Immunoglobulins and Their Functions in Immune Response
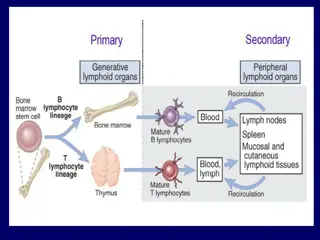
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells. They play a crucial role in the immune response by recognizing and binding to specific antigens such as bacteria or viruses. There are different classes of immunoglobulins, each with unique functions such as IgA in mucous membranes, IgG in blood, IgM as the first responder antibody, IgE against parasitic worms, and IgD signaling B cells for activation. Serological tests help determine different serotypes of microorganisms and detect antibodies in serum. The complement fixation test is utilized to detect specific antibodies or antigens in a patient's serum.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CAPACITOR Aakanksha Bajpai Assistant Professor School of Health Sciences
Device that store electric charges Consists of two plates Separated by an insulator Non-conductive region can either be a vacuum or an electrical insulator known as dielectric (glass, air, paper, semi-conductor). Variety of sizes and shapes Symbol
Types of Capacitor Parallel plate capacitor Cylindrical capacitor
Capacitance Ability to store charge. Unit of capacitance is Farad(F). Capacitance values are normally smaller, such as F, nF or pF. C=Q/V Capacitance of capacitor is directly proportional to Charge store on that capacitor and inversely proportional to Voltage.
Basic Capacitor Construction Two Plates. Dielectric(air, glass, paper or semi-conductor material). Due to dielectric charges store on capacitor plates.
Storing Charge On Capacitor Connect to a voltage source. Positive charges start flowing towards one plate of capacitor and negative towards other. Due to dielectric charges start accumulating on plate surface. Potential rises from zero. Flow of charges stops when capacitor potential become equal to potential of battery. Same case with negative charges. So, charge store on the capacitor
Capacitors In Parallel Voltage remain same The equivalent capacitance of two capacitors connected in parallel is the sum of the individual capacitances.
Capacitor In Series Charge remain same. The reciprocal of the equivalent capacitance of two capacitors connected in series is the sum of the reciprocals of the individual capacitances.
Uses of Capacitor To reduce the variations in the intensity of a rectified current To control the timing of electronic interrupters and surgers To make current more comfortable for the patient To produce a high frequency current To tune SWD machine for maximum transfer of energy from machine circuit to patient circuit.