Impact of World War II on Ireland and Political Changes in the 1930s
Discover the impact of World War II on the lives of Irish people and how Ireland remained neutral during the conflict. Learn about the shortages faced by the Irish, the Emergency Powers Act, and the government's response. Explore the political landscape in Ireland during the 1930s, including the transition of power to Fianna Fáil and the changes they implemented.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
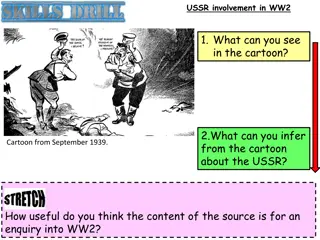
2.8 describe the impact of war (WWII) on the lives of Irish people A LQ: What impact did WWII LQ: What impact did WWII have on people in Ireland? have on people in Ireland? Do now: Renaissance retrieval Look at the two paintings and answer the questions. 1. Identify which painting is from the Renaissance. 2. Name two techniques that Renaissance painters developed that you can see in this painting. B 3. What was the technique called when they painted directly on to wet plaster? Name one famous painter from the Renaissance and one of their paintings. 4.
Do now: Renaissance retrieval ANSWERS A Look at the two paintings and answer the questions. 1. Identify which painting is from the Renaissance. Painting A 2. Name two techniques that Renaissance painters developed that you can see in this painting. Use of perspective/ correct anatomy/ vivid colours/ blending techniques with colour/ creation of shadows or use of light B 3. What was the technique called when they painted directly on to wet plaster? Fresco Name one famous painter from the Renaissance and one of their paintings. Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa, Last Supper Michelangelo Sistine Chapel (Day of Judgement) 4.
How was Ireland impacted by World War II? How was Ireland impacted by World War II? Ireland remained neutral - they did not engage in active warfare and did not (openly) support either side Government brought in the Emergency Powers Act Shortages effected people: Food and rationing Shortages in fuel Gas shortages and glimmer men Government created new organisations to support Ireland during a time when imports were low good for local Irish businesses
What was happening in Ireland in 1930s? What was happening in Ireland in 1930s? Cuman na nGaedheal were still in power in 1932 but were increasingly unpopular because Ireland was still largely agricultural, and they had failed to grow Ireland's industries In 1929, the Wall Street Crash plunged the world into the Great Depression which caused international financial difficulty and high unemployment, emigration and poverty In 1932, an election was called and a coalition government of Fianna Fail (a new party established in 1926 by de Valera when he left Sinn Fein) and the Labour party.
What changes did Fianna Fail make in power? What changes did Fianna Fail make in power? Dismantled the Anglo-Irish Treaty removed the Oath of Allegiance, got rid of the governor-general and removed references to monarch in constitution Created a new constitution, Bunreacht na hEireann (1937) and Douglas Hyde became Ireland's first president Stopped Irish farmers paying back their loans to Britain (land annuities) and introduced tariffs (taxes) to exports to Britain Economic War Introduced welfare payments for widows and orphans (1933) and for unemployment (1935) to reduce poverty Built more houses than the last government Banned the IRA in 1936 and imprisoned 500 active members in 1939 in a bid to bring peace to Ireland
Neutrality and the Emergency Powers Act Neutrality and the Emergency Powers Act Neutrality means that you are not fighting in a war and that you will not support either side. In 1939, the government passed the Emergency Powers Act. This allowed them to take extreme measures to protect Ireland's neutrality including opening post and censoring the media and weather reports.
What reasons did Ireland have for staying neutral? What reasons did Ireland have for staying neutral? Asserting its independence from Britain Did not have the military capability to engage as a nation (but could have sent soldiers to support the allies) Irish economy was weak and would be further damaged by war Supported by all political parties and people What is friendly neutrality? This means when a country declares itself neutral but engages in biased behaviour where they support one side over the other. Examples of Ireland having 'friendly neutrality' with the Allies: Sent weather reports to the Allies Allowed American planes to fly over Donegal German pilots who were captured were imprisoned; Allied pilots were returned to the Northern Ireland border 50,000 Irish men joined the British army Dublin fire brigades went to Belfast to help with the rescue from German bombings
Source work: Read the source and discuss the questions Source work: Read the source and discuss the questions This is an extract from de Valera's speech on neutrality: 1. What was the 'peril (that) brought the country to one magnificent unity' that happened 20 years ago? 2. True or false: de Valera says Ireland is ready to defend itself.
What was life like in Ireland during the Emergency? What was life like in Ireland during the Emergency? Shortages and rationing: Shortages and rationing: Ireland relied on imports for foods and goods impacted by interruptions to and from Britain by German attacks Rationing Rationing means to limit the amount of items that a person can buy. Ration books to keep track of what people buy. Ration books were used Items that were regularly rationed were: tea, sugar, flour, butter.
Sean Sean Lemass Lemass was made Minister for Supplies and he set up organisations to alleviate this: Irish Shipping Company Irish Shipping Company - 15 cargo ships that served Irish needs Compulsory Compulsory Tillage Scheme Tillage Scheme all farmers had to sow a certain amount of wheat to feed people
Fuel shortages and Glimmerman Electricity and gas were in short supply and were rationed. This meant that there were blackouts and curfews Glimmer men were employed to check that people in towns and cities were not overusing gas. After the gas was switched off at supply, there would be a small amount left in pipes. People were not supposed to use this. Glimmer men were not popular. People turned to turf to fuel houses the army were brought in to cut it. Petrol and diesel were also rationed and restricted to only doctors and priests. Irish industry was impacted by these fuel shortages.
Task: write an account of the impact of WWII/ The Task: write an account of the impact of WWII/ The Emergency on a person living in Dublin in 1944 Emergency on a person living in Dublin in 1944 This will be a 15 mark question 5 facts 'state and explain' Cover the following issues: Neutrality and its impact; reasons for and against neutrality Emergency Powers Act and its impact on people Food shortages and rationing Fuel shortages Bombings and threats to Ireland (Belfast Blitz; North Strand Bombings) Daily life what changed/became more difficult? Tips: For each bullet point, start a new paragraph/line State and explain five facts for full marks. Detailed explanation is needed though!