Introduction to Alkenes in Chemistry
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with double bonds, having diverse naming conventions and characteristic properties. Learn about their structure, nomenclature, and preparation methods, including dehydrohalogenation. Explore the E1 and E2 mechanisms involved in the dehydrohalogenation process, shedding light on elimination reactions in alkyl halides.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BSc I YEAR CHEM 101 SECTION D ALKENES CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
ALKENES Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkanes and which are characterized by the presence of a double bond in their molecules are called alkenes. These are also called olefins. The general formula of alkenes is CnH2n where n = 4, 5, 6 ..... etc. COMMON AND IUPAC NAMES Common names: Alkane-ane + ylene = Alkylene IUPAC names: Alkane-ane + ene = Alkene Alkenyl groups: The monovalent alkenyl group obtained by removing a hydrogen atom from ethylene Is called venyl group or ethenyl group and that derived from propylene by removing a hydrogen atom from the doubly bonded carbon atoms is called propenyl group. If, however, a hydrogen atom 1s removed from the methyl group of propylene, the alkenyl group is called allyl group. CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
Examples CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
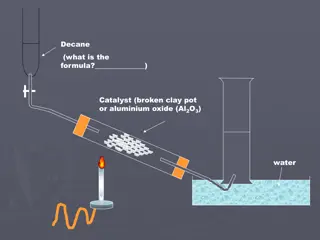
METHODS OF PREPARATION OF ALKENES 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: The removal of the elements of hydrogen halides (HCl, HBr or HI) from the adjacent carbon atoms of an alkyl halide with a strong base such as sodium ethoxide or a concentrated alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide is called dehydrohalogenation. CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
MECHANISM: E1 (Elimination, bimolecular) reaction Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides is an example of elimination reactions. Elimination reactions occur by a number of different mechanisms but we shall discuss here only two of them, i.e., E2and E1. Kinetic studies of this reaction reveal that the reaction follows second-order kinetics, i.e. , the rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of both the alkyl halide and the base, Rate [Alkyl halide] [Base] CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
E2 MECHANISM CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
E1 MECHANISM CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
E1 mechanism step 1 CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB
E1 -STEP 2 (Write few lines on this step) CHEMISTRY DEPTT GC PAONTA SAHIB