Importance of PSHE Education for Children's Wellbeing
PSHE education equips children with essential knowledge and skills to navigate modern life, promoting health, safety, and emotional wellbeing. The recent statutory changes emphasize mental health, healthy relationships, and life skills, ensuring all children receive a comprehensive education. By focusing on key aspects like consent, equality, and respect, PSHE aims to reduce health risks, promote positive behaviors, and prepare students for adulthood. Strengthening PSHE education can significantly impact pupils' life chances and academic success, fostering a safe and healthy learning environment for all.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Information for parents for new RSHE (relationships/sex/health education) Personal, Social, Health and Economic (PSHE) education is a school subject through which pupils develop the knowledge, skills and attributes they need to manage their lives, now and in the future. These skills and attributes help pupils to stay healthy, safe and prepare them for life and work in modern Britain.
What are the new KS 1 & 2 statutory requirements? The Health Education and Relationships Education aspects of PSHE (personal, social, health and economic) education will be compulsory in all primary schools from summer term 2021 (latest September 2021). The law changed in September 2020 but was extended to now due to covid. This covers broad areas of particular relevance and concern to children and young people today. It should ensure that every child is guaranteed a PSHE education that covers mental health and wellbeing, physical health (including healthy lifestyles and first aid) and learning about safe, healthy relationships, including understanding consent and negotiating life online.
Why is PSHE/RSE changing? Why is PSHE/RSE changing? All children deserve to grow up healthy, happy, safe, and able to manage the challenges and opportunities of modern Britain. That is why, in September 2020, it was made compulsory for all primary age children to be taught Relationships and Health Education. These subjects are designed to equip children with knowledge to make informed decisions about their wellbeing, health and relationships as well as preparing them for a successful adult life. The world for all young people looks very different from the way it did 20 years ago when this curriculum was last updated these changes bring the content into the 21st century, so that it is relevant for all children. RSHE education aims to: Help prevent prejudice and racism through its emphasis on equality and respect Promote healthy gender relationships Combat increasing levels of obesity Reduce number of teenage pregnancies Reduce number of hospital treatments for tooth decay Lay the foundations for the importance of consent (taught at secondary school) Increase understanding around mental health issues.
Why is this so important? This strengthening of PSHE education s status can and should have a major impact on the quality of PSHE in all schools for all pupils. These developments mean that all pupils can benefit from an education that keeps them safe, healthy and prepared for the realities of modern life. PSHE education has proven impact on life chances and academic success when delivered well, but has suffered from reduced curriculum time and patchy provision.
Why is this all so important? PSHE education has proven impact on life chances and academic success when delivered well. There is more scope for PSHE education to be a focus of Ofsted inspections under the new framework in providing evidence for key judgements, particularly personal development . The new Ofsted inspection handbook also refers specifically to the inclusion of the new statutory content in the curriculum, and that if a school is failing to meet its obligations, inspectors will consider this when reaching the personal development judgement . These developments mean that all pupils can benefit from an education that keeps them safe, healthy and prepared for the realities of modern life. The evidence shows that personal, social, health and economic (PSHE) education can improve the physical and psychosocial well-being of pupils. A virtuous cycle can be achieved, whereby pupils with better health and well-being can achieve better academically, which in turn leads to greater success.
What is covered in Relationships Education? Relationships Education in primary schools will protect children. The new Government guidance sets out the content under the following headings: Families and people who care for me , Caring friendships , Respectful relationships , Online relationships , Being safe . There is widespread agreement that children need to be able to recognise abusive behaviour and to know how to seek help if they are worried about abuse or experience it. The new guidance states that by the end of primary school all children should know: how to report concerns or abuse, and the vocabulary and confidence needed to do so . RSE aims to put in place the building blocks needed for positive and safe relationships of all kinds. This will start with family and friends, how to treat each other with kindness, and recognising the difference between online and offline friendships. The new Government guidance is compatible with the Equalities Act 2010 Relationships Education should promote equal, safe and enjoyable relationships and be taught in a way which fosters LGBT and gender equality The Sex Education Forum.
Physical health and mental wellbeing education: The focus in primary school should be on teaching the characteristics of good physical health and mental wellbeing. Teachers should be clear that mental wellbeing is a normal part of daily life, in the same way as physical health. Children must be taught by the end of primary: Mental wellbeing, internet safety and harms, physical health and fitness, healthy eating, drugs, alcohol and tobacco, health and prevention, basic first aid and about the changing adolescent body.
Can parents withdraw their children from school RSE? Parents WILL NOT have the right to withdraw their child from relationships education in primary schools. Parents WILL have the right to withdraw their child from sex education in primary schools. (in Year 6) Maintained primary schools are required to teach National Curriculum science, which includes some elements of sex education. Parents do not have a right to withdraw from this.
Engaging with parents: We have an up to date RSE policy in place. This is being sent to parents as part of the consultation process, and includes: an outline of what will be taught to children within the RSE curriculum, a rationale for this learning and a clear procedure for withdrawal from sex education. The DfE statutory guidance states: Parents should be given every opportunity to understand the purpose and content of Relationships Education and RSE. Good communication and opportunities for parents to understand and ask questions about the school s approach help increase confidence in the curriculum.
PSHE association planning a spiral curriculum We use the PSHE association programme builder to ensure we are covering all statutory requirements as well as meeting local needs and issues for our children. We have adapted the question based model across the school. The programme builder is structured around an overarching question for each term or half term. These begin in key stage 1 as What? and Who? questions and build throughout Key Stage 2 into Why? and How? questions. The three core themes from the Programme of Study are fully covered - colour-coding highlights whether the overall topic focus is Health and Wellbeing, Relationships or Living in the Wider World, although some half term blocks will draw on more than one core theme. Teaching builds according to the age and needs of the pupils throughout the primary phase with suggested developmentally appropriate learning objectives given to respond to each key question. New learning builds on prior knowledge. Our curriculum design in all subjects uses a spiral model (based on the research of Bruner) whereby topics/themes are taught and then revisited as pupils progress through the school. This ensures they build on initial foundations and then deepen their knowledge/develop their skills as they revisit and re-encounter areas of learning. Research shows that this means the learning sticks . For PSHE this means children will develop and add to a toolkit for personal development so they are able to negotiate and embrace the challenges of the world they live in and live a happy, healthy and enriched life as a positive member of the community.
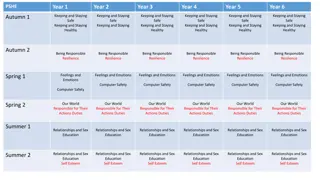
KS1 and KS2 long term plan (school overview) KS1 and KS2 long term plan (school overview) Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Year 1 What is the same and different about us? What helps us stay healthy? What can we do with money? Who helps to keep us safe? How can we look after each other and the world? Who is special to us? Year 2 What makes a good friend? What helps us to stay safe? What helps us grow and stay healthy? How do we recognise our feelings? What is bullying? What jobs do people do? Year 3 How can we be a good friend? What makes a community? Why should we eat well and look after our teeth? Why should we keep active and sleep well? What keeps us safe? What are families like? How can our choices make a difference to others and the Year 4 What strengths, skills and interests do we have? How do we treat each other with respect? How can we manage our feelings? How will we grow and change? How can we manage risk in different places? environment? Year 5 What decisions can people make with money? How can drugs common to everyday life affect health? What jobs would we like? What makes up a person s identity? How can we help in an accident or emergency? How can friends communicate safely? What will change as we become more independent? How do friendships change as we grow? How can we keep healthy as we grow? How can the media influence people? Year 6 Sex Education (summer term)
KS1 KS1 medium term medium term plan (Year 1 and 2 overview) plan (Year 1 and 2 overview) Over the two year cycle pupils will learn about the following. They will have opportunities to revisit and build on prior knowledge as they journey through Key Stage 1, building the foundation for further development in Key Stage 2. Autumn Autumn Spring Spring Summer Summer Relationships Ourselves and others Similarities and differences Our body correct names for body parts Some parts are private Relationships People who care for us Groups we belong to Families who is in our family? Who can I talk to if I am worried? Health & wellbeing Being healthy Hygiene/germs Medicine People who help us with health Living in the wider world Money Making choices Needs and wants Health and wellbeing Keeping safe/how to get help People who help us 999 Living in the wider world How behaviour affects others The world around us Caring for others Growing and changing Year 1 Relationships Friendship Feeling lonely Managing arguments Asking for help Relationships Behaviour Bullying Words and actions Respect for others Living in the wider world People and jobs Money Role of the internet Health and wellbeing Keeping safe (inc. online) Recognising risk Rules Peer pressure Health and wellbeing Being healthy Eating, drinking, playing and sleeping Sun safety Health and wellbeing Feelings/Mood Times of change Loss and bereavement Growing up Year 2
KS2 long term plan (Year 3 and 4 overview) KS2 long term plan (Year 3 and 4 overview) In Year we build on and revisit what has been learned in KS1 so pupils build a toolkit to help them stay safe, recognise and manage risk and build healthy relationships. In Year 4, children begin to become aware of how our bodies change. Autumn Autumn Spring Spring Summer Summer Year 3 Relationships Making positive friendships Managing loneliness Dealing with arguments Asking for help Health and wellbeing Keeping safe at home & school Our bodies are our own Hygiene Medicines/househ old products 999 for help Relationships Different types of families Family life Caring for each other Asking for help if we are worried Living in the wider world Community belonging to groups/diversity Similarities & differences Respect for others Health and wellbeing Being healthy Eating well Dental care Health and wellbeing Being healthy to feel good Keeping active Taking rest Asking for help if we are worried Year 4 Health and wellbeing Self-esteem Personal qualities Setting goals Setbacks/resilie nce Relationships Self-respect Respect others Courteous behaviour Safety Human rights Health and wellbeing Feelings and emotions Expressing feelings Behaviour Health and wellbeing How our body starts to change Personal hygiene as we change Living in the wider world Caring for the environment Shared responsibilities Making choices Health and wellbeing Keeping safe in the local area Managing risk Online actions/reportin g concerns
KS2 long term plan (Year KS2 long term plan (Year 5 5 overview) overview) In Year 5 and 6, we revisit key learning from Year 4 and begin to build towards moving to the next stage of the learning journey. Pupils begin to consider their future aspirations and how to get there. We prepare them for negotiating the wider world and potential pressures and situations that could arise. Autumn Autumn Spring Spring Summer Summer Year 5 Health and wellbeing Identity a range of factors including gender identity Similarities and differences Individuality Stereotypes and how to challenge them Living in the wider world Money deciding how to spend or save Making choices about how to pay for things Risks with money and how it can make people feel Health and wellbeing Basic first aid Accidents Dealing with emergencies The importance of getting adult help 999 Relationships Different types of relationship Online safety Recognising risk in relation to friendships/keep ing safe How to ask for help/respond to pressure Becoming independent Health and wellbeing Drugs, alcohol and tobacco Healthy habits Asking for help with worries about substances Living in the wider world Careers and the attributes needed Aspirations Routes to qualifications Role models Job stereotypes The future and what we want
KS2 long term plan ( KS2 long term plan (Year Year 6 overview) 6 overview) Year 6 is a culmination of all prior learning and pupils are prepared for transition to secondary school. Sex education * is taught in the summer term and parents are invited to see the materials and ask questions about the taught content. Autumn Autumn Spring Spring Summer Summer Year 6 Health and wellbeing Looking after ourselves how mental and physical health are linked How to make choices that support a healthy, balanced lifestyle Growing up, becoming independent, taking more responsibility Healthy and unhealthy habits (including drugs) Recognising signs of health problems physical/mental and where to get help Mental health difficulties can be supported and resolved Living in the wider world Media literacy and digital resilience; influences and decision making; online safety How the media can influence and affect people How text/media can be manipulated How to make decisions about online content and how to report upsetting or inappropriate material To recognise risks online and respond appropriately Consider different viewpoints Relationships Different relationships Committed relationships How friendships change as we grow That marriage should be wanted equally by both people Puberty Reproductive organs how babies are conceived and born * Contraception * How growing up brings more independence and responsibilities Managing change and transition How to get help as we grow up and face challenges or feel uncertain