ghaffar 1999 CCL11 Chemotaxis Kaur 2006 CCL19** Chemotaxis El-Shazly 2006 CX3CL1 Chemotaxis Kaur 2012 Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) ** TH2 allergic response Corticosteroid Insensitivity Robertson 2002 TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) Eosinophil survival Prefontaine 2009 IL-33** Chemotaxis Th2 allergic response Airway remodelling Joubert 2012 CCL15 Chemotaxis Olgart Hoglund 2002 Nerve growth factor (NGF) ASM migration Mast cell activation and survival Zhang 2012 Pentraxin (PTX3)** Chemokine secretion (ASM) ASM migration Foley 2007; Lee 2006 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 33 (ADAM33)** Impaired lung function ASM contractile function Hassan 2010 Heparin-binding EGF** ASM remodelling **Denotes mediators still expressed in patients with severe asthma
Table 2 : Glucocorticoid-insensitive proteins induced by TNF /IFN in ASM cells Author Immuno-modulatory mediators Role in asthma Clarke 2010; Chachi 2013 CXCL10 Chemotaxis Chachi 2013 CCL5 Chemotaxis Sukkar 2004; Chachi 2013 CX3CL1 Chemotaxis Prefontaine 2009 IL-33** Chemotaxis Th2 allergic response Airway remodelling Joubert 2012 CCL15 Chemotaxis Tliba 2008 IRF-1 Transcription of inflammatory genes Inhibition of GR transactivation via GRIP-1 depletion Chachi 2013 CCL11 Chemotaxis Tliba 2006 CD38 Airway inflammation Airway hyperresponsiveness GR Inhibition of GR transactivation via dominant negative action Tliba 2006 Inhibition of GR transactivation via ser211 dephosphorylation Bouazza 2012; Chachi 2013 PP5 **Denotes mediators still expressed in native ASM tissues in severe asthmatics
Figure 1 : Role of the immuno-modulatory factors produced in vivo by ASM in asthma pathogenesis Asthmatic ASM bundles Airway remodelling/ Hyper-responsiveness NGF CCL19 CCL11 Pentraxin 3 ADAM33 HB-EGF TRAIL IL-33 TSLP CCL5 CCL11 CCL19 CX3CL1 CCL15 Activation Survival GC insensitivity Alteration of ASM function Migration Proliferation Contractility Chemoattraction of inflammatory cells T cells Mast cells Eosinophils Airway remodelling Airway Inflammation
Figure 2 : Potential molecular mechanisms mediating cytokine-induced GC insensitivity in ASM cells TNF /IFN GC KCa3.1 Airway smooth muscle P Impaired GR phosphorylation 4-6 hr PP5 GC Rapid mechanisms P GRIP-1 GR IRF-1 Impaired GR transactivation activity 12-24 hr GR Delayed mechanisms Corticosteroid Insensitivity
