Introduction to Cryptography: Key Concepts and Security Services
Explore the fundamentals of cryptography, including key terms such as plaintext, ciphertext, and cryptanalysis. Understand essential security services like authentication, access control, data confidentiality, integrity, nonrepudiation, and availability to enhance information protection.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
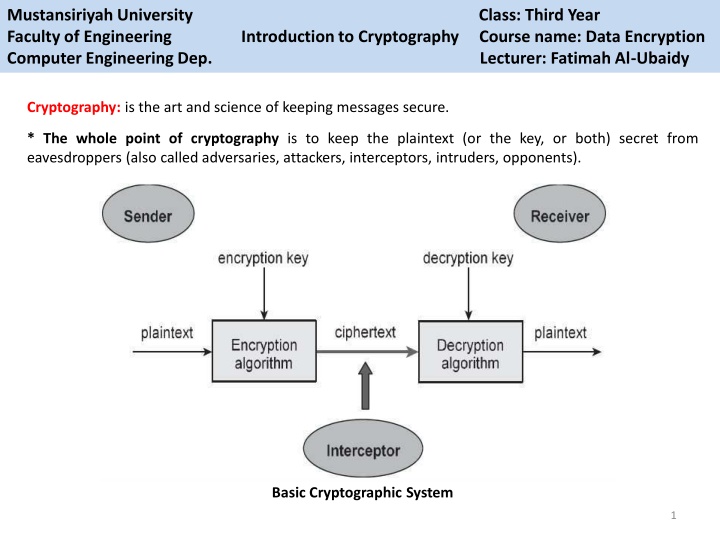
Mustansiriyah University Faculty of Engineering Introduction to Cryptography Course name: Data Encryption Computer Engineering Dep. Lecturer: Fatimah Al-Ubaidy Class: Third Year Cryptography: is the art and science of keeping messages secure. *The whole point of cryptography is to keep the plaintext (or the key, or both) secret from eavesdroppers (also called adversaries, attackers, interceptors, intruders, opponents). Basic Cryptographic System 1
Mustansiriyah University Faculty of Engineering Introduction to Cryptography Course name: Data Encryption Computer Engineering Dep. Lecturer: Fatimah Al-Ubaidy Class: Third Year Key Terms Key: The piece of information that allows you to either encrypt or decrypt your data. Plaintext: The information that you want to keep hidden, in its unencrypted form. The plaintext can be any data at all: a picture, a spreadsheet, .etc. Ciphertext: The information in encrypted form. Cipher: The algorithm that converts plaintext to ciphertext and vice-versa. Cryptanalysis: is the science of recovering the plaintext of a message with/without access to the key. Security attack: Any action that compromises the security of information owned by an organization. It can be divided into passive and active attacks Security mechanism: A process that is designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack such as encryption algorithms, digital signatures, and authentication protocols.. Security service: A processing or communication service that enhances the security of the data processing systems and the information transfers of an organization such as access control. Key management: allows to negotiate, setup and maintain keys between communicating entities. 2
Mustansiriyah University Faculty of Engineering Introduction to Cryptography Course name: Data Encryption Computer Engineering Dep. Lecturer: Fatimah Al-Ubaidy Class: Third Year Security Services Authentication: The assurance that the communicating entity is the one that it claims to be. Access Control: The prevention of unauthorized use of a resource (i.e., this service controls who can have access to a resource, under what conditions access can occur, and what those accessing the resource are allowed to do). Data confidentiality: The protection of data from unauthorized disclosure. Data integrity: The assurance that data received are exactly as sent by an authorized entity (i.e., contain no modification, insertion, deletion, or replay). Nonrepudiation: Provides protection against denial by one of the entities involved in a communication of having participated in all or part of the communication. Availability: guarantees that the system services are always available when needed. 3
Mustansiriyah University Faculty of Engineering Introduction to Cryptography Course name: Data Encryption Computer Engineering Dep. Lecturer: Fatimah Al-Ubaidy Class: Third Year Security Attack (1) Passive attack is in the nature of eavesdropping on, or monitoring of, transmissions. The goal of the opponent is to obtain information that is being transmitted. Two types of passive attacks are release of message contents and traffic analysis. 4