Imperialism: British Influence in Egypt and India
Egypt, a semi-independent province of the Ottoman Empire, saw reforms under Muhammad Ali in the early 1800s. Ali introduced political, economic reforms, and military modernization. The construction of the Suez Canal led to increased European control and eventually British dominance. In India, the British East India Company expanded its influence as the Mughal Empire declined, exploiting diversity to conquer significant territories.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Imperialism The British in Africa and India
Egypt Early 1800s: Egypt was a semi- independent province of the Ottoman Empire making strides toward reform It s success due to Muhammad Ali, a soldier appointed governor of Egypt by the Ottomans When Napoleon invaded Egypt in 1805, Ali used the opportunity to seize power
Egypt Ali introduced political and economic reforms Improving tax collection Reorganizing the landholding system Backing large irrigation projects Ali increased Egypt s participation in world trade, expanding cotton production and encouraging industrial development
Egypt Ali brought in Western military experts to help him build a modern army and then conquered Arabia, Syria, and Sudan Ali s successors lacked his skills, and Egypt increasingly fell under foreign control In 1858, a French entrepreneur organized a company to build the Suez Canal
Egypt During the building of the canal, European nations gained power over the Ottomans by extending loans at high interest rates In 1875, the Egyptian ruler could not repay the loans, and sold his shares of the canal to the British to repay his debts, giving the British controlling interest in the canal
Egypt 1882: Egyptian nationalists revolt against foreign influence in Egypt Britain made Egypt a protectorate The governor of Egypt was still an official of the Ottomans The governor followed policies dictated by British Though Egypt was further modernized, nationalist sentiments continued to simmer
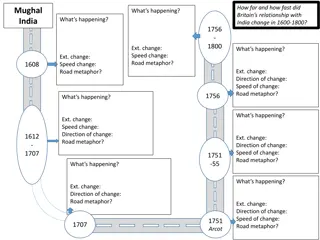
The British Take India For more than 200 years the Mughal empire ruled over India In the early 1600s, the British East India Company won trading rights on the fringe of the Mughal empire As the Mughal empire began to decline in the mid- 1700s, the company s influence began to grow in India
The British Take India By exploiting India s diversity, the British were able to conquer 3/5s of India by the mid-1800s Even during the Mughal empire, India was composed of many different peoples with unique languages and cultures Unable to unite against the British, the British encouraged competition and disunity against rival princes
Implementing British Policies The main goal of the East India Company was to make money The company did work to improve roads, preserve peace, and reduce banditry By the early 1800s, British officials introduced Western education and legal procedures
Implementing British Policies The British also pushed for social change, working to end slavery and the caste system They also improved the position of women within the family One law banned the practice of sati where widows were called to join their husbands in death by casting themselves on their husband s funeral fire
Growing Discontent The East India Company made several unpopular moves in the 1850s They required Indian soldiers to serve in company service either in India or overseas They also passed a law allowing widows to remarry, moves that Hindus saw as a Christian conspiracy to undermine their beliefs
Rebellion Angry Indian soldiers began rising up against their British officers Several Indian regiments marched off to Delhi where they hailed the last Mughal ruler as their leader Though soldiers brutally massacred British men, women, and children, the British soon rallied and crush the revolt
Rebellion The rebellion left a bitter legacy of fear, hatred, and mistrust on both sides It brought changes in British policy 1858: Parliament ended the rule of the East India Company and brought India directly under the British crown The British sent more troops to India and taxed the Indians to pay for the occupying force
Impact of British Rule After bringing India under crown rule, Parliament set up a system of colonial rule called the British Raj A British viceroy governed in the name of the queen and top positions in the civil service and army held by British officials Indians held most other positions, and British saw their cooperation as helping to make India the brightest jewel in the crown of their empire
Impact of British Rule British felt they were helping India to modernize, which meant also adopting Western culture and technology British saw India as a market and source of raw materials British built up infrastructure to better trade and maintain control over India After the Suez Canal opened in 1869, trade with India continued to soar
Impact of British Rule Though many of these innovations helped the Indians, it remained an unequal partnership favoring the British Many of the innovations forced Indians to change their culture such as forcing nomadic herders into farming Clearing new farmlands would lead to massive deforestation in an attempt to grow cash crops such as cotton and jute
Impact of British Rule The British introduced medical improvements and new farming methods which led to rapid population growth The growing population put a strain on the food supply As a result, terrible famines swept India in the late 1800s
Benefits of British Rule British revised the legal system to promote justice for Indians regardless of class or caste Improved infrastructure allowed easier movement and communication for Indians Better contact helped build national unity Upper class sent their children to Britain for education and landowners grew rich from exporting cash crops
Nationalism Grows During British rule, a class of Western-educated Indians arose Though it was hoped this class would bolster British power, they spearheaded the nationalist movement In 1885, nationalist leaders organized the Indian National Congress which called for greater democracy which would bring more power to Indians