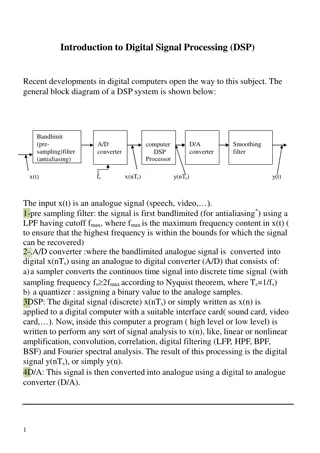
Intelligent Signal Processing in Quantization: Understanding Error Calculation
The concept of quantization in intelligent signal processing, focusing on error calculation methods and common word-lengths. Learn about uniform and non-uniform quantization, bit rate calculation, and examples of quantization techniques.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
? Intelligent Signal Processing Test Angelo Ciaramella
Question 4 Question The quantisation error is calculated as the difference between the signal and the closest level as the difference between the signal and the farthest level as the absolute value of the sampled signal . ISP Verification tests
Quantization Quantization is the procedure of constraining something from a continuous set of values (such as the real numbers) to a relatively small discrete set (such as the integers) Quantization replaces each real number with an approximation from a finite set of discrete values (levels) values are represented as fixed-point words or floating- point words ISP Verification tests common word-lengths are 8-bit (256 levels), 16-bit (65,536 levels), 32-bit (4.3 billion levels 3
Example of quantization ISP Verification tests ( ) n ( ) n ( ) n = e x x quantization error q d 4
Coding Amplitude time ISP Verification tests levels We start with an uniform quantization 5
Coding With N bits K = 2Nquantization levels are obtained at each level a code of N bits can be associated ISP Verification tests 3-bit resolution with eight levels 6
Bit rate Bit rate number of bits per second product between the sampling frequency and the number of quantization bits bit rate = fc N ISP Verification tests 7
Non-linear quantization ISP Verification tests non-uniform quantization 8
Logarithmic quantization logarithm uniform ISP Verification tests non-uniform 9
Example ISP Verification tests Uniform quantization 10
Example ISP Verification tests non-uniform quantization 11
Comparison ISP Verification tests 4 bit linear 3 bit logarithmic 12
Comparison Quality the dynamic range of the 8-bit logarithmic quantization corresponds to 13-14 bits linear quantizer Signal to Noise Rate (SNR) a 8-bit logarithmic converter is better than a 8-bit linear at low amplitudes, but worse at high amplitudes ISP Verification tests 13
References Material Slides Video Lessons Books Signal Processing Book (Ciaramella) free download on the e-learning platform Discrete-time signal processing, A. V. Oppenheim, R. W. Schafer, J.R. Buck, Upper Saddle River, N.J., Prentice Hall, 1999, ISBN 0-13-754920-2 Digital Signal Processing, J. Proakis, D. Manolakis, Prentice Hall, 4 edition, 2006 ISP Verification tests