Improving NDN Forwarding States Freshness
Explore how Jianxun Cao, Dan Pei, and other researchers from Tsinghua University and University of Arizona are enhancing the freshness of NDN forwarding states through new probing strategies. This study delves into the limitations, new probing strategies, simulation results, and conclusions related to NDN routing and forwarding. Discover the comparison between NDN and IP, the significance of the routing and forwarding planes, and the use of smart and stateful approaches in NDN forwarding. Interface ranking, color classification, and data reception mechanisms for maintaining routing efficiency are also discussed in detail.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
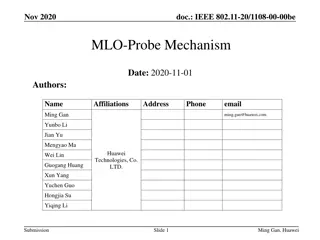
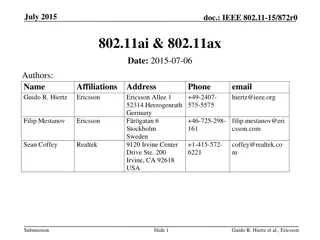
Improving the Freshness of NDN Forwarding States Jianxun Cao*, Dan Pei*, Zhelun Wu*, Xiaoping Zhang*, Beichuan Zhang , Lan LanWang Wang , Youjian Zhao* *Tsinghua University University of Arizona University of Memphis *Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNList) 2025/6/30 1
Outline Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Limitations and Problem Description New Probing Strategy Simulation Results Conclusion 2025/6/30 2
Outline Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Limitations and Problem Description New Probing Strategy Simulation Results Conclusion 2025/6/30 3
Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Compared with IP IP IP NDN NDN Routing Plane Forwarding Plane Smart Dumb Static/ Smart Stateful NDN Routing OSPFN, NLSR NDN Forwarding[1] NACK, Interface Ranking [1] C. Yi, A. Afanasyev, I. Moiseenko, L. Wang, B. Zhang, and L. Zhang, A case for stateful forwarding plane, Computer Communications, vol. 36, no. 7, April 2013. 2025/6/30 4
Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Interface Ranking Periodical measurement Interface Ranking For a given prefix, to maintain the ranking metrics for interface ranking, the router periodically sends a copy of the Interest packet to all the interfaces to measure various metrics (such as SRTT) used in forwarding policies. 2025/6/30 5
Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Interface Ranking Periodical measurement Color classification is used to record an outgoing interface s working status for each prefix. Interface Ranking Color Classification 2025/6/30 6
Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Interface Ranking Data Recieved Initialize GREEN YELLOW Periodical measurement Data Timeout Color classification is used to record an outgoing interface s working status for each prefix. Interface Ranking RED Color Classification 2025/6/30 7
Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Interface Ranking Ranking Rules Periodical measuremen t 200 200 Interface Ranking 180 180 250 250 Color 330 330 150 150 Classification 2025/6/30 8
Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Interface Ranking Forwarding based on Ranking Rules 150 150 Periodical measuremen t 200 200 Interface Ranking 150 150 180 180 250 250 Color Classification 330 330 2025/6/30 9
Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Interface Ranking Forwarding based on Ranking Rules Periodical measuremen t 150 150 Interface Ranking 180 180 Triggerd Probing 200 200 180 180 250 250 Color Classification 330 330 2025/6/30 10
Outline Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Limitations and Problem Description New Probing Strategy Simulation Results Conclusion 2025/6/30 11
Limitations of Interface Ranking Periodical measurement With the in-network cache, the uncertainty of location where Interest packets are satisfied leads to the frequent changing of network metrics. Problem: SRTT slow-convergence. 2025/6/30 12
Limitations of Interface Ranking: SRTT slow-convergence 152ms SRTT can reflect the real RTT: convergence. 151ms 179ms Sampled RTT 152ms 149ms 151ms 153ms 151ms 150ms 156.7ms 154.8ms 152ms 151.8ms 152.0ms 151.4ms 155.8ms 153.8ms SRTT 2025/6/30 13
Limitations of Interface Ranking SRTT slow-convergence 152ms SRTT slow-convergence 50ms 51ms 53ms Sampled RTT 152ms 151ms 51ms 153ms 151ms 50ms 132.1ms 103ms 152ms 151.8ms 152.0ms 151.8ms 115.9ms 92.3ms SRTT 2025/6/30 14
Limitations of Interface Ranking Periodical measurement With the in-network cache, the uncertainty of location where Interest packets are satisfied leads to the frequent changing of network metrics. Problem: SRTT slow SRTT slow- -convergence convergence. Color Classification and Triggered Probing The change of interface color is done at the packet-level feedback for each prefix. When faced with burst congestions, the colors might frequently change between GREEN and YELLOW back and forth. Problem: Probing Oscillation Probing Oscillation. 2025/6/30 15
Limitations of Interface Ranking Probing Oscillation ?3 ?3 ?3 ?2 ?2 ?1 ?1 ?2 ?1 ?1 ?2 ?2 ?1 ?4 ?4 ?4 Loss Rate: 1% ?? ?1 ?2 ??? ?? ??? ?3 ?5 ?4 ?6 2025/6/30 16
Limitations of Interface Ranking Periodical measurement With the in-network cache, the uncertainty of location where Interest packets are satisfied leads to the frequent changing of network metrics. Problem: SRTT slow SRTT slow- -convergence convergence. Out-of-date States SRTT Slow-convergence Throughput of Forwarding Color Classification and Triggered Probing The change of interface color is done at the packet-level feedback for each prefix. When faced with burst congestions, the colors might frequently change between GREEN and YELLOW back and forth. Problem: Probing Oscillation Probing Oscillation. Probing Oscillation 2025/6/30 17
Outline Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Limitations and Problem Description New Probing Strategy Simulation Results Conclusion 2025/6/30 18
New Probing Strategy New Probing Strategy SRTT Slow-convergence Probing Oscillation Problem Adaptive SRTT Update Approach Proactive Probing Dynamical Sample Frequency Probability-based Probing Path Backup Core idea 2025/6/30 19
New Probing Strategy Adaptive SRTT Update How frequently to probe the Probing packets to each GREEN interface ? 152ms ?: the number of Interest packets between two consecutive probing. ?: Normalized distance between RTT and SRTT. ??? ???? ??? + ???? ? = 50ms Dynamical Sample Frequency 51ms 53ms Sampled RTT 152ms 151ms 51ms 153ms ??= max( ????, 1 ?? ?? 1),? ?? ??? ??? min( ????, 1 + ? ?? 1),? < ?? ??? ??? 152ms 151.8ms 152.0ms 151.8ms 151ms 50ms 132.1ms 132.1ms 62ms 60.2ms 58.1ms 103ms 115.9ms 92.3ms SRTT 2025/6/30 20
New Probing Strategy Adaptive SRTT Update How frequently to probe the Probing packets to each GREEN interface ? ?: the number of Interest packets between two consecutive probing. ?: Normalized distance between RTT and SRTT. ??? ???? ??? + ???? ? = Dynamical Sample Frequency ??= max( ????, 1 ?? ?? 1),? ?? ??? ??? min( ????, 1 + ? ?? 1),? < ?? ??? ??? 2025/6/30 21
New Probing Strategy Proactive Probing ?3 ?3 ?2 ?1 ?1 ?4 Path Backup Loss Rate: 1% Set more than one GREEN interface to ensure some backup paths. ?? ?1 Probability-based Probing 35% 35% ?2 30% 30% The smaller the COST is, the higher the probability of the optimal choice will be. ??? ?? 25% 25% ??? Probing Probability Function (PPF) ?3 ?5 10% 10% 1/????? 1/???? ?4 ? ? = 1/????? 1/???? ?6 ? ? = *Path backup is explained in the paper instead of slides. 2025/6/30 22
Outline Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Limitations and Problem Description New Probing Strategy Simulation Results Conclusion 2025/6/30 26
Simulations Sub-Topology of TUNET We use NDNSim 2.0 to evaluate our design. A sub-topology of Tsinghua Network Topology and a larger topology ? denotes the loss rate of ??, ranged from 1% to 10% ? denotes the loss rate of ?? ?????= 100?? ????= 120?? ? = 100?? 2025/6/30 27
Simulations Sub-Topology of TUNET SRTT Slow-convergence Time of SRTT convergence is reduced by~37.9% Probing overhead is reduced by~46.7% 2025/6/30 28
Simulations Sub-Topology of TUNET Probing Oscillation (? = 10%) *More simulation details and results are shown in paper. The time of solving Probing Oscillation is reduced by~88.2% The probing overhead is reduced by~94.1% 2025/6/30 29
Outline Overview of NDN routing and forwarding Limitations and Problem Description New Probing Strategy Simulation Results Conclusion 2025/6/30 30
Conclusion Limitations of the current Adaptive Forwarding Plane in NDN SRTT Slow-convergence Probing Oscillation Objective: Improve the Freshness of NDN Forwarding States Propose a new probing strategy to achieve up-to-date forwarding states to solve the above two problems Dynamical Sample Frequency Path Backup Probability-based Probing Our results show that SRTT convergence time is reduced by 37.9% and the loss rate is reduced by 75% to 94.75% with little extra overhead. 2025/6/30 31
Thank you! Improving the Freshness of NDN Forwarding States Jianxun Cao*, Dan Pei*, Zhelun Wu*, Xiaoping Zhang*, Beichuan Zhang , Lan LanWang Wang , Youjian Zhao* *Tsinghua University University of Arizona University of Memphis *Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNList) 2025/6/30 32