Ions and Atom Structure
Explore the world of ions and atoms, including their charges, types, and implications on chemical reactions. Learn about the significance of electron balance in creating neutral atoms and the formation of ions with net charges. Discover the characteristics of anions and cations, along with the behavior of highly reactive species in their gaseous state. Dive into the concept of ions and their impact on chemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Recap What is an atom made of?
What is the overall charge of the nucleus? How do you know?
What are ions? If an atom has the same number of protons and electrons, it is electronically neutral. However, if the total number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, the atom has a net electrical charge.
Ions Ion- Any atom or molecule with a net charge, either positive or negative Monoatomic ion: an ion consisting of a single atom Polyatomic ion consisting of two or more atoms The positive electric charge of a proton is equal in magnitude to the negative charge of an electron net electric charge of an ion is equal to its number of protons minus its number of electrons
Highly reactive species Generally found in a gaseous state and do not occur in abundance on Earth They are repelled by like electric charges and are attracted to opposite charges. Ions
Types of Ions Anions have more electrons than protons and so have a net negative charge Anions are generally larger than the parent molecule or atom, because the excess electrons repel each other and add to the physical size of the electron cloud Cations have more protons than electrons and so have a net positive charge Cations are generally smaller than their parent atom or molecule due to the smaller size of their electron clouds
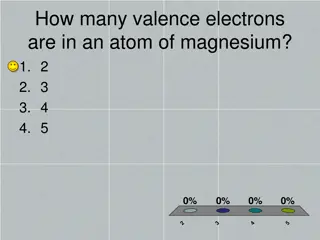
What is the overall charge of a Sodium Ion if it had 11 electrons? What type of ion is it? How would we denote (write its symbol) it?
What is the overall charge of a Sodium Ion if it had 9 electrons? What type of ion is it? How would be denote (write its symbol) it?
What are the trends of the periodic table for ionic charges?