Importance of Sequence Evolution Models
Explore the significance of sequence evolution models in analyzing genetic differences between taxa, detecting multiple hits, supporting the correct tree structure, and avoiding long-branch attraction in evolutionary studies.
Uploaded on | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
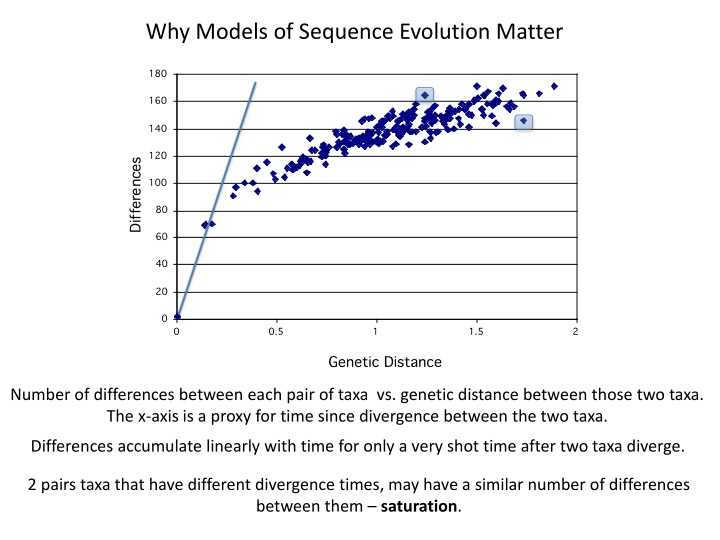
Why Models of Sequence Evolution Matter Number of differences between each pair of taxa vs. genetic distance between those two taxa. The x-axis is a proxy for time since divergence between the two taxa. Differences accumulate linearly with time for only a very shot time after two taxa diverge. 2 pairs taxa that have different divergence times, may have a similar number of differences between them saturation.
Multiple Hits. 3 So even though there have been 4 substitutions, when we compare these two lineages, we only can detect 3 differences. Models of sequence evolution expect multiple hits.
Why Models Matter Let s assume a true tree. A ATCGAGCAGCCTGGGAGAGAGACTTATTTGACAAACGTAA B ATTGGGGAGTAGCGTAAACACTCTTATTTGACGAAATTAT C ATCGTGGGTTAGAGTAGAGACTCTCATTTGACGAAATTAT D AACGTGGCGAATAGTAGTCAAAAAATGTGTACCAGATTAC This tree is 37 steps, and the true tree is 38 steps.
Why Models Matter Let s assume a true tree. Support for Wrong Tree 100 90 80 70 60 50 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 Increase # replicates keeps happening. Increase # bp happens with certainty.
Why Models Matter Now let s subject the sequences to an ME search. First, we need to convert the character by taxon matrix to a matrix of pairwise distances: above diagonal are p-distances, below are JC distances. A ------- 0.572 0.572 1.091 B 0.400 -------- 0.232 0.903 C D 0.400 0.200 ------- 0.752 A B C D 0.575 0.525 0.475 -------
Why Models Matter Optimum tree is the true tree. We re getting pretty lousy estimates of branch lengths but, under these conditions, branch-length estimates would converge on true values with more data. Thus, in the simulation, the methods that are agnostic with respect to multiple hits (MP and ME using p-distances) incorrectly unite the long-branch taxa (A & D). ML can avoid long-branch attraction
Long-branch attraction 1 2 1 2 Let s assume that there is an A in both the short-branch taxa. There are four possibilities for states at the other two terminals. 1) The long-branch taxa could have A 2 & 3) One of the long-branch taxa has a substitution to nucleotide X ( = G, C, or T)
Long-branch attraction 1 2 1 2 4) There could be substitutions to X1 and X2 along both long branches. If X1 X2 , the site is uninformative. If X1 = X2 , the site is misleading. X1 X2 X1 X2 X1 X2 C C C C G T G G G C G T T T T C G T So, 1/3 of all possibilities result in a convergence.
Look at Original Data A ATCGAGCAGCCTGGGAGAGAGACTTATTTGACAAACGTAA B ATTGGGGAGTAGCGTAAACACTCTTATTTGACGAAATTAT C ATCGTGGGTTAGAGTAGAGACTCTCATTTGACGAAATTAT D AACGTGGCGAATAGTAGTCAAAAAATGTGTACCAGATTAC 2 sites that distinguish among topologies under parsimony are misleading and favor the LBA tree. Remember, these data were simulated on a known tree that is not the tree that the characters support under parsimony.
The Importance of Branch Lengths Fitch Optimization {A} :0 {A C G}:1 Large # of terminals with A, this is a slowly evolving site. C at node 2, transversion to A along short branch , no change along and change to G along . G at node 2, transition to A along short branch , no change along and change to C along . A at node 2, no change along short branch , a change to C along and change to G along .
The Importance of Branch Lengths {A} {A} All reconstructions are permitted and accounted for, but the reconstruction with A at node 2 (& node 1) contributes the most to the single-site likelihood. ML can voice a preference here, where parsimony can t. This is because ML accounts for branch lengths in calculating reconstruction probabilities. No change along a short branch and changes along both long branches is more likely than a change along the short branch coupled with no change along one of the long branches.





