Inference Concepts: Hypothesis Testing for Introverts' Close Friends
Explore a hypothesis test assessing if the mean number of close friends for introverts differs significantly from the general U.S. population. Using a 1-sample z-test with known population standard deviation, data analysis reveals a rejection of the null hypothesis and supports the investigator's prediction.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
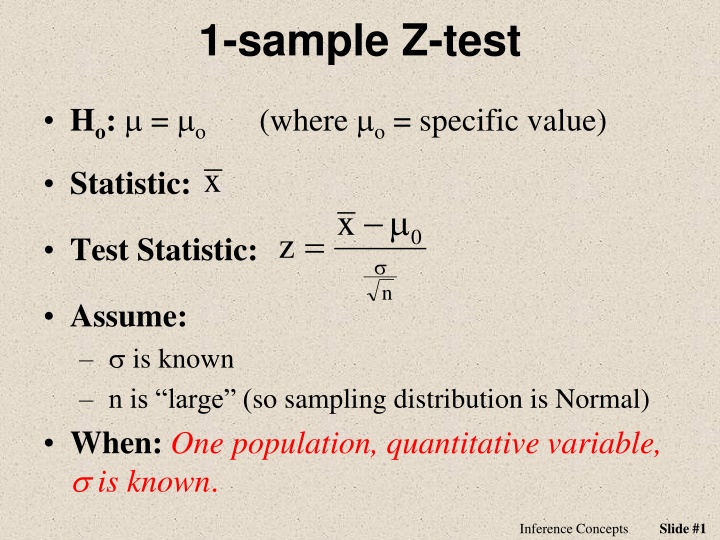
1-sample Z-test Ho: = o (where o = specific value) x Statistic: x = z 0 Test Statistic: n Assume: is known n is large (so sampling distribution is Normal) When:One population, quantitative variable, is known. Slide #1 Inference Concepts
Full Example The mean number of close friends for the population of people living in the U.S. is 5.7. The standard deviation in this slightly skewed population is 1.3. An investigator predicts that the mean number of close friends for introverts will be significantly different from the mean of the general population. The mean number of close friends for a random sample of 26 introverts is 6.5. Do these data support, at the 5% level, the investigator's prediction? Slide #2 Inference Concepts
Recipe for any Hypothesis Test 1) State the rejection criterion ( ) =0.05 2) State the null & alternative hypotheses, define the parameter(s) Ho: = 5.7 Ha: 5.7 . is mean number of close friends for all introverts 3) Determine which test to perform Explain! 1-sample z-test because (a) a single population (introverts in U.S.), (b) quantitative variable (number of close friends), and (c) is known (=1.3). Slide #3 Inference Concepts
Recipe for any Hypothesis Test 4) Collect the data (address type of study and randomization) (i) Observational study (no control imparted on introverts) (ii) A random sample (n=26) was taken 5) Check all necessary assumption(s) (i) is known (=1.3) (ii) n>15 and population is only slightly skewed (in background) 6) Calculate the appropriate statistic(s) x = 6.5 (in background) Slide #4 Inference Concepts
Recipe for any Hypothesis Test 7) Calculate the appropriate test statistic x z 7 . 5 8 . 0 5 . 6 = = = = 0 . 3 137 . 0 255 3 . 1 26 n 8) Calculate the p-value > 2*distrib(3.137,lower.tail=FALSE) [1] 0.001706861 Slide #5 Inference Concepts
Recipe for any Hypothesis Test 9) State your rejection decision p-value (0.0017) < (0.05) . Reject Ho 10) Summarize your findings in terms of the problem The mean number of close friends for all introverts appears to be different than that (=5.7) for the population of people living in the U.S. Slide #6 Inference Concepts
Recipe for any Hypothesis Test 11) If rejected H0, compute a 100(1- )%confidence region for parameter (i) 100(1-0.05)% = 95% (ii) Confidence interval because Ha was not equals (two-sided) (iii) Z* = 1.96 from distrib(0.025,type= q ) (iv) 6.5 1.96*0.255 6.5 0.50 (6.0, 7.0) (v) I am 95% confident that the mean number of close friends for all introverts is between 6.0 and 7.0. Slide #7 Inference Concepts
