Innovations in UWB Sensing for Wireless Personal Area Networks
Explore the latest advancements in Ultra-Wideband (UWB) sensing technology for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs), including radar sequence selection, interference mitigation, and improved link budget. Key functionalities highlighted include high-integrity ranging, localization for indoor navigation, and presence detection.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
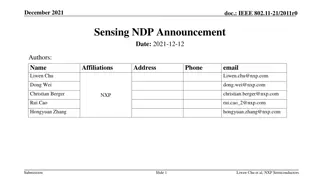
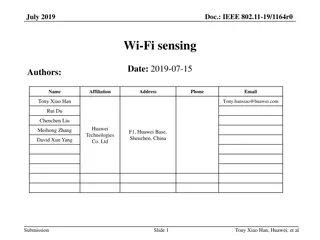
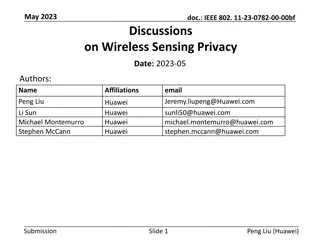
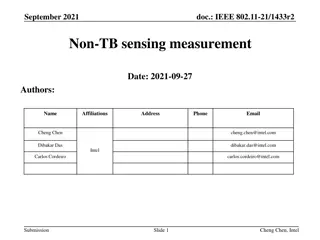
September 2022 Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> Submission Title: [UWB Sensing Sequence Selection] Date Submitted: [13 September, 2022] Source: [Frank Leong, Wolfgang K chler, Riku Pirhonen, David Veit] Company [NXP Semiconductors] Re: [Input to the Working Group] Abstract: [Presentation, UWB, sensing] Purpose: [] Notice: discussion and is not binding on the contributing individual(s) or organization(s). The material in this document is subject to change in form and content after further study. The contributor(s) reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. Release: The contributor acknowledges and accepts that this contribution becomes the property of IEEE and may be made publicly available by P802.15. This document has been prepared to assist the IEEE P802.15. It is offered as a basis for Submission Slide 1 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors
September 2022 doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> PAR Objective Safeguards so that the high throughput data use cases will not cause significant disruption to low duty-cycle ranging use cases Interference mitigation techniques to support higher density and higher traffic use cases Other coexistence improvement Backward compatibility with enhanced ranging capable devices (ERDEVs) Improved link budget and/or reduced air-time Additional channels and operating frequencies Improvements to accuracy / precision / reliability and interoperability for high-integrity ranging Reduced complexity and power consumption Hybrid operation with narrowband signaling to assist UWB Enhanced native discovery and connection setup mechanisms Sensing capabilities to support presence detection and environment mapping Low-power low-latency streaming Higher data-rate streaming allowing at least 50 Mbit/s of throughput Support for peer-to-peer, peer-to-multi-peer, and station-to- infrastructure protocols Infrastructure synchronization mechanisms Proposed Solution (how addressed) Sequence selection for radar Submission Slide 2 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors
September 2022 doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> UWB Sensing Sequence Selection Submission Slide 3 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors
September 2022 doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> Sensing Context Recap Focus on key functionalities to be provided by UWB: 1.Ranging with high integrity (handsfree access use cases) 2.Localization (indoor navigation use cases) 3.Sensing (presence detection use cases) 4.Coordination & scheduling to support the above Provide accurate ranging via a low-cost, mass-market solution a. Low energy-per-ranging b. Low channel-occupancy-per-ranging a.k.a. spectral efficiency (many devices operating at the same time & place) c. Re-use of hardware between use cases Submission Slide 4 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors
September 2022 doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> Sensing Packets Two approaches: Dedicated sensing packet design (see [1]) Sensing sequence as drop-in STS replacement Periodic (repeating a basic sequence a number of times) With or without MMS Piggy-backing on ranging (no dedicated packet structure) With or without MMS [1] https://mentor.ieee.org/802.15/dcn/22/15-22-0175-00-04ab-sensing-device.pptx Submission Slide 5 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors
September 2022 doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> Dedicated Sensing Packet Structure Sense Symbol Sense Symbol Sense Symbol SHR ... Time Submission Slide 6 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors
September 2022 doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> Sensing Sequences Selection Criteria Achievable ACF maximum side lobe level (CFO sweep) o Using multi-bit ADC architectures o Considering residual CFO / Phase Noise (i.e., realistic compensation performance) CCF maximum (CFO sweep) Unambiguous range o Undesired reflections may obscure desired targets Correlator complexity o Length o Template switch and need for parallel templates CFO sweep proposal: {0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10} ppm (ACF = AutoCorrelation Function, CCF = Cross-Correlation Function) Submission Slide 7 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors
September 2022 doc.: <15-22-0489-00-04ab> Some Thoughts Achievable sensing performance is determined by ACF Assuming a suitable pulse shape When sensing, a receiver may encounter other sensing networks Typical sensing packet transmission rates assumed to be higher than ranging packet transmission rates Co-location of sensing networks TDMA typically yields the best results (separation via CDMA is limited, whatever the selected codes) Especially in case of an NBA-MMS based sensing approach, low sensing sequence CCF maximum may help to mitigate accumulation of undesired transmitter energy Submission Slide 8 Leong/K chler/Pirhonen/Veit, NXP Semiconductors