Introduction to Jinja Template Engine
Jinja Template Engine is a modern templating language primarily used by Python developers to create HTML, XML, and other markup formats for web applications. It offers features such as sandboxed execution for testing automation, powerful HTML escaping to prevent XSS attacks, and template inheritance. Learn how Jinja 2 simplifies web development and enhances web application security.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
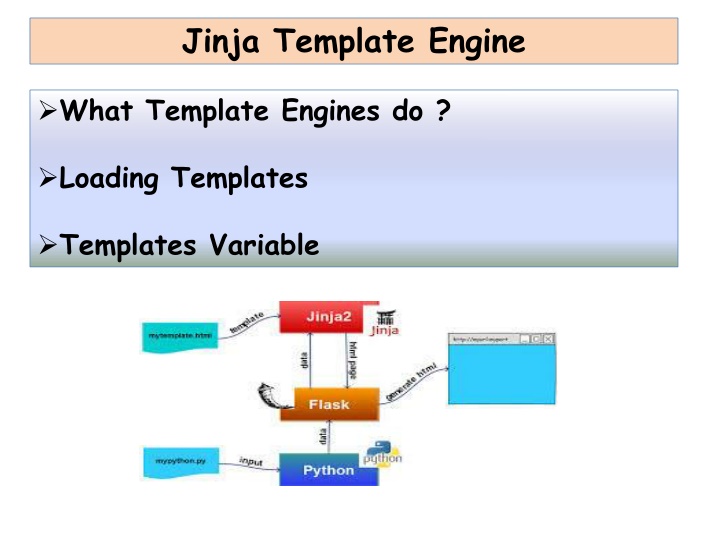
Jinja Template Engine What Template Engines do ? Loading Templates Templates Variable
What is Jinja 2? Jinja2 is a modern day templating language for Python developers. It was made after Django s template. It is used to create HTML, XML or other markup formats that are returned to the user via an HTTP request. How To Get Jinja 2 pip install jinja2easy_install jinja2 Rendering Pages in Flask using Jinja
Why do we need Jinja 2? Sandboxed Execution: It provides a protected framework for automation of testing programs, whose behaviour is unknown and must be investigated. HTML Escaping: Jinja 2 has a powerful automatic HTML Escaping, which helps preventing Cross-site Scripting (XSS Attack). There are special characters like >,<,&, etc. which carry special meanings in the templates. So, if you want to use them as regular text in your documents then, replace them with entities. Not doing so might lead to XSS-Attack. Template Inheritance: This is the most important feature, which I will expand on to later in the post
Simple Example {{name}} had a little {{animal}}. If name= Mary and animal= Lamb Would be Mary had a little Lamb
Python Script Outputs from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) http://127.0.0.1:5000/ Hello @app.route('/') def home(): return "Hello" Outputs Python Script from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) http://127.0.0.1:5000/Radhika Hello Radhika @app.route('/<name>') def hello(name): return '<h1>Hello %s</h1>' %name
from flask import Flask, render_template app = Flask(__name__) <html> <body> <h1>Hello !</h1> </body> </html> @app.route('/') def hello(): return render_template('thirteen.html') http://127.0.0.1:5000/ Hello ! from flask import Flask, render_template app = Flask(__name__) <html> <body> <h1>Hello {{ name }}!</h1> </body> </html> @app.route('/<user>') def hello(user): return render_template('twelve.html', name = user) http://127.0.0.1:5000/Radhika Hello Radhika!
from flask import Flask,render_template app=Flask(__name__) @app.route('/<login>/<password>') def home(login,password): return render_template("login.html",loginname=login,passwd=password) html> <body> <h1>Login Name {{loginname}}!</h1> <h2>Password {{passwd}} </body> </html> http://127.0.0.1:5000/abc/abc@123 Login Name abc! Password abc@123